NGC 2857
NGC 2857 (also known as Arp 1 and PGC 26666) is a spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered on January 9, 1856 by R. J. Mitchell.[1]
| NGC 2857 (ARP 1) | |
|---|---|
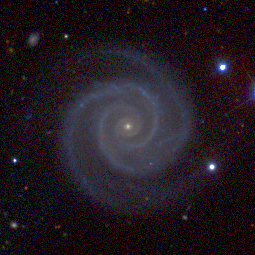 Image of NGC 2857 (Arp 1) Visible-spectrum image of Arp 1 taken by the European Southern Observatory | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Ursa Major [1] |
| Right ascension | 09h 24m 37.698s [2] |
| Declination | +49° 21′ 25.69″ [2] |
| Redshift | 0.016301 ± 0.000023 [3] |
| Helio radial velocity | 4887 ± 7 km/s [3] |
| Galactocentric velocity | 4917 ± 7 km/s [3] |
| Distance (comoving) | 69.050 ± 00 kpc (225.21 ± 0.00 kly)h−1 0.73 [3] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 12.27 [2] |
| Apparent magnitude (B) | 12.90 [2] |
| Absolute magnitude (V) | -21.92 ± 0.22 [3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | SA(s)c [3] |
| Size | 125,000 [1] |
| Apparent size (V) | 1.70′ × 1.43′ [3] |
| Other designations | |
| NGC 2857, Arp 1, APG 1, PGC 26666, UGC 5000 | |
NGC 2857 is the first object in Halton Arp's Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies, and one of six Arp objects in the 'Low Surface Brightness Galaxies' section. The other five low surface brightness galaxies are Arp 2 (UGC 10310), Arp 3, Arp 4, Arp 5 (NGC 3664), and Arp 6 (NGC 2537).[4]
Supernova 2012fg
On October 10, 2012, Supernova 2012fg was observed in NGC 2857 by the MASTER-Kislovodsk auto-detection system.[5][6] Its absolute magnitude was calculated to be -19.8.[7] The spectrum of SN 2012fg was recorded and analyzed by multiple teams of scientists as it changed rapidly in the days following its detection.[8][9]
References
- Seligman, Courtney. "New General Catalog Objects: NGC 2850 - 2899". Retrieved 2015-11-29.
- "SIMBAD Astronomical Database". Results for NGC 2857. Retrieved 2015-11-29.
- "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 2857. Archived from the original on 1997-12-22. Retrieved 2015-11-29.
- Arp, Halton (1966). "Atlas of Peculiar Galaxies". Retrieved 2015-11-25.
- Pruzginskaya; et al. "ATel #4489: Folow [sic] up B,V,R,I photometry bright SN 2012fg in NGC 2857 discovered by MASTER". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
- Shumkov; et al. "ATel #4459: Bright PSN in NGC2857". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
- Cellier-Holzem; et al. "ATel #4466: Spectroscopic Observation of the Bright PSN in NGC2857 by the Nearby Supernova Factory II". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
- Fabrika; et al. "ATel #4496: Spectrum of bright SN 2012fg in NGC 2857". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
- Fabrika; et al. "ATel #4520: Spectrum change of bright SN 2012fg in NGC 2857". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
External links

- Full Arp Atlas
- Halton Arp's image of Arp 1
- Constellation Locator
- SIMBAD Astronomical Database
- NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database
- SN 2012fg detection announcement