Oberstocken
Oberstocken is a former municipality in the administrative district of Thun in the canton of Bern in Switzerland. On 1 January 2014 the former municipalities of Oberstocken, Niederstocken and Höfen merged into the new municipality of Stocken-Höfen.[1]
Oberstocken | |
|---|---|
 Oberstocken village from the peak of the Stockhorn | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Oberstocken 
| |
 Oberstocken  Oberstocken | |
| Coordinates: 46°42′N 7°33′E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Bern |
| District | Thun |
| Area | |
| • Total | 4.12 km2 (1.59 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 691 m (2,267 ft) |
| Population (Dec 2011) | |
| • Total | 277 |
| • Density | 67/km2 (170/sq mi) |
| Postal code | 3632 |
| SFOS number | 0765 |
| Surrounded by | Därstetten, Erlenbach im Simmental, Höfen, Niederstocken, Pohlern |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |
History

Oberstocken is first mentioned in 1351 as Stogken.[2]
During the Middle Ages the village was part of the lands and parish of the college of canons at Amsoldingen. In 1485 the office of canon was abolished and the Amsoldingen lands were acquired by Bern. In 1505, it was incorporated into the Bernese district of Thun, where it remained until 1803. At that time it joined the Niedersimmental District. Between 1898 and 1926 the Stockentalbahn railroad company unsuccessfully attempted to build a railroad through the Stockental valley to Oberstocken. There were several unsuccessful attempts to combine the villages of Oberstocken and Niederstocken, the most recent was in 1988.[2]
Geography
Before the merger, Oberstocken had a total area of 4.1 km2 (1.6 sq mi).[3] As of 2012, a total of 1.68 km2 (0.65 sq mi) or 40.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while 1.73 km2 (0.67 sq mi) or 42.0% is forested. The rest of the municipality is 0.16 km2 (0.062 sq mi) or 3.9% is settled (buildings or roads), 0.03 km2 (7.4 acres) or 0.7% is either rivers or lakes and 0.5 km2 (0.19 sq mi) or 12.1% is unproductive land.[4]
During the same year, housing and buildings made up 2.7% and transportation infrastructure made up 1.2%. A total of 36.4% of the total land area is heavily forested and 2.7% is covered with orchards or small clusters of trees. Of the agricultural land, 4.6% is used for growing crops and 20.6% is pasturage and 14.8% is used for alpine pastures. All the water in the municipality is flowing water. Of the unproductive areas, 6.8% is unproductive vegetation and 5.3% is too rocky for vegetation.[4]
Oberstocken lies near the Niedersimmental region in the Stocken valley of the Bernese Alps. It stretches from the valley floor to the heights of the Stockhorn mountain chain. The neighboring municipalities starting from the north in a clockwise direction are: Höfen, Niederstocken, Erlenbach im Simmental, Därstetten and Pohlern.
On 31 December 2009 Amtsbezirk Niedersimmental, the municipality's former district, was dissolved. On the following day, 1 January 2010, it joined the newly created Verwaltungskreis Thun.[1]
Coat of arms
The blazon of the municipal coat of arms is Per fess Argent a Stump Sable between two Mullets Gules and if the last a Rose of the first barbed and seeded proper. The coat of arms is an example of canting arms with the stump (German: Stock) placed in the upper (German: ober) half of the shield. The neighboring municipality of Niederstocken has the stump in the lower half.[5]
Demographics
Oberstocken had a population (as of 2011) of 277.[3] As of 2010, 4.9% of the population are resident foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years (2001-2011) the population has changed at a rate of -2.8%. Migration accounted for -2.1%, while births and deaths accounted for -0.7%.[3]
Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks German (261 or 99.2%) as their first language with the rest speaking French.[6]
As of 2008, the population was 47.7% male and 52.3% female. The population was made up of 129 Swiss men (45.3% of the population) and 7 (2.5%) non-Swiss men. There were 142 Swiss women (49.8%) and 7 (2.5%) non-Swiss women.[7] Of the population in the municipality, 86 or about 32.7% were born in Oberstocken and lived there in 2000. There were 151 or 57.4% who were born in the same canton, while 18 or 6.8% were born somewhere else in Switzerland, and 7 or 2.7% were born outside of Switzerland.[6]
As of 2011, children and teenagers (0–19 years old) make up 24.9% of the population, while adults (20–64 years old) make up 63.5% and seniors (over 64 years old) make up 11.6%.[3]
As of 2000, there were 103 people who were single and never married in the municipality. There were 131 married individuals, 17 widows or widowers and 12 individuals who are divorced.[6]
As of 2010, there were 40 households that consist of only one person and 12 households with five or more people.[8] In 2000, a total of 106 apartments (89.8% of the total) were permanently occupied, while 6 apartments (5.1%) were seasonally occupied and 6 apartments (5.1%) were empty.[9] The vacancy rate for the municipality, in 2012, was 0.75%. In 2011, single family homes made up 56.4% of the total housing in the municipality.[10]
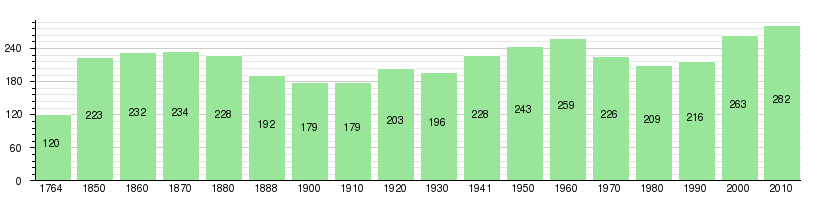
The historical population is given in the following chart:[2][11][12]
Politics
In the 2011 federal election the most popular party was the Swiss People's Party (SVP) which received 51.7% of the vote. The next three most popular parties were the Conservative Democratic Party (BDP) (9.5%), the Federal Democratic Union of Switzerland (EDU) (7.8%) and the Green Liberal Party (GLP) (7.4%). In the federal election, a total of 91 votes were cast, and the voter turnout was 44.2%.[13]
Economy
As of 2011, Oberstocken had an unemployment rate of 0.36%. As of 2008, there were a total of 41 people employed in the municipality. Of these, there were 10 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 4 businesses involved in this sector. 5 people were employed in the secondary sector and there was 1 business in this sector. 26 people were employed in the tertiary sector, with 6 businesses in this sector.[3] There were 137 residents of the municipality who were employed in some capacity, of which females made up 39.4% of the workforce.
