Maryland Route 410
Maryland Route 410 (MD 410) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland and known for most of its length as East–West Highway. The highway runs east to west (hence its name) for 13.92 miles (22.40 km)–from Pennsy Drive in Landover Hills to MD 355 in Bethesda. MD 410 serves as a major east–west commuter route through the inner northern suburbs of Washington, D.C., connecting the commercial districts of Bethesda, Silver Spring, and Hyattsville. In addition, the highway serves the industrial area of Landover Hills and the residential suburbs of Chevy Chase, Takoma Park, Chillum, Riverdale, and East Riverdale. The road also connects many of the arterial highways and freeways that head out of Washington. Additionally, it provides a highway connection to transit and commercial hubs centered around Washington Metro subway stations in Bethesda, Takoma Park, Hyattsville, Silver Spring, and New Carrollton–the latter two of which provide additional connections to MARC and Amtrak trains.
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
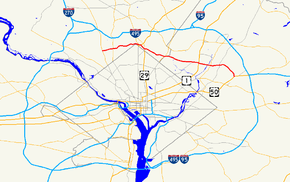 Maryland Route 410 highlighted in red | ||||
| Route information | ||||
| Maintained by MDSHA | ||||
| Length | 13.92 mi[1] (22.40 km) | |||
| Existed | 1930–present | |||
| Major junctions | ||||
| West end | ||||
| ||||
| East end | Pennsy Drive in Landover Hills | |||
| Location | ||||
| Counties | Montgomery, Prince George's | |||
| Highway system | ||||
| ||||
MD 410 was originally built along a mostly new alignment between Bethesda and Silver Spring in the late 1920s. The Montgomery County portion has not changed much in the ensuing decades. In the mid-1930s, the highway was extended east to Hyattsville in Prince George's County. where it has been realigned and extended multiple times. These changes included: an extension along existing roads further into Hyattsville in the mid-1940s; a realignment within Hyattsville in the mid-1950s; an extension through Riverdale in the late 1960s; and the final extension to New Carrollton and Landover Hills in the early 1990s.
Route description
MD 410 is maintained by the Maryland State Highway Administration (MDSHA) except for three municipally maintained segments in the city of Takoma Park and a short stretch maintained by Prince George's County in East Riverdale.[1][2]
The segments maintained by the city of Takoma Park run from Chestnut Avenue to near Cedar Avenue for 0.17 miles (0.27 km); from Maple Avenue to MD 195 for 0.27 miles (0.43 km); and from the second junction with MD 195 to Elm Avenue, the longest non-state maintained portion with a length of 0.53 miles (0.85 km).[1][2]
In Prince George's County, in East Riverdale, MD 410 is county maintained for 0.35 miles (0.56 km), from the Baltimore-Washington Parkway to its turn from Riverdale Road onto Veterans Parkway.[1] Here, in its final 2.6 miles, MD 410 becomes a part of the National Highway System, serving as a principal arterial for US 50. Past Route 50, MD 410 reaches its eastern terminus at Pennsy Drive.[1][2]
Montgomery County
MD 410 begins at a pair of junctions with MD 355 (Wisconsin Avenue) and MD 187 (Old Georgetown Road) on either side of Bethesda station on the Washington Metro's Red Line in downtown Bethesda. Westbound MD 410 ends at the intersection of two-way MD 355 and the southern terminus of MD 187, which begins one-way northbound along Old Georgetown Road. Traffic from the southbound direction of MD 187 follows Woodmont Avenue and Montgomery Lane to the start of eastbound MD 410 at the intersection of MD 355 and Montgomery Avenue.[1][3]
MD 410 heads east as a one-way pair—East–West Highway westbound and Montgomery Avenue eastbound—to the eastern edge of downtown Bethesda, where the two directions converge east of Bethesda-Chevy Chase High School. From that intersection, traffic can use a U-turn lane from Montgomery Avenue to enter westbound East–West Highway back towards Maryland 355 or use a merge lane to enter MD 410 heading east. From there, the highway continues east as a four-lane, undivided East–West Highway.[1][3]
_just_east_of_Maryland_State_Route_384_(Colesville_Road)_in_Silver_Spring%2C_Montgomery_County%2C_Maryland.jpg)
MD 410 crosses over the Capital Crescent Trail. It then follows the northern edge of the town of Chevy Chase; crosses Coquellin Run; and runs along the southern edge of the Columbia Country Club to its intersection with MD 185 (Connecticut Avenue).[1][3]
MD 410 then leaves Chevy Chase and passes through an unincorporated area of Chevy Chase, within which the highway meets the northern end of MD 186 (Brookville Road). It descends into the valley of Rock Creek, where it intersects with Jones Mill Road and Beach Drive–the main road through Rock Creek Park). MD 410 then crosses over Rock Creek, passes to the north of Meadowbrook Park, and leaves the valley as a four-lane divided highway with a narrow median and flanking service roads.[1][3]
