Metal oxide adhesion
The strength of metal oxide adhesion effectively determines the wetting of the metal-oxide interface. The strength of this adhesion is important, for instance, in production of light bulbs and fiber-matrix composites that depend on the optimization of wetting to create metal-ceramic interfaces.[1] The strength of adhesion also determines the extent of dispersion on catalytically active metal.[1] Metal oxide adhesion is important for applications such as complementary metal oxide semiconductor devices. These devices make possible the high packing densities of modern integrated circuits.
Oxide thermodynamics
Metal oxides are formed consistent with minimizing surface energy and minimizing system entropy. The formation reactions are chemical in nature, forming bonds between oxygen dimers and pure metals or metal alloys. The reactions are endothermic for transition metals and semi-metals. At isothermic and isobaric conditions at atmosphere, the probability for a free metal surface to bind an oxygen dimer via oxidation is a function of the partial pressure of oxygen, the surface energy between the crystal and the liquid or vapor phase (see heat of formation), and time.
In standard conditions, the determining factors for phase change are temperature and pressure. The idea here is that oxygen is making a phase change from gas to solid, and at the same time a bond is forming between oxygen and a metal. The instantaneous breaking of one bond and forming a different one required an energy contribution higher than the enthalpy of bond dissociation for molecular gaseous oxygen at 298K is +498.34 kJ/mol and is typically expressed as ∆Hf since it is also the heat of formation.
The majority of contributed entropy in the formation of metal-oxides is from O2(g). Gaseous oxygen molecules have high translation entropy, due to the excited vapor phase. This allows the transport of oxygen from the system to the interface or reaction surface. The change in entropy (ΔS) for oxidation is negative (exothermic) for semi-metals, transition metals, alkali earth metals and lanthanides/actinides. This fact is due to the elevated surface energy of an exposed pure metal and the ability of the tiny oxygen dimer to attract to high energy sites. The trend for oxide formation is that the reaction rate increases as atomic number increases.
Areas with elevated surface electron density will always oxidize prefentially, as is demonstrated beautifully in the formation of electro-anodized titanate. The formation of oxides is dominated by interactions between the Gibbs free energy surfaces of constituents. The intersections of Gibbs surfaces at a given temperature and pressure would be represented in 2D space as phase diagrams. In real world applications, Gibbs surfaces are subject to the additional dimension entropy. This third dimension constitutes a Cartesian coordinate space and the surface mapped out by the Gibbs energy for a given reaction gives a threshold energy needed for a phase transition. These values can be found in ASM library volumes, or online as the "standard heats of formation."
∆G=∆H-T∆S
standard state change of enthalpy is independent and thus the gradient of the change in Gibbs free energy as a function of temperature is linear. This dictates that an oxide becomes less thermodynamically stable with increasing temperature.
An important distinction between equilibrium wetting and non-equilibrium wetting is that the non-equilibrium condition occurs when a chemical reaction is taking place. This non-equilibrium wetting is an irreversible thermodynamic process that accounts for the changes of the chemical potential when forming a new boundary phase, such as an oxide.
Work of adhesion
The ideal work of separation Wsep is the reversible work needed to separate the interface into two free surfaces.[2] Important as a state function depending on the mechanical properties.[2] It is referred to as ideal because when the two free surfaces create an interface, the concentration of the interface will only be identical to the bulk at the instant the surface is created. In order to reach chemical equilibrium, the process of diffusion will take place which will increase any measurement of the work of separation.[2] The work of adhesion is the reversible free energy change for making free surfaces from interfaces.[2] It is represented by the equation:
where:
Wad is the work of adhesion
γm and γo are the respective surface energies of the metal and oxide
γmo is the surface energy between the two materials in contact
The following table gives some common metals and their corresponding surface energies. All the metals are face-centered cubic crystal structure and these surface energies correspond to the (100) surface plane.
| Material | Surface Energy |
|---|---|
| Al | 1.347 |
| Pb | 0.377 |
| Yb | 0.478 |
| Cu | 2.166 |
| Pd | 2.326 |
| Ag | 1.200 |
| Pt | 2.734 |
| Au | 1.627 |
Oxide stability
Ellingham diagrams are generated according to the second law of thermodynamics and are a graphical representation of the change in the Gibbs free energy with respect to changing temperature for the formation of oxides.
Solid-gas interface
Structure
Real surfaces may be macroscopically homogeneous, but their microscopic heterogeneity plays a crucial role in the relationship between the metal and its oxide.
