Neuleiningen
Neuleiningen is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bad Dürkheim district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Neuleiningen | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Neuleiningen within Bad Dürkheim district 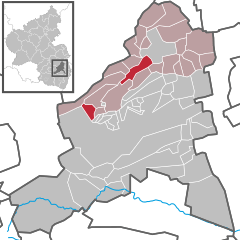  | |
 Neuleiningen  Neuleiningen | |
| Coordinates: 49°32′31″N 8°8′22″E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | Rhineland-Palatinate |
| District | Bad Dürkheim |
| Municipal assoc. | Leiningerland |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Franz Adam (CDU) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 9.07 km2 (3.50 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 300 m (1,000 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 772 |
| • Density | 85/km2 (220/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 67271 |
| Dialling codes | 06351, 06356, 06359 |
| Vehicle registration | DÜW |
| Website | www.neuleiningen.de |
Geography
Location
On a foothill near the northern end of the Haardt, Neuleiningen gathers round the like-named castle at an elevation of some 300 m above sea level. To the west and southwest stretches the Palatinate Forest, to the northwest the North Palatine Highland, and to the east spreads the Upper Rhine Plain behind the Leiningerland’s vineyard-covered hills. Neuleiningen belongs to the Verbandsgemeinde of Leiningerland, whose seat is in Grünstadt, although that town is itself not in the Verbandsgemeinde.
Constituent communities
The hamlet of Neuleiningen-Tal (Tal means “dale” or “valley” in German), administratively part of Neuleiningen and consisting of only a few houses, lies south of the main centre at an elevation of 183 m, making it quite a bit lower than the main centre. Neuleiningen-Tal lies on the Eckbach. Downstream the valley opens onto a hilly landscape planted with vineyards on the western edge of the Upper Rhine Plain. It abuts the neighbouring municipality of Kleinkarlbach just to the east.
History
Neuleiningen – as with neighbouring Altleiningen a few kilometres away – draws its name from the noble family, the House of Leiningen, to whom the Leiningerland – also named for these counts – once belonged and who also built the castle in the 13th century. (The prefixes Alt— and Neu— simply mean “old” and “new” respectively). It was not long before a settlement had sprung up around this and begun to grow. Neuleiningen belonged until 1969 to the now abolished district of Frankenthal. The Verbandsgemeinde into which the municipality was later grouped was formed in 1972.
Politics
Municipal council
The council is made up of 12 council members, who were elected at the municipal election held on 7 June 2009, and the honorary mayor as chairman.
The municipal election held on 7 June 2009 yielded the following results:[2]
| SPD | CDU | FWG | Total | |
| 2009 | 1 | 8 | 3 | 12 seats |
| 2004 | 1 | 9 | 2 | 12 seats |
Coat of arms
The municipality's arms might be described thus: Per bend azure semé of six crosses Or an eagle displayed argent armed and langued gules, the sinister wing couped at the partition, and sable semé of ten crosses of the second a key bendwise of the third, the wards to chief and turned to base.
The eagle is the heraldic device that was borne by the Counts of Leiningen. The key symbolizes the Prince-Bishopric of Worms.
Culture and sightseeing
Sightseeing in the main town
Many buildings have histories reaching back to the Middle Ages.
- Neuleiningen Castle
Burg Neuleiningen is typologically of the model of French castles of the so-called “castrum type” found in the Île de France. It was built under Count Friedrich III of Leiningen-Dagsburg in the 1240s and is thereby one of the earliest castrum-type castles on German soil. From the castle's lookout tower one has an outstanding view of the Upper Rhine Plain in the east and the Palatinate Forest’s mountains in the west. The villages of Sausenheim and Kleinkarlbach below Neuleiningen can be seen. In good weather one can also make out Ludwigshafen, Mannheim, the Odenwald and even aircraft taking off from Frankfurt Airport.
- Town fortifications
The fortifications with their four towers were built in connection with the castle and likewise come from the 13th century. They were restored and expanded in the 15th century. Of the once three town gates, only the western one from the latter half of the 15th century is preserved.
- Saint Nicholas’s Parish Church
The Pfarrkirche St. Nikolaus was built in the 13th century as a castle chapel at the same time as the castle itself. It is also called Wallfahrtskirche der Gnadenmutter zu Neuleiningen (“Pilgrimage Church of the Mother of Grace at Neuleiningen”). The miraculous image at the festival of the Birth of Mary on 8 September is a Gothic statue of Mary with the Christ Child in a mandorla. In the 15th century, the quire was expanded and the tower added. The single-nave inner space has after several restorations been thoroughly altered. Besides a Baroque statue of Saint Nicholas with his hand raised in blessing, the church houses several other Late Gothic wooden sculptures.
- Rectory
The former Wachenheimer Hof (1561, thoroughly altered), where the former castle administrators, the Lords of Wachenheim lived, now serves as a rectory. The complex was part of Neuleiningen Castle’s outer bailey.