MD 410 reaches the top of a hill at Grubb Road and descends into the valley of a branch of Rock Creek. The highway becomes undivided at Sundale Drive and crosses the branch stream just west of the northern corner of the District of Columbia and its attendant boundary marker. It then leaves the stream valley and ascends to an intersection with MD 390 (16th Street) at the western edge of downtown Silver Spring.[1][3]
MD 410 intersects MD 384 (Colesville Road) next to the headquarters of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration and just south of the Metro's Silver Spring station, which serves the Washington Metro's Red Line and the MARC Brunswick Line. The highway parallels CSX's Metropolitan Subdivision and the Red Line southeast to a five-way intersection with US 29 (Georgia Avenue) and 13th Street.[1][3]
Here MD 410 crosses Georgia Avenue to Burlington Avenue. (No direct access exists from eastbound MD 410 to northbound Georgia Avenue (US 29) or from southbound Georgia Avenue US to eastbound MD 410.) MD 410 continues east on three-lane Burlington Avenue (two lanes westbound and one lane eastbound) and crosses over the rail and Metro lines. At Fenton Street, the highway veers southeast onto two-lane Philadelphia Avenue, where it enters the city of Takoma Park as it passes by the Takoma Park/Silver Spring campus of Montgomery College.[1][3]
MD 410 intersects MD 320 (Piney Branch Road) and then a four-way stop at Holly Avenue next to Takoma Park Elementary School. The highway continues through an intersection with Maple Avenue, next to the Takoma Park Library; then follows Philadelphia Avenue to its end at MD 195 (Carroll Avenue) at Takoma Junction; runs concurrently with MD 195 for one block; continues east along Ethan Allen Avenue, which it follows–through a three-way stop at Jackson Avenue–to the eastern city limit of Takoma Park and the Montgomery-Prince George's county line at MD 650 (New Hampshire Avenue).[1][3]
Prince George's County
MD 410's name becomes East–West Highway again as it heads east from MD 650 as a four-lane undivided highway through the northern part of Chillum. The highway has frontage roads on either side of its crossing of Sligo Creek, then becomes divided ahead of its intersection with MD 212 (Riggs Road).[1][3]
As it heads southeast briefly on Ager Road, MD 410 briefly has six lanes. Ager Road eventually passes the West Hyattsville station on the Washington Metro's Green and Yellow lines. MD 410 has a partial intersection with Ager Road; the missing movements between MD 410 and Ager Road are made via 23rd Avenue to the east.[1][3]
MD 410 then branches into its own road again, where it becomes a four lane divided highway. It crosses the Northwest Branch Anacostia River and enters Hyattsville. The highway expands to six lanes as it passes between The Mall at Prince George's and Metro's Prince George's Plaza station. Beyond University Town Center and the headquarters of the National Center for Health Statistics, MD 410 approaches a four-way intersection with the northern end of MD 500 (Queens Chapel Road) and the southern end of Adelphi Road.[1][3]
The six-lane divided highway continues east, between Hyattsville to the south and University Park to the north. Eventually the south side of the highway is flanked by the town of Riverdale Park. As MD 410 crosses US 1 (Baltimore Avenue), it fully enters Riverdale Park, where it reduces to four lanes. It crosses over CSX's Capital Subdivision tracks, which also carry the MARC Camden Line. (The Camden Line can be boarded at the Riverdale station within the Riverdale Park Historic District to the south, which also contains the Riversdale Mansion.) A tributary of the Northeast Branch Anacostia River briefly runs within the median of the highway shortly before it crosses over the Northeast Branch. Then MD 410 intersects and crosses MD 201 (Kenilworth Avenue) leaving the town of Riverdale Park.[1][3]
The highway continues as Riverdale Road, a four-lane road with a center turn lane, through the unincorporated area of East Riverdale on its way to a diamond interchange with the Baltimore–Washington Parkway (unsigned MD 295).[1][3]
MD 410 then continues east on Riverdale Road and turns southeast onto Veterans Parkway, a four-lane divided highway (while Riverdale Road continues toward New Carrollton). The divided highway briefly enters the city of New Carrollton around its intersection with MD 450 (Annapolis Road). MD 410 continues south and intersects Ellin Road (unsigned MD 594F) before passing through a diamond interchange with US 50 (John Hanson Highway).[1][3]
