Manaoag, Pangasinan
Manaoag, officially the Municipality of Manaoag (Pangasinan: Baley na Manaoag; Ilocano: Ili ti Manaoag; Tagalog: Bayan ng Manaoag), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Pangasinan, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 69,497 people.[3]
Manaoag | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Manaoag | |
.jpg) Minor Basilica of Our Lady of Manaoag | |
 Seal | |
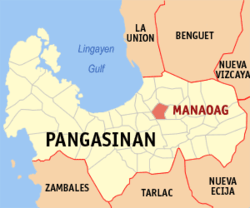 Map of Pangasinan with Manaoag highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Manaoag Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 16°02′38″N 120°29′08″E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Ilocos Region (Region I) |
| Province | Pangasinan |
| District | 4th district |
| Founded | October 7, 1600 |
| Barangays | 26 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Kim Mikael D. Amador |
| • Vice Mayor | Domyciano Z. Ching |
| • Congressman | Christopher George Martin P. De Venecia |
| • Electorate | 46,989 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 55.95 km2 (21.60 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 69,497 |
| • Density | 1,200/km2 (3,200/sq mi) |
| • Households | 14,633 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 1st municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 11.62% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 135,872,875.43 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 2430 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)75 |
| Climate type | tropical monsoon climate |
| Native languages | Pangasinan Ilocano Tagalog |
| Website | www |
Manaoag is bordered by Pozorrubio in the north, Urdaneta City and Mapandan in the south, Laoac in the east, and San Jacinto in the west.
Etymology
Manaoag came from the Pangasinan word "Mantaoag" which means "to call".
Barangays
Manaoag is politically subdivided into 26 barangays:
- Babasit
- Baguinay
- Baritao
- Bisal
- Bucao
- Cabanbanan
- Calaocan
- Inamotan
- Lelemaan
- Licsi
- Lipit Norte
- Lipit Sur
- Matulong
- Mermer
- Nalsian
- Oraan East
- Oraan West
- Pantal
- Pao
- Parian
- Poblacion
- Pugaro
- San Ramon
- Santa Ines
- Sapang
- Tebuel
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1903 | 16,793 | — |
| 1918 | 22,279 | +1.90% |
| 1939 | 29,030 | +1.27% |
| 1948 | 34,304 | +1.87% |
| 1960 | 41,164 | +1.53% |
| 1970 | 48,091 | +1.57% |
| 1975 | 48,450 | +0.15% |
| 1980 | 36,742 | −5.38% |
| 1990 | 45,339 | +2.13% |
| 1995 | 49,705 | +1.74% |
| 2000 | 54,743 | +2.09% |
| 2007 | 62,684 | +1.89% |
| 2010 | 64,578 | +1.09% |
| 2015 | 69,497 | +1.41% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][5][6][7] | ||
Our Lady of Manaoag
The town is a popular local pilgrimage site as it enshrines a 17th-century ivory statue of St Mary under the title of Nuestra Señora del Rosario de Manaoag ("Our Lady of the Rosary of Manaoag"). Legend has it that a young man had a vision of St Mary, who told him to have the shrine built. Famous souvenirs include candles, rosaries, and ampullae of blessed oil with flowers (which supposedly has healing properties), as well as less religious ones such as bagoóng monamon and tupig.
Climate
| Climate data for Manaoag, Pangasinan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 29 (84) |
29 (84) |
30 (86) |
32 (90) |
33 (91) |
33 (91) |
33 (91) |
33 (91) |
33 (91) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 21 (70) |
21 (70) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
23 (73) |
22 (72) |
21 (70) |
23 (73) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 127.5 (5.02) |
115.8 (4.56) |
129.7 (5.11) |
141.1 (5.56) |
248.2 (9.77) |
165 (6.5) |
185.3 (7.30) |
161.9 (6.37) |
221.4 (8.72) |
299.5 (11.79) |
199 (7.8) |
188.7 (7.43) |
2,183.1 (85.93) |
| Average rainy days | 17 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 20 | 19 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 20 | 17 | 19 | 221 |
| Source: World Weather Online[8] | |||||||||||||
List of Cultural Properties of Manaoag
| Cultural Property wmph identifier |
Site name | Description | Province | City/municipality | Address | Coordinates | Image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minor Basilica of Our Lady of the Rosary of Manaoag | first chapel built in 1600s; rebuilt during World War II | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 16.044044°N 120.488858°E | |||
| Our Lady of Manaoag College | formerly an old convent beside Manaoag Church | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 16.043014°N 120.489346°E |  | ||
| Manaoag Town Hall | where the Municipal Government of Manaoag is located | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 16.043631°N 120.487125°E | |||
| Veterans Freedom Hall | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 16.043500°N 120.487178°E | ||||
| Llamido House | Constructed in 1960's | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 351 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042757°N 120.487908°E | ||
| Lazaro Corpuz House | Constructed in 1935 | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042459°N 120.488209°E | ||
| Macario Corpuz House | Constructed in 1920s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 285 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042353°N 120.488329°E | ||
| Filomena House | Constructed in 1950s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 281 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042447°N 120.488539°E | ||
| Tanguilig House | Constructed in 1920s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 240 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.041939°N 120.488616°E | ||
| Dionisio Guico House | Constructed in 1958 | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 272 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042013°N 120.488932°E | ||
| Mendoza House | Constructed in 1930s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 279 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042287°N 120.488692°E | ||
| Felipe Guico House | Constructed in 1940s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 270 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.042119°N 120.488817°E | ||
| Berceles House | Constructed in 1960s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | 271 N. Garcia Road (Guico Street) | 16.041851°N 120.488730°E | ||
| Bautista House | Constructed in 1930s | Pangasinan | Manaoag, Pangasinan | Guico Street | 16.041473°N 120.488806°E |
Images
- Manaoag Town Hall (Poblacion)
- Manaoag Tourism Youth Center
- St. Camillus College of Manaoag and Maternity & Polyclinic
 Basilica of Our Lady of the Holy Rosary of Manaoag
Basilica of Our Lady of the Holy Rosary of Manaoag- Hotel Manaoag (Soriano Street
- Aloragat bridge and Aloragat River
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Pangasinan". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region I (Ilocos Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region I (Ilocos Region)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region I (Ilocos Region)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Pangasinan". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "Manaoag, Pangasinan: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". World Weather Online. Retrieved 12 October 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Manaoag. |
- Manaoag Profile at PhilAtlas.com
- Municipal Profile at the National Competitiveness Council of the Philippines
- Manaoag at the Pangasinan Government Website
- Local Governance Performance Management System
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Our Lady of Manaoag
- Manaoag Shrine