- Town Hall
The town hall on Mittelgasse, like the adjoining church, belonged in the 14th and 15th centuries to the Carmelite monastery Zum Heiligen Kreuz (“To the Holy Cross”), which was dissolved in the Reformation. In 1902, the municipality acquired the complex and converted it into its present form. Since 1957, the church, which was Lutheran from 1555 to 1582 and thereafter a synagogue until 1902, has once again been in Evangelical hands.
- Timber-frame houses
Well preserved timber-frame houses (16th/17th century), some with oriel windows, characterize the village centre's narrow lanes, particularly the rows along the parallel Obergasse, Mittelgasse and Untergasse.
- Lion sculpture
The lion sculpture standing on a column at the Marktbrunnen (“Market Fountain”) on Mittelgasse from 1782 formerly bore the so-called Fasseiche, an official standard for wine barrel measurement. Today it bears the arms of the Prince-Bishops of Worms.
- Market Fountain
Below the Marktbrunnen on Untergasse, the Spülbrunnen (“Washing Fountain”) has been preserved. It caught water in a basin that had spilt out of the Market Fountain that was still suitable for washing wine barrels.
Sightseeing in Neuleiningen-Tal
- Eckbachweiher
Upstream from (west of) the two mills, the Eckbach is dammed up to form the Eckbachweiher, a manmade lake. This once served on the one hand as a guard against flooding, and on the other hand as a water reservoir for running the mills even in time of drought.
- Obermühle
The Obermühle (“Upper Mill”), first mentioned in a document in 1615, is a former gristmill and papermill. In 1864 it was converted into a porcelain and earthenware factory that ended up in financial difficulties after the First World War and had to be liquidated in 1937. The converted complex is used now, in the 21st century, by a forwarding company.
- Felsenmühle
The Felsenmühle (“Crag Mill”), standing roughly 300 m downstream, was first mentioned in a document in 1490. It is made up of the main house in the north, a dwelling wing in the east, a big, old barn in the south and the mill wing in the west. In the middle spreads a cobbled inner yard. The main house's ground floor sits one floor's height above the yard, which is reached by a double stairway built onto the middle.
In the mid 18th century, the Felsenmühle was bought at auction by miller Matthias Geißler, the owner of the Obermühle after he put his craftiness to work: Instead of transferring his tailwater, as the last owner had, along a channel running parallel to the Eckbach and down to the Felsenmühle, he had it flow right back into the Eckbach. Since this flowed by the Felsenmühle about 50 m to the south, the lower mill was left high and dry, bereft of its very reason for existing. Geißler then acquired it and soon thereafter was running it himself. In 1749, he received approval for a wine bar at the mill. In the 19th and 20th centuries, it served various purposes: glaze making for the earthenware factory that was then running at the Obermühle, then a bar, and in the Second World War a prison camp.
From 1994 it was once again an inn in which were also run a wine parlour and a bed and breakfast. In the guest parlour, a gigantic undershot waterwheel could be seen. After the innkeeper had to shut the complex down in 2004 owing to his advancing age, it stood empty and suffered damage from both frost and breakins. After being renovated, it has been open once again since the summer of 2007.
- Eckbachmühlen-Rad- und Wanderweg
A section of the Eckbachmühlen-Rad- und Wanderweg (cycling and hiking path) runs along the Eckbach, linking 23 of the region's mills, some of which have been restored. This includes the two described above.
Gastronomy
The castle's vaulted cellar has been expanded into a “castle bar”, and adjacent to the castle is the Alte Pfarrey (“Old Rectory” – archaically spelt with a Y instead of an I), which today is as much a restaurant for fine dining as Liz’ Stuben on the village's outskirts.
Air sports
On one of the municipality's hills is found the model aircraft site of the Luftfahrtvereins Grünstadt und Umgebung e. V. (“Grünstadt and Area Air Travel Club”).
Economy and infrastructure
Winegrowing
Winegrowing is, more so than tourism, the municipality's main livelihood. The vineyards lie in the east of the municipality towards the Upper Rhine Plain. The way the slopes lean towards the morning sun has two advantages: The soil warms up early after it has cooled off during the night, and colder air masses can swiftly flow off onto the plain, forestalling late frosts early in the year that damage the new shoots.
Winegrowing in Neuleiningen has tradition. There are several wineries in the municipality whose existence goes back to the 18th century. They make both white wines (Riesling, Chardonnay, Pinot blanc, Müller-Thurgau) and red wines (Pinot noir, Dornfelder, Pinot Meunier, Blauer Portugieser). Some wines are aged in oaken casks. Smaller areas are also planted with new grape varieties. In autumn, Federweisser is on offer at the wineries, and at Christmastime, they also have mulled wine made with their own products.
References
- "Bevölkerungsstand 2018 - Gemeindeebene". Statistisches Landesamt Rheinland-Pfalz (in German). 2019.
- Kommunalwahl Rheinland-Pfalz 2009, Gemeinderat
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Neuleiningen. |
- Municipality’s official webpage (in German)
- Neuleiningen in the collective municipality’s Web pages (in German)
- Neuleiningen’s mills (in German)