Northern Formosan languages
The Northern Formosan languages is a proposed grouping of Formosan languages that includes the Atayalic languages, the Western Plains languages (Papora, Hoanya, Babuza, and Taokas), and the Northwest Formosan languages (Pazeh and Saisiyat; Li places Western Plains with this grouping).
| Northern Formosan | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | Taiwan |
| Linguistic classification | Austronesian
|
| Glottolog | west2572 (Western Plains)[1] nort2899 (Northwestern)[2] |
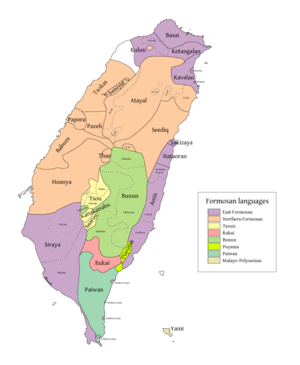 (orange) Li's Northern Formosan | |
The Northern Formosan subgroup was first proposed by Paul Jen-kuei Li in 1985.[3] Blust (1999) rejects the unity of the proposed Northern Formosan branch. A 2008 analysis of the Austronesian Basic Vocabulary Database, however, supports the unity of the Northern Formosan branch with a 97% confidence level (see Austronesian languages#Classification).
Evidence
The following sound changes from Proto-Austronesian occurred in the Northern Formosan languages (Li 2008:215).[4]
- *S2, *H1 > h
- *S2, *H1, *s > h (Atayalic languages and Saisiyat only)
Also, Pazeh, Saisiyat, and Thao are only Formosan languages that allow for SVO constructions, although this may be due to intensive contact with Taiwanese.[5]
Also, the Atayal, Seediq, and Pazeh languages have devoiced final consonants that were present in the Proto-Austronesian (Blust 2009:616).
Northwestern Formosan
Li (2003) considers six western Plains languages to have split off from Proto-Northwestern Formosan. The classification is as follows.
| Northwestern |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The four coastal languages of Taokas, Babuza, Papora, and Hoanya share the following innovations (Li 2003).
- Loss of *k
- Loss of *-y
- Merger of *s and *t in non-final position
- Complete merger of *ŋ and *n
Thao shares the following innovations with the four coastal languages (Li 2003).
- Merger of *s and *t
- Merger of *ŋ and *n
Pazih has undergone the following two sound changes.
- Merger of *j and *s as /z/
- Merger of *C and *S1 as /s/
Li (2003) does not consider Pazih to be very closely related to Saisiyat (Li 2003:946).
Notes
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Western Plains Austronesian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Northwest Formosan". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (1985). "The position of Atayal in the Austronesian family." In Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 2004. Selected Papers on Formosan Languages, vol. 2. Taipei, Taiwan: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 2008. "Time perspective of Formosan Aborigines." In Sanchez-Mazas, Alicia ed. Past human migrations in East Asia: matching archaeology, linguistics and genetics. Taylor & Francis US.
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 1998. "台灣南島語言 [The Austronesian Languages of Taiwan]." In Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 2004. Selected Papers on Formosan Languages. Taipei, Taiwan: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.
References
- Li, Paul Jen-kuei (2003). "The Internal Relationships of Six Western Plains Languages." In Li, Paul Jen-kuei. 2004. Selected Papers on Formosan Languages, vol. 2. Taipei, Taiwan: Institute of Linguistics, Academia Sinica.