The highway crosses over US 50; Amtrak's Northeast Corridor railroad tracks, also used by MARC's Penn Line; and Washington Metro's Orange Line. South of the railroad tracks, MD 410 quickly reaches its eastern terminus at Pennsy Drive. The nearby New Carrollton Metro station serves as the eastern terminus of the Orange Line subway and hosts MARC and Amtrak service and commuter and Intrastate bus service. Nearby Ardwick Ardmore Road provides access to the primary entrance to the Metro New Carrollton station. Secondary access to the station is provided by Ellin Road north of US 50.[1][3]
History
The Bethesda-Silver Spring Highway was conceived in the late 1920s as a means of directly connecting the two Montgomery County inner suburbs on the north side of Washington.[4] The highway was under construction between 1927 and 1929, and it was signed as MD 410 by 1930.[4][5]
When completed, MD 410 extended between what was then US 240 in Bethesda and 16th Street in Silver Spring, which had been extended north from the District of Columbia in 1928.[4][5] Continuing to the present center of Silver Spring required heading south on 16th Street to Blair Portal, then east on Colesville Road, which had been extended to Blair Portal in 1927, to Georgia Avenue.[4]
Most of MD 410 was built on a new alignment with the exception of the part between present day MD 186 and Jones Mill Road, which followed the old Brookville Road.[5]

By 1933, the new state highway was the busiest road in Montgomery County.[4] The road, which became known as East-West Highway, was originally built with a width of 20 feet, but the heavy traffic led the Maryland State Roads Commission (SRC), the predecessor of MDSHA, to suggest in 1934 that the road be widened to 40 feet in the near future. The SRC also recommended extending East-West Highway through Silver Spring and Takoma Park to Hyattsville.[6]
By 1935, the highway was extended along a new alignment east from 16th Street to Takoma Park, then placed on Philadelphia Avenue and Ethan Allen Avenue within Takoma Park.[7] The extension to MD 212 in Hyattsville was completed in 1936.[8]
| |
|---|---|
| Location | Chillum–Hyattsville |
| Existed | 1927–c. 1946 |
After World War II, MD 410 was extended even further east and saw significant improvement on its extant sections. By 1946, MD 410 was extended over Hyattsville's Ager Road, Hamilton Street, 38th Avenue, and Jefferson Avenue–roads then designated MD 209–to a new eastern terminus at US 1 in Hyattsville.[9][10]
In addition, the pre-1946 course saw completion of efforts to widen the road to 40 feet. The highway between Connecticut Avenue (then MD 193) and Georgia Avenue (US 29) was widened in 1946 and 1947.[11] In 1950, two segments were widened: Wisconsin Avenue (US 240) to Connecticut Avenue (MD 193), and MD 650 (New Hampshire Avenue) in Takoma Park to US 1 in Hyattsville.[12]
| |
|---|---|
| Location | Hyattsville–Riverdale |
| Existed | 1942–1956 |
Beyond minor improvements, the configuration of MD 410 in Montgomery County has remained much same since 1950. The only major change was the highway being split onto a one-way pair of streets in Bethesda in 1988.[13]
The Prince George's County section has seen more substantial changes over the intervening decades. The first major change in alignment occurred in 1956, when MD 410 was completed on a new alignment as a four-lane divided highway between Ager Road (just east of MD 212) and MD 500.[14][15]
MD 410 was subsequently extended east over the former MD 403 (Colesville Road), which ran between MD 500 and US 1 in Riverdale.[16] By 1970, this segment was upgraded to a multi-lane divided highway.[17]
Then, between 1967 and 1970, MD 410 was extended as a four-lane divided highway on a new alignment east from US 1, past MD 201, to the Baltimore-Washington Parkway interchange at Riverdale Road.[18] This extension bypassed and replaced MD 412 between US 1 and the B-W Parkway.[16]
Finally, MD 410 was completed in 1991 when it extended east on Veterans Parkway past US 50 to its current terminus at Pennsy Drive.[19]
The sections of MD 410 in Takoma Park from Chestnut Avenue to Cedar Avenue and from Maple Avenue to Elm Avenue were transferred from municipal to state maintenance in an agreement dated February 16, 2013. The portion of MD 410 between MD 295 and Veterans Parkway in Prince George's County was transferred from county to state maintenance in an agreement dated May 11, 2017.[20]
Junction list
| County | Location | mi [1] | km | Destinations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Montgomery | Bethesda | 0.00 | 0.00 | Western terminus; southern terminus of MD 187 | |
| Chevy Chase | 1.01 | 1.63 | |||
| 1.38 | 2.22 | Northern terminus of MD 186 | |||
| 1.89 | 3.04 | Beach Drive south / Jones Mill Road north – Rock Creek Park | |||
| Silver Spring | 3.48 | 5.60 | |||
| 3.71 | 5.97 | ||||
| 4.24 | 6.82 | No direct access from eastbound MD 410 to northbound US 29 or from southbound US 29 to eastbound MD 410 | |||
| Takoma Park | 4.96 | 7.98 | |||
| 5.56 | 8.95 | West end of concurrency with MD 195 | |||
