Greater Ring of the Moscow Railway
The Greater Ring of the Moscow Railway (Russian: Большое кольцо Московской железной дороги) is the common name for a system of connector lines between the railways that radiate from Moscow. The general configuration of the Greater Ring is a ring around the main part of Moscow (outside Moscow).[1] It forms part of the radial-ring structure of the Moscow railways. The Greater Ring crosses the rail lines in all 11 radial directions from the railway stations of Moscow. It totals 584 kilometres (363 mi) in length. For its entire length, the ring is equipped with an automatic locking system, permitting, where necessary, two-way single-track operation; elsewhere, there are two track and multiple track sections.[2]
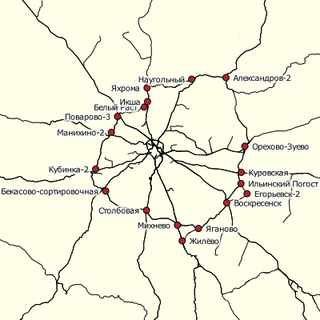
Moscow Outer Ring Railway | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ring allows freight trains to be transferred from one railway to another without entering Moscow; to a lesser extent, it is used for the same purpose by long-distance passenger trains as well. This reduces the transit traffic volume on the innermost sections of the radial rail lines, and makes more time slots available for running commuter trains between Moscow's rail terminals and the city's suburbs. The ring also serves transportation needs of towns and industrial customers located along it.
History
Different segments of the Greater Ring were constructed independently from each other, starting from the late 19th century. The entire ring was completed in 1942-1944, during World War II.
Links with radial lines
The Greater Ring links with the most important radial railway lines that begin and end in Moscow as follows:
- The Kubinka I station (to the west of central Moscow, near Kubinka) provides a link with the Moscow – Smolensk (–Minsk) railway; trains that serve this radial route, as well as the trains of the ring railway, stop here.
- Manikhino I train station near the city of Istra is at the intersection with the Moscow – Riga line.
- To get from the ring railway to the Saint Petersburg–Moscow Railway, a passenger must get off at 142 km and cover a five-minute walk to the Povarovka stop on the St. Petersburg – Moscow railway line.
- Near Iksha, to the north of central Moscow, the ring flows into the Savyolovsky suburban railway line and branches off from it only three stations north, namely at Yakhroma/Dmitrov.
- On the northeastern edge of the city of Sergiyev Posad (81 km railway stop), the ring section coming from Dmitrov flows into the Trans-Siberian Railway, branching off from it at Alexandrov I.
- Another section leads from Alexandrov I to Orekhovo-Zuyevo, to the east of central Moscow, where the Great Railway Ring is crossed by the Moscow – Vladimir – Nizhny Novgorod line.
- The Kurovskaya (Kurovskoye) station is a point of connection with the line Moscow – Lyubertsy – Murom.
- The Voskresensk station is a link with the Moscow – Ryazan – Kazan route.
- The Mikhnevo station is the connection point with the Moscow – Kashira – Pavelets route.
- The Stolbovaya station near Chekhov, to the south of central Moscow, is an intersection with the Moscow – Tula – Kursk line.
- The Bekasovo I junction near the city of Naro-Fominsk is a crossing point with the Moscow – Bryansk – Kiev route.
From here, the ring section to the north of it leads back to Kubinka I.
Operation
The Greater Ring itself entirely belongs to the three regions of the Moscow Railway:
- The western semicircle (from Platform 39 km (40 km) to Sandarovo / Platform 283 km) belongs to the Moscow – Smolensk Railway Division
- The part in the southeast (Nepetsino – Berendino / Yegoryevsk I and II) belongs to the Moscow – Ryazan Railway Division
- The remaining two sections between them (Stolbovaya - Osёnka in the south and Naugolny – Ilyinsky Pogost in the north-east) are part of the Moscow – Kursk Railway Division.
This line is primarily used to let freight traffic bypass Moscow. The two biggest freight stations are Orekhovo and Bekasovo, they are main classification yards for Moscow region, and also have locomotive depots, for freight electric locomotives operating around Moscow.
Some overnight passenger trains also use some segments of Ring to bypass Moscow. Since the late 2000s most, but not all of these trains run through Moscow instead. Commuter traffic is very low, about 3-5 trains per day, and may be delayed due to overload of freight trains. The most used section is Aleksandrov - Karabanovo - Kirzach - Orekhovo, which was built first as a separate line.
