Madalag
Madalag, officially the Municipality of Madalag (Aklanon: Banwa it Madalag; Hiligaynon: Banwa sang Madalag; Tagalog: Bayan ng Madalag), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Aklan, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 18,389 people.[3]
Madalag | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Madalag | |
 Aklan River in Madalag | |
 Seal | |
| Motto(s): Madalagnon Ako Banwa Ko Amligan Ko | |
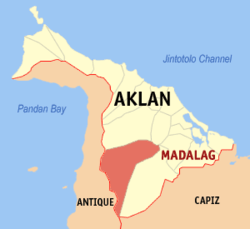 Map of Aklan with Madalag highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Madalag Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 11°31′N 122°18′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Western Visayas (Region VI) |
| Province | Aklan |
| District | 1st district of Aklan |
| Founded | 1948 |
| Barangays | 25 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Alfonso 'Dindo' A. Gubatina |
| • Vice Mayor | Rex T. Gubatina |
| • Congressman | Carlito S. Marquez |
| • Electorate | 12,836 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 269.6 km2 (104.1 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[3] | |
| • Total | 18,389 |
| • Density | 68/km2 (180/sq mi) |
| • Households | 4,239 |
| Demonym(s) | Madalagnon |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 4th municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 28.77% (2015)[4] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 84,186,338.12 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 5603 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)36 |
| Climate type | tropical climate |
| Native languages | Aklan Hiligaynon Tagalog |
Madalag was formerly an arrabal and part of Libacao. In 1948, it was separated and constituted as a separate town, with the following barrios: Logohon, Singay, Balactasan, Cabangahan, Cabilawan, Pangitan, San Jose, Talimagao, Talangban, Alaminos, Catabana, Bakyang, Calicia, Mercedes, Maria Cristina, Dit-ana, Guinato-an, Tigbauan, Alas-as, Mamba, Medina, Panikyason, and Paningayan.[5]
Geography
According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the municipality has a land area of 269.6 square kilometres (104.1 sq mi) [2] constituting 14.80% of the 1,821.42-square-kilometre- (703.25 sq mi) total area of Aklan.
Madalag is situated in the south-central section of the province, bounded on the east by Balete, west by the Province of Antique, north by Malinao and Banga, and south by Libacao. It is 192 kilometres (119 mi) away from regional capital, Iloilo City, and 34 kilometres (21 mi) south from the provincial capital Kalibo.
Climate
Madalag has a Type III climate which is relatively dry from March to May and wet for the rest of the year.
| Climate data for Madalag, Aklan | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 27 (81) |
28 (82) |
30 (86) |
32 (90) |
32 (90) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
29 (85) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 22 (72) |
22 (72) |
22 (72) |
23 (73) |
25 (77) |
25 (77) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
24 (74) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 47 (1.9) |
33 (1.3) |
39 (1.5) |
48 (1.9) |
98 (3.9) |
150 (5.9) |
169 (6.7) |
147 (5.8) |
163 (6.4) |
172 (6.8) |
118 (4.6) |
80 (3.1) |
1,264 (49.8) |
| Average rainy days | 11.4 | 8.2 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 19.1 | 25.6 | 27.4 | 25.5 | 25.5 | 25.2 | 18.5 | 14.5 | 219.9 |
| Source: Meteoblue [6] (Use with caution: this is modeled/calculated data, not measured locally.) | |||||||||||||
Soil
There are four (4) varied soil types found in the municipality. They are the San Miguel Clay Loam, Alimodian clay loam, Sapcan clay and Sigcay clay. San Miguel clay is found in barangay Panipiason and Medina. Alimodian clay is found in barangay San Jose, Ma. Cristina and Galicia. Sapian clay is found in the barangay of Mercedes, Bacyang and Alaminos. Sigcay clay is found in the Poblacion, Logohon and Cabilawan.
Land Use
Some 7,717.0251 hectares (19,069.184 acres) or 28.80% of Madalag land area is planted with high value crops leaving only about 17,772.1917 hectares (43,916.042 acres) (66.35) as timber land and 24.6342 hectares (60.872 acres) or .09% are utilized as dwelling areas majority of which are in the Poblacion.