| 5.63 | 9.06 | East end of concurrency with MD 195 | |||
| 6.31 | 10.15 | ||||
| Prince George's | Chillum | 7.17 | 11.54 | ||
| Hyattsville | 8.96 | 14.42 | Northern terminus of MD 500 | ||
| Riverdale Park | 9.48 | 15.26 | |||
| 10.56 | 16.99 | ||||
| East Riverdale | 11.33 | 18.23 | Diamond interchange | ||
| New Carrollton | 12.83 | 20.65 | |||
| 13.19 | 21.23 | Ellin Road (MD 594 east) | Western terminus of unsigned MD 594F | ||
| Landover Hills | 13.46 | 21.66 | US 50 exit 5 | ||
| 13.92 | 22.40 | Pennsy Drive to Ardwick Ardmore Road | Eastern terminus | ||
1.000 mi = 1.609 km; 1.000 km = 0.621 mi
| |||||
Auxiliary route
MD 410 has one former auxiliary route. MD 410A was the designation for the 0.25-mile (0.40 km) portion of Belcrest Road between MD 500 and MD 410 in Hyattsville.[21] The route was assigned by 1999.[22] MD 410A was transferred to county maintenance in 2004.[23]
See also

References
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2013). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2015-05-14.
- Montgomery County (PDF).
- Prince George's County (PDF).
- National Highway System: Washington, DC-VA-MD (PDF) (Map). Federal Highway Administration. October 1, 2012. Retrieved 2015-05-14.
- Staff. Maryland General Highway Statewide Grid Map (PDF) (Map) (2014 ed.). Maryland State Highway Administration. §§ F10B, F11A, F11C, F11D. Retrieved 2015-05-18.
- Oshel, Robert E.; Slatick, Marilyn S. (1998). Homesites of Distinction: The History of Woodside Park. Silver Spring, MD: Woodside Park Civic Association. Retrieved 2010-01-27.
- Maryland Geological Survey (1930). Map of Maryland Showing State Road System: State Aid Roads and Improved County Road Connections (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- Byron, William D.; Lacy, Robert (December 28, 1934). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1931–1934 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 20, 37. Retrieved 2010-01-25.
- Maryland Geological Survey (1935). Map of Maryland Showing State Road System: State Aid Roads and Improved County Road Connections (Map). Baltimore: Maryland Geological Survey.
- Tabler, H.E.; Wilkinson, C. Nice; Luthardt, Frank F. (December 4, 1936). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1935–1936 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 105. Retrieved 2010-01-25.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1940). Map of Maryland Showing Highways and Points of Interest (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1946). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map) (1946–1947 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Reindollar, Robert M.; George, Joseph M.; McCain, Russell H. (February 15, 1949). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1947–1948 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 114. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- Reindollar, Robert M.; George, Joseph M.; McCain, Russell H. (December 20, 1950). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1949–1950 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. pp. 126, 152. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- "Traffic Volume Map" (PDF). Maryland State Highway Administration. 1988. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1956). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Bonnell, Robert O.; Bennett, Edgar T.; McMullen, John J. (November 2, 1956). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1955–1956 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 148. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- McCain, Russell H.; Bennett, Edgar T.; Kelly, Bramwell (November 12, 1954). Report of the State Roads Commission of Maryland (1953–1954 ed.). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission. p. 163. Retrieved 2010-01-26.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1970). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Maryland State Roads Commission (1967). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Roads Commission.
- Maryland State Highway Administration (1991). Maryland: Official Highway Map (Map). Baltimore: Maryland State Highway Administration.
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2018). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved March 21, 2020.
- Montgomery County (PDF).
- Prince George's County (PDF).
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2003). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- Prince George's County (PDF).
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 1999). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- Prince George's County (PDF).
- Highway Information Services Division (December 31, 2004). Highway Location Reference. Maryland State Highway Administration. Retrieved 2015-05-22.
- Prince George's County (PDF).
