Arnsberg
Arnsberg (German pronunciation: [ˈaʁnsbɛʁk] (![]()
Arnsberg | |
|---|---|
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Arnsberg within Hochsauerland district 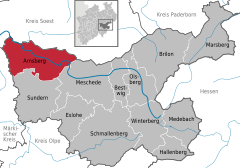  | |
 Arnsberg  Arnsberg | |
| Coordinates: 51°23′N 8°5′E | |
| Country | Germany |
| State | North Rhine-Westphalia |
| Admin. region | Arnsberg |
| District | Hochsauerland |
| Subdivisions | 15 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ralf Paul Bittner (SPD) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 193.45 km2 (74.69 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 212 m (696 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[1] | |
| • Total | 73,628 |
| • Density | 380/km2 (990/sq mi) |
| Time zone | CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) |
| Postal codes | 59755, 59757, 59759, 59821, 59823 |
| Dialling codes | 02931 Arnsberg 02932 Neheim-Hüsten 02935 Wennigloh 02937 Oeventrop |
| Vehicle registration | HSK |
| Website | www.arnsberg.de |

Geography
Location
Arnsberg is located in the north-east of the Sauerland in the Ruhr river valley. The river Ruhr meanders around the south of the old town of Arnsberg. The town is nearly completely encircled by forest, and the nature parkArnsberger Wald lies to the north".
Arnsberg is connected by Federal Motorway 46 (Autobahn 46) Brilon in the east and (using the Federal Motorway 445) Werl in the west. It is also connected by several railroad stations, which provide a connection to the major city Dortmund and the Ruhrgebiet. There is also a regional airport, located in the city district of Vosswinkel, which is exclusively used for small private aircraft.
The municipal territory spans a distance of up to 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) from the southern to the northern limits.
Subdivisions
After the local government reforms of 1975 Arnsberg consists of 15 boroughs (Ortsteile):
- Neheim (23,448 inhabitants)
- Arnsberg (19,355 inhabitants)
- Hüsten (11,304 inhabitants)
- Oeventrop (6,713 inhabitants)
- Herdringen (4,118 inhabitants)
- Bruchhausen (3,337 inhabitants)
- Müschede (2,870 inhabitants)
- Voßwinkel (2,523 inhabitants)
- Niedereimer (2,082 inhabitants)
- Holzen (2,022 inhabitants)
- Rumbeck (1,305 inhabitants)
- Wennigloh (1,004 inhabitants)
- Bachum (959 inhabitants)
- Breitenbruch (219 inhabitants)
- Uentrop (346 inhabitants)
History
Arnsberg was first mentioned in 789 in the Carolingian records (Urbar) as belonging to the abbey of Werden. The town was built by the counts of Werl in the 11th century. They built a castle there whose remains can still be visited and are occasionally used for public celebrations. It was destroyed in the Seven Years' War in 1769.
In the 12th century, old Arnsberg became the seat of Westphalian jurisdiction (whose coat of arms is still used today by the Hochsauerlandkreis). Later, the city lost its independence and was subject to the Archbishops of Colognea. In 1816, it came under Prussian rule and was made a local administrative centre.
In 1794 the French attacked Cologne, so parts of the treasure of the Cologne Cathedral were brought to safety to Arnsberg, also the relics of the Biblical Magi. In 1804 the treasure was returned to Cologne. A plaque in the Propsteikirche reminds of those years.
The current city of Arnsberg was created in 1975 by merging 14 cities and municipalities into one city. Old Arnsberg itself and Neheim-Hüsten are the two urban parts, while the other parts are very rural. Neheim and Hüsten were merged in 1941.
In the Second World War, Arnsberg first suffered widespread destruction and catastrophic loss of lives when RAF Lancasters breached the dam of the Möhne Reservoir in the night from 16 to 17 May 1943 (Operation Chastise). The nearby Abbey Himmelpforten was completely washed away.
Later, dozens of Arnsberg citizens were killed in several British air raids aimed at destroying the railway viaduct. The targets were finally destroyed on 19 March 1945 using a Grand Slam bomb.
Demographics
Religion
Arnsberg's population is mostly Roman Catholic. Arnsberg belongs to the Archdiocese of Paderborn. Catholic churches include the "Propsteikirche" or the "Heilig-Kreuz Kirche"; the "Auferstehungskirche" is a Protestant church. There is also a New Apostolic congregation. In the last years Arnsberg's Muslim minority grew considerably. There's a mosque. The cemeteries are mostly Catholic but there is also a Jewish cemetery.
Arts and culture
The Kunstverein Arnsberg operates in Arnsberg. Founded in 1987 and devoted to contemporary art, Kunstverein Arnsberg has presented solo exhibitions by artists including George Baselitz, Thomas Ruff, Karin Sander, Dan Perjovschi, Boris Mikhailov, Gregor Schneider, Erwin Wurm, the Turner Prize winner Susan Philipsz and the Marcel Duchamp Prize winner Laurent Grasso.
Government
City arms
The arms of the city depict a white eagle on a blue field. Earlier it was a white eagle on a red field, introduced in 1278 and as used by the counts of Arnsberg . In the 17th century the red was changed to blue, reflecting the Bavarian blue of the House of Wittelsbach.
Mayors
Mayors of the new town Arnsberg
| Years | Mayor | Party | |
| 1975–1984: | Gerhard Teriet | CDU | |
| 1984–1999: | Alex Paust | SPD | |
| 1999–2017: | Hans-Josef Vogel | CDU | |
| 2018–today: | Ralf Paul Bittner | SPD | |
Twin towns - sister cities
Arnsberg is twinned with:[2]





