Orange Line (VTA)
The Orange Line is a light rail line in Santa Clara County, California, and part of the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA) light rail system. It serves 26 stations in the cities of Mountain View, Sunnyvale, Santa Clara, San Jose, and Milpitas, traveling between Downtown Mountain View and Alum Rock stations. The line connects the Caltrain line at Mountain View to the Bay Area Rapid Transit (BART) system at Milpitas station, stopping at Ames Research Center, Great America, and Levi's Stadium along the way. The line runs for 20 hours per day on weekdays, with headways of 15 minutes for most of the day. On weekends, the train runs at 20-minute headways for most of the day. After around 8 pm on weekdays and weekends trains run at 30-minute headways.
Route description
The Orange Line starts from the Downtown Mountain View station in Mountain View, California, travels toward the east, passing under U.S. Route 101 at Ellis Avenue, following Mathilda Avenue to Java Drive, crossing State Route 237 and turning east on Tasman Drive, which eventually becomes Capitol Avenue. For the rest of the trip, the line follows Capitol Avenue until it reaches its eastern terminus, the Alum Rock Transit Center.
Construction history
The route that the Orange Line now runs on was constructed through three different expansion projects: the original Guadalupe line, the Tasman West extension, and the Vasona extension.
Guadalupe line
The trackway between Old Ironsides station and First Street is part of the Guadalupe line, the first light rail line constructed in Santa Clara county. The Guadalupe line opened for revenue service on December 10, 1987, originally running from Old Ironsides station to Civic Center station in San Jose. Champion station was not part of the original line; it was added as intermediate stop as part of the Tasman West project.[1][2]
Tasman West extension
The Tasman West extension project was constructed with funds from the 1996 Measure B sales tax measure. Champion station was the first to open as an infill stop along the existing Guadalupe line trackway, opening March 24, 1997.[3] On December 17, 1999, 7.6 miles (12.2 km) of trackway and 12 new light rail stations added between the existing Old Ironsides station and the new Downtown Mountain View station. On the same day, Baypointe station opened just east of the intersection of 1st and Tasman.
Tasman East/Capitol extension
The first phase of the Tasman East extension opened in May 2001 between Baypointe and Alder stations.[4][5]
On June 24, 2004, the 8.3-mile (13.4-km) Tasman East/Capitol extension was opened, incorporating 8 new stations. This extension runs from Alder station east along the Great Mall Parkway in Milpitas, then into East San Jose on Capitol Avenue to Alum Rock Transit Center on Alum Rock Avenue. This extension brings service to the Great Mall of the Bay Area in Milpitas. The total cost of this extension was $432.9 million.[5]
Light Rail Efficiency Project
In 2014, a new storage track and crossover was constructed between Old Ironsides and Reamwood as part of improvements to support events at Levi's Stadium and the future Silicon Valley BART extension.[6]
To provide better headways and service reliability, a second track was constructed between Whisman and Downtown Mountain View. Work began in summer 2014 and was completed in late 2015. Evelyn Station was permanently closed in mid-March 2015 as part of track construction.[7]
2019 reconfiguration
Ahead of the opening of the Silicon Valley BART extension to Milpitas station and Berryessa/North San José, the Orange Line was created. Starting in early 2019, station signage was changed reflect the new configuration, displaying line colors rather than terminus icons.[8]
Station stops
| Station | Transfer to |
|---|---|
| Downtown Mountain View | |
| Evelyn (closed) | |
| Whisman | |
| Middlefield |
|
| Bayshore/NASA | |
| Moffett Park | |
| Lockheed Martin |
|
| Borregas |
|
| Crossman |
|
| Fair Oaks |
|
| Vienna | |
| Reamwood |
|
| Old Ironsides |
|
| Great America | |
| Lick Mill | |
| Champion |
|
| Baypointe |
|
| Cisco Way |
|
| Alder |
|
| Great Mall |
|
| Milpitas |
|
| Cropley | |
| Hostetter |
|
| Berryessa |
|
| Penitencia Creek |
|
| McKee |
|
| Alum Rock |
|
Proposed Capitol Expressway extension
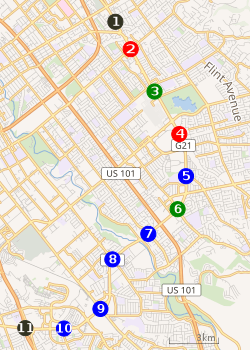 |
Proposed stations for Capitol Expressway Light Rail Extension
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
VTA has proposed a future extension to this line which would extend the line 2.4 miles (3.9 km) south along the median of the Capitol Expressway from its current eastern terminus at the Alum Rock Transit Center to the Eastridge Transit Center with one intermediate stop at Story Road. The project has been under study since the early 2000s and is part of a larger project to transform the Capitol Expressway into a major transit corridor. The Eastridge Transit Center, which was completed in 2015, was designed to accommodate a future light rail station. Bus Rapid Transit stations were also added along Capitol Expressway in 2017 for the Rapid 522 route which parallels this corridor. The extension will have elevated crossings at Capitol Avenue, Story Road, and Tully Road. Major construction is expected to begin in late 2020 and the line is expected to open by Fall 2025. The $453 million project will be primarily funded by local sales taxes.[9]
An earlier version of the project also included a station at Ocala, but it was eliminated in 2014.[10][11] However, Ocala is served by a Bus Rapid Transit station along the parallel Rapid 522 route.
The final approved and funded project is a small portion of a much more ambitious project studied in 2005 that would have extended the line in a hook shape, along the Capitol Expressway, past the Caltrain Capitol station to connect with the Blue Line's Capitol Station at Route 87. As seen in the map, the originally proposed extension would have also included stations at Nieman Boulevard, McLaughlin Avenue, Senter Road, Monterey Road, and Vista Park Drive, with potential infill station at Silver Creek Road.[12]:1–8, 3–11
References
- Robinson, Bert (December 11, 1987). "All Aboard - It's Off and Rolling". San Jose Mercury News. et al. Sec A:1.
- Grant, Joanne (November 6, 1987). "Mishap Won't Delay Light Rail". San Jose Mercury News. Sec B:3.
- Barnacle, Betty (March 24, 1997). "Light Rail Opens New Stop; First Station on Tasman Line to Serve North S.J. High-Tech Firms". San Jose Mercury News. Sec B:1.
- "VTA Facts: Light Rail System" (PDF). Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. 2006-11-30. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2008-07-04. Retrieved 2008-08-27.
- "Tasman East/Capitol Project Description". Completed projects. Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. 2008-05-12. Archived from the original on 2011-06-05. Retrieved 2008-11-16.
- "Light Rail Efficiency". Light Rail Efficiency. Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. Retrieved May 13, 2015.
- "Mountain View Double Track". Mountain View Double Track. Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. Retrieved May 13, 2015.
- "Downtown Mountain View station". Mapillary. February 27, 2019. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
- "Eastridge to BART Regional Connector-Capitol Expressway Light Rail Project | VTA". www.vta.org. Retrieved May 24, 2020.
- "Capitol Expressway Light Rail to Eastridge". Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. June 2013. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- Jaworski, Christine (May 29, 2018). "Notice of Preparation of a Draft Second Supplemental Environmental Impact Report for the Eastridge to BART Regional Connector: Capitol Expressway Light Rail Project" (PDF). Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. Retrieved 2 March 2019.
- Capitol Expressway Corridor: Final Environmental Impact Report (Report). 1. Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority. April 2005. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
.jpg)