In 2008 there were a total of 23 full-time equivalent jobs. The number of jobs in the primary sector was 6, all in agriculture. The number of jobs in the secondary sector was 3, all in manufacturing. The number of jobs in the tertiary sector was 14. In the tertiary sector; 4 or 28.6% were in wholesale or retail sales or the repair of motor vehicles, 2 or 14.3% were in a hotel or restaurant, 3 or 21.4% were in education and 4 or 28.6% were in health care.[14]
In 2000, there were 9 workers who commuted into the municipality and 107 workers who commuted away. The municipality is a net exporter of workers, with about 11.9 workers leaving the municipality for every one entering. A total of 30 workers (76.9% of the 39 total workers in the municipality) both lived and worked in Oberstocken.[15] Of the working population, 8.8% used public transportation to get to work, and 69.3% used a private car.[3]
In 2011 the average local and cantonal tax rate on a married resident, with two children, of Oberstocken making 150,000 CHF was 13.5%, while an unmarried resident's rate was 19.8%.[16] For comparison, the average rate for the entire canton in the same year, was 14.2% and 22.0%, while the nationwide average was 12.3% and 21.1% respectively.[17] In 2009 there were a total of 107 tax payers in the municipality. Of that total, 22 made over 75,000 CHF per year. There was one person who made between 15,000 and 20,000 per year. The greatest number of workers, 37, made between 50,000 and 75,000 CHF per year. The average income of the over 75,000 CHF group in Oberstocken was 100,505 CHF, while the average across all of Switzerland was 130,478 CHF.[18]
Religion
From the 2000 census, 229 or 87.1% belonged to the Swiss Reformed Church, while 10 or 3.8% were Roman Catholic. Of the rest of the population, there were 13 individuals (or about 4.94% of the population) who belonged to another Christian church. 11 (or about 4.18% of the population) belonged to no church, are agnostic or atheist.[6]
Education
In Oberstocken about 64.3% of the population have completed non-mandatory upper secondary education, and 13.6% have completed additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule).[3] Of the 21 who had completed some form of tertiary schooling listed in the census, 76.2% were Swiss men, 19.0% were Swiss women.[6]
As of 2000, there were a total of 34 students attending any school in the municipality. Of those, 32 both lived and attended school in the municipality, while 2 students came from another municipality. During the same year, 4 residents attended schools outside the municipality.[15]
Civil Defense
With its 290 inhabitants[19] this rural valley is designated as a civil defense evacuation site, with over 350 small bunkers. The main civil defense building is temporarily used as a garage which houses 16 vehicles.[20]
References
- Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz (in German) accessed 13 December 2014
- Oberstocken in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived January 5, 2016, at the Wayback Machine accessed 21 January 2014
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office-Land Use Statistics 2009 data (in German) accessed 25 March 2010
- Flags of the World.com accessed 7 November 2013
- STAT-TAB Datenwürfel für Thema 40.3 - 2000 Archived April 9, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 2 February 2011
- Statistical office of the Canton of Bern (in German) accessed 4 January 2012
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Haushaltsgrösse Archived October 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 8 May 2013
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB - Datenwürfel für Thema 09.2 - Gebäude und Wohnungen Archived September 7, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- Statistischer Atlas der Schweiz - Anteil Einfamilienhäuser am gesamten Gebäudebestand, 2011 accessed 17 June 2013
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Bevölkerungsentwicklung nach Region, 1850-2000 Archived September 30, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 29 January 2011
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Ständige Wohnbevölkerung in Privathaushalten nach Gemeinde und Haushaltsgrösse Archived July 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 12 August 2013
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office 2011 Election Archived November 14, 2013, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 8 May 2012
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office STAT-TAB Betriebszählung: Arbeitsstätten nach Gemeinde und NOGA 2008 (Abschnitte), Sektoren 1-3 Archived December 25, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 28 January 2011
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office - Statweb (in German) accessed 24 June 2010
- Statistischer Atlas der Schweiz - Steuerbelastung, 2011 Politische Gemeinden (in German) accessed 15 May 2013
- Swiss Federal Tax Administration - Grafische Darstellung der Steuerbelastung 2011 in den Kantonen (in German and French) accessed 17 June 2013
- Federal Tax Administration Report Direkte Bundessteuer - Natürliche Personen - Gemeinden - Steuerjahr 2009 Archived October 6, 2014, at the Wayback Machine (in German and French) accessed 15 May 2013
- Homepage de la commune d'Oberstocken Archived 2006-07-27 at the Wayback Machine
- Willkommen in Oberstocken: Porträt unserer Gemeinde Archived 2006-01-18 at the Wayback Machine in German
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oberstocken. |