Transition metal oxides
Certain transition metals form multiple oxide layers that have different stoichiometric compositions. This is because the metal has multiple valency states with fewer or more electrons in the valence shell. These different valency states allow for multiple oxides to be formed from the same two elements. As the local composition of the material changes through diffusion of atoms, different oxides form as layers, one on top of another. The total adhesion in this situation involves the metal-oxide interface and oxide-oxide interfaces, which adds increasing complexity to the mechanics.[3]
Roughness
Increasing surface roughness increases the number of dangling bonds at the metal-oxide interface. The surface free energy of a crystal face is:
where:
E is the binding energy of the material
T is the temperature of the system
S is the surface entropy of the material
The binding energy favors a smoother surface that minimizes the number of dangling bonds, while the surface entropy term favors a rougher surface with increasing dangling bonds as the temperature is increased.[4]
Heterogeneity
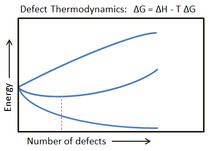
Solid adsorption of an oxygen molecule depends on the heterogeneity of the substrate. Crystalline solid adsorption is dependent on the exposed crystal faces, grain orientations, and inherent defects because these factors provide adsorption sites with different steric configurations. Adsorption is largely determined by the reduction of Gibbs free energy associated with the exposed substrate.
Crystallographic orientation
A material's charge remains neutral when a surface is created by the law of charge conservation, but individual Bravais lattice planes, defined by their Miller indices, may be non-polar or polar based on their symmetry. A dipole moment increases the surface Gibbs free energy, but the greater polarizability of oxygen ions as compared to metals allows polarization to decrease the surface energy and thus increase the ability of metals to form oxides. Consequently, different exposed metal faces may adhere weakly to non-polar oxide faces, but be able to perfectly wet a polar face.
Defects
Surface defects are the localized fluctuations of surface electronic states and binding energies. Surface reactions, adsorption, and nucleation can be drastically affected by the presence of these defects.[5]
Vacancies
Oxide growth is dependent upon the flux (diffusion) of either coupled or independent anions and cations through the oxide layer.[6][7] Stoichiometric oxides have an integer ratio of atoms can only support coupled diffusion of anions and cations through the lattice migration of Schottky defects (paired anion/cation vacancies) or Frenkel defects (complete anion lattice with cation vacancies and interstitials).[6][7] Non-stoichiometric oxide films support independent ion diffusion and are either n-type (extra electrons) or p-type (extra electron holes). Although there are only two valence states, there are three types:[6][7]
- cation excess (n-type)
- anion deficit (n-type)
- cation deficit (p-type)
Non-stoichiometric oxides most commonly have excess metal cations as a result of insufficient oxygen during the creation of the oxide layer. Excess metal atoms with a smaller radius than O2− anions are ionized within the crystal lattice as interstitial defects and their lost electrons remain free within the crystal, not taken by the oxygen atoms. The presence of mobile electrons within the crystal lattice significantly contributes to the conduction of electricity and the mobility of ions.[6]
Impurities
Impurity elements in the material can have a large effect on the adhesion of oxide films. When the impurity element increases the adherence of the oxide to the metal it is known as the reactive element effect or RE effect. Many mechanics theories exist on this topic. The majority of them attribute the increase in adhesion strength to the greater thermodynamic stability of the impurity element bonded with oxygen than the metal bonded to the oxygen.[2][8] Inserting yttrium into nickel alloys to strengthen the oxide adhesion is an example of the reactive element effect.
Dislocations
Dislocations are thermodynamically unstable, kinetically trapped defects. Surface dislocations often create a screw dislocation when stress is applied. In certain cases, screw dislocations can negate the nucleation energy barrier for crystal growth.[5]
Oxide-support relationship
The adsorption of a monolayer of gas atoms is either commensurate or incommensurate. Commensurate adsorption is defined by having a crystal structure relationship between substrate-adsorbate layer that produces a coherent interface. Wood's notation is a description of the relationship between the simplest repeating unit area of the solid and adsorbate. The difference between the resulting commensurate interfaces can be described as an effect of misfit. The interfacial interaction can be modeled as the sg plus the stored elastic displacement energy due to lattice misfit. A large misfit corresponds to an incoherent interface where there is no coherency strain and the interface energy can be taken as simply the sg. In contrast, a small misfit corresponds with a coherent interface and coherency strain that results in the interfacial energy equivalent to the minimum sg.[9]
Strength of bond
The strength of the bond between the oxide and metal for the same nominal contact area can range from Pa to GPa stresses. The cause of this huge range stems from multiple phenomena dealing with at least four different types of adhesion. The main types of bonding that form adhesion are electrostatic, dispersive (van der Waals or London forces), chemical and diffusive bonding. As the adhesive forces increase, separation in crystalline materials can go from elastic debonding to elastic-plastic debonding. This is due to a larger number of bonds being formed or an increase in strength of the bonds between the two materials. Elastic-plastic debonding is when local stresses are high enough to move dislocations or make new ones.[10]
Solid-gas kinetics
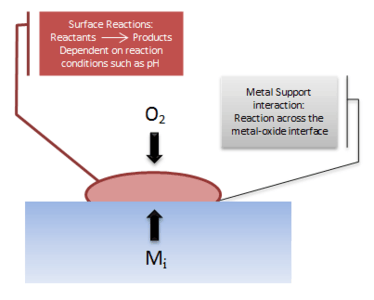
When a gas molecule strikes a solid surface the molecule may either rebound or be adsorbed. The rate at which gas molecules strike the surface is a large factor in the overall kinetics of oxide growth. If there molecule is absorbed there are three potential outcomes. The surface interaction can be strong enough to dissociate the gas molecule into separate atoms or constituents. The molecule may also react with surface atoms to change its chemical properties. The third possibility is solid surface catalysis, a binary chemical reaction with a previously adsorbed molecule on the surface.