Pictures


Notable people
- Karl Brüggemann (1896-1977), honorary district in Kreis Arnsberg from 1961 to 1969
- Fritz Cremer, (1906-1993), artist
- Meinolf Finke, (born 1963), poet
- Andrea Fischer (born 1960), politician (Alliance '90 / The Greens) and journalist, former Federal Minister of Health
- Helena Fromm (born 1987), taekwondo athlete, won bronze medal at the 2012 Summer Olympics
- Franz von Fürstenberg (1729-1810), statesman and reformer school in Archbishopric Münster, founder of the Münster University

- Betsy von Furstenberg, (1931-2015), actress
- Hans Bernd Gisevius, (1904-1974), diplomat
- Wilhelm Hasenclever, (1837-1889), politician
- Franz Müntefering, (born 1940), politician (SPD)
- Georg Poplutz, tenor
- Abbé Franz Stock (1904-1948), since 1934 pastor of the German Catholic community in Paris, during the German occupation chaplain for French prisoners (companion sentenced to death), 1945 Head of a prisoner of war seminar in Chartres, formerly advocate of Franco-German reconciliation

People related to Arnsberg
- Paul Moder (1896-1942), German politician (NSDAP), Freikorps member and SS officer
- Fritz Cremer (1906-1993), sculptor ( Buchenwald Memorial)

- Meinolf Finke (born 1963), poet
- Stephan Kampwirth (born 1967 in Neheim-Hüsten), theater actor, film actor and voice actor
- Georg Poplutz, tenor (V. A Early Music)
- Walther Neye (1901-1989), jurist and rector of the Humboldt University in Berlin
- Lothar Collatz (1910-1990), mathematician
- Philipp Hofmann (born 1993), football player
- Günter Keute (born 1955), former football player
- Rouven Schröder (born 1975) former German footballer
- Friedrich Merz (born 1955 in Brilon) German attorney and politician, member of the CDU
See also
References
- "Bevölkerung der Gemeinden Nordrhein-Westfalens am 31. Dezember 2018" (in German). Landesbetrieb Information und Technik NRW. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- "Partnerstädte". arnsberg.de (in German). Arnsberg. Retrieved 2019-11-23.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Arnsberg. |
- Official website (in German)
- Kunstverein Arnsberg
- Neheim Notgeld (emergency currency)