Moscow-Kazan high-speed railway
The Moscow-Kazan High-Speed Railway is a planned 772-kilometre long high-speed railway line connecting the two major cities of Moscow and Kazan in the Russian Federation,[4][5] going through the intermediate cities of Vladimir, Nizhny Novgorod and Cheboksary.[6] The project has an expected completion date of 2023, and is slated to be the first segment of an ambitious transnational high-speed railway set to connect Beijing and Moscow over a distance in excess of 7,000 kilometres, which is currently under consideration by the governments of Russia and China.[7] Planning work was finished in September 2017.[8] Construction started in spring 2018.[9]
| Moscow–Kazan High-Speed Railway ВСМ Москва – Казань | |
|---|---|
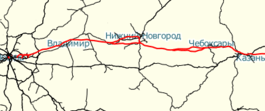 Proposed routes | |
| Overview | |
| Type | High-speed rail |
| Status | Design |
| Locale | Russia |
| Termini | Moscow Yaroslavskaya railway station Kazan |
| Stations | 15 |
| Services | Moscow - Vladimir - Nizhny Novgorod - Kazan (- Vladivostok/Beijing/India) |
| Operation | |
| Planned opening | 2023[1] |
| Operator(s) | Russian Railways |
| Technical | |
| Line length | 762 km (473 mi)[2] |
| Number of tracks | 2 Russian gauge[3] |
| Track gauge | 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) Russian gauge |
| Loading gauge | Russian T |
| Electrification | 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead lines 3 kV DC overhead lines inside of the Greater Ring of the Moscow Railway |
| Operating speed | up to 350 km/h (217 mph) |
Details

Proposed corridor for linking Asian and European rails.
- Route: Moscow - Vladimir - Nizhny Novgorod - Kazan (- Vladivostok/Beijing/India)
- Route length: 762 km
- Track gauge: 1,520 mm (4 ft 11 27⁄32 in) Russian gauge
- Number of tracks: 2 Russian gauge tracks[3]
- Electrification: 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead lines (with 3 kV DC overhead lines inside of the Greater Ring of the Moscow Railway)
- Loading gauge: Russian T loading gauge
- Platform heights: 200 mm (7.9 in) and 550 mm (21.7 in)
- Future travel time Moscow - Kazan: 3 hours 17 minutes.[5]
- Avg speed: 235 km/h
Rolling stocks
Proposed rolling stocks for this line which include:
- Talgo Avril Russian gauge version
- Sapsan trainsets, which need to be modified including retractable steps for low platforms and main transformers for AC overhead lines
- Shinkansen-based trainsets, with Russian gauge and low doors
gollark: Even if they're invisible they can still infect you.
gollark: It's a feature, not a bug.
gollark: Everyone! COVID party in the nether!
gollark: The nether is safe from dynmap somehow too.
gollark: E!
See also
References
- https://www.vedomosti.ru/business/news/2017/02/28/679314-rzhd-proekt-vsm
- Moscow to Kazan route details
- Специальные технические условия для проектирования и строительства ВСМ Москва — Казань, СТУ №7, page 6 (in Russian).
- Sonne, Paul (June 19, 2015). "China to Design New Russian High-Speed Railway". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved October 13, 2015.
- "Руководители ОАО "Скоростные магистрали" и Главгосэкспертизы России осмотрели участки строительства будущей ВСМ Москва - Казань" [Heads of JSC "High-Speed Railways" and Glavgosexpertiza of Russia inspected the construction sites of the future high-speed railway Moscow-Kazan]. hsrail.ru (official site of the Russian high-speed rail) (in Russian). 28 April 2017. Retrieved 14 May 2017.
- "Russia & China to invest $15bn in high-speed rail link from Moscow to Kazan". Russia Today. September 1, 2015. Retrieved October 13, 2015.
- "Russia & China to invest $15bn in high-speed rail link from Moscow to Kazan". Business Insider-Agence France-Presse. October 17, 2014. Retrieved October 13, 2015.
- "РЖД завершили проектирование высокоскоростной магистрали Москва — Казань". Retrieved 2018-05-11.
- Мосузел прирастёт станциями
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.