Most of the line is two-track, except the northern part. The section Bekasovo – Iksha was converted to one-track in 1990s due to economic crisis. The Dmitrov - Naugolny section was built with one track in wartime, with steepest curves and low speed restriction, so it is rarely used by freight trains. This section is in a state of modernisation in 2010s, with construction of a second track.
Administrative regions
Parts of the Greater Ring are located within three regions (federal subjects) of Russia:
- A small section in the north-east (Arsaki – Alexandrov – Belkovo – Vetchi) is located in Vladimir Oblast. (It crosses 3 districts out of the 16 districts into which that oblast is divided)
- The part to the south-west (Pozhitkovo – Bekasovo I – Vyatkino length of 49 km) is located within the City of Moscow (it crosses Troitsky Administrative Okrug, a territory that was annexed to the City of Moscow from Moscow Oblast in 2012)
- The two largest sections of the ring (the section between Platform 173 km and Sandarovo, in the SE part of the ring, and the one between Platform 90 km and Pozhitkovo, in the NW part of the ring) are located in Moscow Oblast. They cross 11 out of the 29 districts and 5 out of 39 urban districts of that oblast.
Pozhitkovo station is situated both in Moscow and Moscow Oblast, split in half by the city boundary; Bekasovo I is similarly divided, with only a small part of being within Moscow Oblast.
Passenger operation
Suburban passenger traffic is served by OAO Central PPK.
Stations
Alexandrov I to Iksha
- Alexandrov I
- Strunino
- Arsaki
- 90 km
- Buzhaninovo
- 83 km
- 81 km
- Naugolny
- 40 km
- Bubyakovo
- 47 km
- Zhyoltikovo
- 62 km
- Kostino
- 68 km
- 71 km
- 74 km
- Drachyovo
- 80 km
- Ivantsevo
- Yakhroma
- Turist
- Morozki
- Iksha
Iksha to Yaganovo
- Iksha
- 109 km
- Bely Rast
- 116 km
- 120 km
- Bukharovo
- 128 km
- Povarovo II
- 142 km
- Povarovo III
- Depo
- Zhilino
- 155 km
- 159 km
- Manikhino II
- 165 km
- Lukino
- 174 km
- 177 km
- 183 km
- Dyudkovo
- 190 km
- 192 km
- Yastrebki
- 199 km
- Kubinka II
- Kubinka I
- 211 km
- 214 km
- Akulovo
- 221 km
- Pozhitkovo
- Bekasovo I
- Posyolok Kiyevsky
- Bekasovo-Sortirovochnoye
- Bekasovo-Tsentralnoye
- 240 km
- 241 km
- Machikhino
- 250 km
- 252 km
- Kresty
- Novogromovo
- Chernetskoye
- 274 km
- Vyatkino
- Sandarovo
- 283 km
- Stolbovaya
- Detkovo
- Povadino
- 309 km
- 312 km
- Usady-Okruzhnye
- Mikhnevo
- 328 km
- 332 km
- Malino
- 341 km
- Yaganovo
Zhilyovo to Voskresensk
- Zhilyovo
- Shmatovo
- Kolychevo
- Sotnikovo
- Yaganovo
- Lyutik
- Myakinino
- Shubatovo
- Lesnye Dary
- Shkin
- Osyonka
- Nepetsino
- Ratmirovo
- Voskresensk
Voskresensk to Ilyinsky Pogost via Yegoryevsk
- Voskresensk
- Khorlovo
- Rudnikovskaya
- Yegoryevsk II
- 32 km
- Ilyinsky Pogost
Voskresensk to Ilyinsky Pogost via Lopatino
- Voskresensk
- 88 km
- Lopatino
- Berendino
- Ilyinsky Pogost
Ilyinsky Pogost to Alexandrov I
- Ilyinsky Pogost
- Nerskaya
- Davydovo
- Dulyovo
- 122 km
- Tsentralny Blokpost
- Depo
- Severny
- Orekhovo-Zuyevo
- Potochino
- 178 km
- 173 km
- Vetchi
- 168 km
- Sanino
- 157 km
- Ileykino
- Kirzhach
- 138 km
- Belkovo
- 126 km
- Karabanovo
- Alexandrov II
- Alexandrov I
See also
- Little Ring of the Moscow Railway, also known as MKZD, Moscow Central Circle Line, or the MK MZD (The Small Ring of the Moscow Railway)
References
- (Moscow) Finance and other services- Transportation: Rail www.britannica.com, accessed 5 June 2020
- Kirill Golovkin, Translated by Alexandra Tumarkina: The Greater Ring of the Moscow Railway: The secret life of a forgotten suburban line at strelka.com, accessed 5 June 2020