Aurisina
Aurisina (until 1927 Nabresina, Slovene: Nabrežina) is a town in the karst part of the comune of Duino-Aurisina (Slovene: Devin-Nabrežina) near Trieste, Italy, in a region of Slovene minority. It lies 15 kilometres northwest of Trieste, and according to the 2003 census had a total of 2,406 inhabitants, 60% of them Slovenes.
Aurisina Nabrežina | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 | |
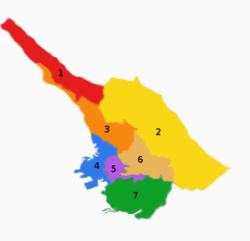 Sections of Trieste; Aurisina is located in section 1 | |
 Aurisina Sections of Trieste; Aurisina is located in section 1 | |
| Coordinates: 45°45′1.35″N 13°40′28.51″E | |
| Country | Italy |
| Region | Friuli-Venezia Giulia |
| Municipality | Trieste |
| Population (2003) | |
| • Total | 2,406 |
Overview
The town of Aurisina was inhabited in the Roman era because of nearby quarry with a well-known limestone, called Aurisina marble, used to build Roman Aquileia. The settlement was first mentioned as Lebrosina in 1308, and it grew in importance as the Vienna-Trieste railway was built in 1857. The world wars devastated Aurisina. Many Slovene people, including educated persons, escaped to Yugoslavia during fascist rule. Before and during World War II, the Italian fascist regime and later the German Nazi regime deported many inhabitants to concentration camps throughout Europe. After World War II, Aurisina, together with Trieste, became part of the Free Territory of Trieste. When this entity was disbanded in 1954, it was annexed to Italy.
The settlement lies on top of the Karst Plateau, where the cliffs descend to the sea. Its elevation is 143 m. Around the village there are four rises named Ojstri vrh, Gradec, Mount Babiza (Monte Babiza, Slovene: Babica, 197 m), and Mount Berciza (Monte Berciza, Slovene: Brščice, 219 m). Aurisina has typical karst architecture with houses made of limestone. The old village stands around a church dedicated to Saint Roch.
Aurisina is the birthplace of the Slovenian poet Igo Gruden and the marine biologist Miroslav Zei. The Silesian linguist Florian Biesik spent the last decade of his life in the village.