Barangays
Madalag is politically subdivided into 25 barangays.[7]
| PSGC | Barangay | Population | ±% p.a. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015[3] | 2010[8] | |||||
| 060410001 | Alaminos | 6.8% | 1,257 | 1,071 | 3.10% | |
| 060410002 | Alas-as | 3.9% | 710 | 684 | 0.71% | |
| 060410003 | Bacyang | 2.8% | 509 | 439 | 2.86% | |
| 060410004 | Balactasan | 4.0% | 735 | 722 | 0.34% | |
| 060410005 | Cabangahan | 2.4% | 433 | 494 | −2.48% | |
| 060410006 | Cabilawan | 2.6% | 487 | 616 | −4.38% | |
| 060410007 | Catabana | 2.4% | 448 | 513 | −2.55% | |
| 060410008 | Dit-Ana | 2.4% | 441 | 395 | 2.12% | |
| 060410009 | Galicia | 2.0% | 363 | 362 | 0.05% | |
| 060410010 | Guinatu-an | 2.4% | 445 | 404 | 1.86% | |
| 060410011 | Logohon | 2.7% | 504 | 523 | −0.70% | |
| 060410012 | Mamba | 4.5% | 830 | 756 | 1.79% | |
| 060410013 | Maria Cristina | 4.8% | 887 | 938 | −1.06% | |
| 060410014 | Medina | 6.0% | 1,105 | 1,085 | 0.35% | |
| 060410015 | Mercedes | 3.0% | 546 | 543 | 0.10% | |
| 060410016 | Napnot | 2.8% | 517 | 789 | −7.73% | |
| 060410017 | Pang-itan | 4.9% | 906 | 893 | 0.28% | |
| 060410018 | Paningayan | 6.1% | 1,127 | 1,352 | −3.41% | |
| 060410019 | Panipiason | 8.1% | 1,484 | 1,326 | 2.17% | |
| 060410020 | Poblacion | 9.7% | 1,775 | 1,562 | 2.46% | |
| 060410021 | San Jose | 5.1% | 937 | 863 | 1.58% | |
| 060410022 | Singay | 2.2% | 413 | 450 | −1.62% | |
| 060410023 | Talangban | 2.8% | 506 | 437 | 2.83% | |
| 060410024 | Talimagao | 1.9% | 347 | 345 | 0.11% | |
| 060410025 | Tigbawan | 3.7% | 677 | 606 | 2.13% | |
| Total | 18,389 | 18,168 | 0.23% | |||
Demographics
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[3][8][9][10] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In the 2015 census, Madalag had a population of 18,389.[3] The population density was 68 inhabitants per square kilometre (180/sq mi).
Madalag being predominantly a rural community has a slow growing population. It had a total population of 17,889 persons in 2007, a reduction of .05 percent or 897 persons from the 1995 population, basically due to migration towards industrial and trade centers of the country such as Manila, Cebu, Iloilo and other highly urbanized provinces and municipalities.
The municipality has twenty-five (25) component barangays with two (2) barangays, Poblacion and Alaminos as urban area and the twenty three (23) remaining barangays as rural areas. Barangay Poblacion is the most populous with 1,775 residents, followed by Panipiason (1,484 residents) and Alaminos (1,257).[3]
Economy
Agriculture
Madalag basically has an agricultural economy. Some 7,717.0251 hectares (19,069.184 acres) of the municipality land is devoted to agriculture. Farming and home industries are the main source of livelihood among the people. Rice is grown in almost all the twenty five (25) barangays. Corn is also planted in some upland areas. Other crops are in pineapple, camote and ube. The municipality also produces fruit trees, like lanzones, rambutan, marang and commercial crops such as coconut and abaca.
The hilly and mountainous areas produce high valued forest products such as narra, acacia, and mahogany and minor product like buri, rattan, bamboo, nipa sap and firewood.
Industry
The center of commercial activities in Madalag is situated along the 1.50 kilometres (0.93 mi) stretch of Navarette Street and at the Madalag Public Market located in the Poblacion.
The municipality has 93 commercials establishment dominated by the sari-sari stores (37 or 39%). The others establishment (26 or 28.60%) serve as outlet for bakery, carinderias and other recreational services.
Transportation
The total length of all roads types within the geographical boundaries of the municipality is 38.50 kilometres (23.92 mi) in 2011. Of these lengths, ten (10) percent are paved. A total of fifty (50) percent of the road surface is earth fill while thirty (30) percent is gravel surface. All barangays are accessible by roads except, Medina and Panipiason, that cannot be reach by four (4) wheel vehicle. Generally, the barangays connected to the national road have better road condition compared to the interior barangays.
Utilities
Water supply system
Water is supplied by the Poblacion Water District and Poblacion Spring Development. The other barangays are dependent from their Spring Development and artesian and shallow wells.
Communication
The communication system are operated by a wireless handset (cellPhone) distributed by SMART, GLOBE and SUN while the postal system is managed by the Philippines Postal Corporation. The post office is managed by a postal master, and a mail sorter/carrier. There are no mail distribution and collection centers in the barangays, hence the residents go to the Poblacion to post or get their mails.
Power facilities
There are 100 household in the barangay Poblacion of Madalag served by electricity with only (5) percent of households not served by power.The remaining twenty four (24) have electrical power.
Health
Madalag has one rural health unit (RHU) and one municipal hospital. The RHU is manned by one physician, two nurses, seven midwives, one sanitary inspector, ten trained hilots and 143 barangay health workers.
The Madalag Municipal Hospital (Don Leovigildo N. Diapo Sr Memorial Hospital) is staffed by four (4) doctors, five (5) medical technologist, eleven (11) nurses, one dentist, three midwives, one administrative officer, two (2) pharmacist, one ambulance driver, three (3) permanent and one (1) casual nursing attendants, three utility workers, four (4) admin casual employees.
Education
Madalag has 21 primary and 8 elementary schools with a total enrollment of 2,927 pupils and 108 teachers. It has three secondary public schools with a total enrollment of 1,368 students and 43 teachers.
References
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Aklan". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region VI (Western Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 12 October 2019.
- "Republic Act No. 297; An Act Creating the Municipality of Madalag in the Province of Capiz". The Corpus Juris. 17 June 1948. Archived from the original on 21 October 2016. Retrieved 21 October 2016.
- "Madalag: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- "Municipal: Madalag". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region VI (Western Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region VI (Western Visayas)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Aklan". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
External links
![]()