Dispersion
Most often it is kinetically favorable for the growth of a single oxide monolayer to be completed before the growth of subsequent layers. Dispersion in general can be modeled by:
where:
Ns is the number of atoms on the surface
Nt is the total number of atoms in the material
Dispersion is crucial to the growth of oxides because only atoms that are exposed to the interface can react to form oxides.
Diffusion
After the initial oxide monolayer is formed, new layers begin to build and the ions must be able to diffuse through the oxide in order to increase thickness of the oxide. The rate of oxidation is controlled by how fast these ions are able to diffuse through the material. As the thickness of the oxide increases, the rate of oxidation decreases because it requires the atoms to travel a further distance. This rate can quantified by calculating the rate of diffusion of vacancies or ions using Fick's first law of diffusion.[11]
where:
J is the flux and has units of mol·m−2·s−1
D is the diffusivity of the ions in the material
δC is the change in concentration of the material
δx is the thickness of the oxide layer
Solid surface catalysis
In 2007 the Nobel Prize in chemistry was awarded to Gerhard Ertl for the study of solid-gas interface molecular processes. One such process is the oscillatory kinetic catalysis. Oscillatory kinetic catalysis can be explained by different crystal surfaces favoring unmodified faces and reconstruction to reduce surface strain. The presence of CO can cause the reversal of surface reconstruction past a certain percent coverage. Once the reversal occurs, oxygen can be chemisorbed on the reverted surfaces. This produces an adsorption pattern with areas of surface coverage rich in CO and others O2.[12]
Driving force
The driving force of catalysis is determined by the difference between the unprimed equilibrium and the instantaneous interfacial free energies.[2]
See also
- Oxide
- Crystallographic defect
- Corrosion
- Oxidation potential
- Reduction potential
- Pourbaix diagram
- Ellingham diagram
- MOSFET
- Metal oxide varistor
- Surface Properties of Transition Metal Oxides
References
- Peden, C; K.B. Kidd; N. D. Shinn (1991). "Metal/Metal-Oxide Interfaces: A surface science approach to the study of adhesion". Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology. 9 (3): 1518–1524. doi:10.1116/1.577656.
- Finnis, M W (1996). "The theory of metal-ceramic interfaces". Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter. 8 (32): 5811–5836. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/8/32/003.
- Henrich, Victor; Cox P A (1996). The Surface Science of Metal Oxides. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-56687-2.
- Libbrecht, Kenneth (2005). "The physics of snow crystals". Reports on Progress in Physics. 68 (4): 855–895. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/68/4/R03.
- Butt, Hans-Jurgen; Karlheinz Graf; Michael Kappl (2006). Physics and Chemistry of Interfaces. WILEY-VCH. pp. 167–169.
- Kasap, S.O. (2006). Principle of Electron Materials and Devices. McGraw-Hill. pp. 73–75. ISBN 978-0-07-295791-4.
- Behrens, Malte. "Solid State Kinetics" (PDF). Lecture Series. Fritz Haber Institute of the Max Planck Society Department of Inorganic Chemistry. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 May 2011. Retrieved 1 June 2011.
- Pint, B A (2010). "Progress in Understanding the Reactive Element Effect Since the Whittle and Stringer Literature Review". Metals and Ceramics Division. 18 (18): 2159–2168.
- Johansson, Sven; Mikael Christensen; Goran Wahmstrom (2005). "Interface energy of semicoherent metal-ceramic interfaces". Physical Review Letters. 95 (22): 226108. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.226108. PMID 16384245.
- Gerberich, W W; M J Cordill (2006). "Physics of Adhesion". Reports on Progress in Physics. 69 (7): 2157–2204. doi:10.1088/0034-4885/69/7/R03.
- Rutter, N A. "Environmental Stability of Materials". Lecture Series. University of Cambridge. Archived from the original on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 6 June 2011.
- Ertl, Gerhard. "Chemical Processes on Solid Surfaces" (PDF). Nobel Prize. The Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 June 2011. Retrieved 6 June 2011.