Velbert
Velbert is a large town in the district of Mettmann, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. The city is renowned worldwide for the production of locks and fittings.
Velbert | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Velbert within Mettmann district 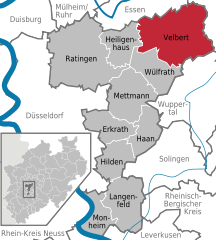  | |
 Velbert  Velbert | |
| Coordinates: 51°20′N 7°3′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Düsseldorf |
| District | Mettmann |
| Subdivisions | 3 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Dirk Lukrafka |
| Area | |
| • Total | 74.9 km2 (28.9 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 230 m (750 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 81,984 |
| • Density | 1,100/km2 (2,800/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 42549–42555 |
| Dialling codes | 02051–02053 |
| Vehicle registration | ME |
| Website | www.velbert.de |
Geography
Velbert is located on the hills of 'Niederberg' (meaning Lower Berg), part of the Berg region, approx. 20 kilometres north-east of the state capital Düsseldorf and 12 kilometres north-west of Wuppertal on the left side of the Ruhr river.
Velbert stands on the highest part of the Niederberg region and also in its centre. Its average elevation is around 230 metres above sea level; its highest point, at 303 metres, is the Hordt-Berg, and its lowest, at around 70.6 metres, is in Nierenhof am Deilbach. The highest point in Velbert itself is 263 metres above sea level, at the corner of Friedrichstraße and Langenberger Straße.
Incorporation
As part of the reform of local government districts in North Rhine-Westphalia that came into effect on 1 January 1975, the formerly independent cities of Velbert, Neviges and Langenberg were merged to form the present city of Velbert.
History
Velbert was first mentioned in AD 875 as Feldbrahti and was ruled by the abbey at Werden.
Administration
Velbert is divided into three administrative areas, reflecting the three former cities: Velbert-Mitte (Central Velbert), Neviges and Langenberg. There are also numerous suburbs, including Tönisheide, Losenburg, Nordpark, Langenhorst, Birth, Röttgen and Hefel.
Coat of arms
The first coat of arms was created in 1882 and abolished in local government reform of 1975. It showed the lion of the Counts, later Dukes, of Berg (originally the symbol of Limburg) and keys referring to locksmithing, a traditional industry in Velbert.
After 1975 a new coat of arms was created that included heraldic symbols for all three formerly independent towns. The key, referring to Velbert's main traditional industry, was retained with a simpler design. Langenberg is represented by an oak leaf, referring to the oak in the old arms of Langenberg. The chevrons in the bit of the key refer to the coat of arms of the lords of Hardenberg, from the coat of arms of Neviges.
Economics
The main traditional industry of Velbert is small scale manufacturing, mostly metal based, typical products include locks, hinges, small tools, hoseclamps. Most companies are small to medium scale and many evolved from backyard forges. There are also companies producing parts for the automotive industry, for example the suppliers of vehicle access systems Witte Automotive and Huf. As well as this Stein & Co Gmbh, the makers of Sebo vacuum cleaners, are based in the town.
Transportation
Since December 2003, Velbert's S-Bahn connection has been line S9, running Haltern am See–Marl–Bottrop–Essen-Langenberg-Neviges-Wuppertal, which is an attractive line to commuters. The old town of Velbert has no railway connection left. In 2011 most of the former railway line within the town was converted to a cyclepath. The former station buildings at Velbert-West and Velbert-Central are now restaurants, and the station at Velbert-Tönisheide is disused. All three were on the discontinued Niederberg Railway (Wülfrath-Velbert-Heiligenhaus–Kettwig). The operational stations serving the city are Langenberg, Neviges, Nierenhof and Rosenhügel.
Velbert also used to have a tram service, and was the meeting point of tramlines from Heidhausen, Neviges, Wülfrath and Hösel with Heiligenhaus. Nowadays a number of bus routes connect Velbert to the surrounding cities. The city belongs to the Verkehrsverbund Rhein-Ruhr.
International relations
Velbert is twinned with:[2]



Velbert has friendly connection with:

Sites of interest
Theatres
- The central theatre of the city is in Forum Niederberg.
Museums
The city's museum is also located in Forum Niederberg. It is the Deutsches Schloss- und Beschlägemuseum ("German museum for locks and metal fittings"). The Schloss- und Beschlägemuseum exhibits a broad variety of keys and locks.
Buildings
- Maria, Königin des Friedens, or Nevigeser Wallfahrtsdom, also known as Mariendom, in Neviges which was designed by the famous architect Gottfried Böhm
- Schloss Hardenberg (Hardenberg Castle) in Neviges
- Historical town centres in Neviges and Langenberg
- Eventkirche (Event church) in Langenberg
- Bürgerhaus (Citizen's house) in Langenberg
- Transmission towers in Langenberg for MW, FM and TV (303.7 m and 170m high)
- Rathaus (Town hall) incl. Thomas-Carré in Velbert-Mitte
- The Art Nouveau church called Christuskirche (Christ Church) in Velbert-Mitte
Notes
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "Partnerstädte". velbert.de (in German). Velbert. Retrieved 2019-11-23.
References
- Horst Degen, Christoph Schotten, Stefan Wunsch (authors), Bergischer Geschichtsverein Abteilung Velbert / Hadenberg e.V. (editor): Velbert – Geschichte dreier Städte, J.P. Bachem Verlag, Cologne, 2009, ISBN 978-3-7616-1843-1.