Luigi Ferdinando Marsili
Count Luigi Ferdinando Marsili (or Marsigli, Lat. Marsilius; 10 July 1658 – 1 November 1730) was an Italian scholar and eminent natural scientist, who also served as an emissary and soldier.[1]
Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli | |
|---|---|
 Conte Ferdinando de Marsigli | |
| Born | 10 July 1658 Bologna |
| Died | 1 November 1730 Bologna |
| Nationality | |
| Other names | De Marsili, Marsili |
| Occupation | Scientific scholar, soldier and emissary |
| Known for | Accademia delle Scienze dell'Istituto di Bologna |
.svg.png)
Biography
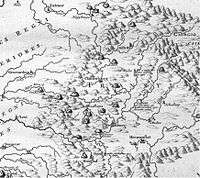
Born in Bologna, he was a member of an ancient patrician family and was educated in accordance with his noble social rank. He supplemented his reading by studying mathematics, anatomy, and natural history helped by the best Bolognese tutors and enhanced by his personal observations. After a course of scientific studies in his native city he travelled throughout Asia Minor collecting data on the Ottoman Empire's military organisation, as well as on its natural history.
On his return he entered the service of the Emperor Leopold (1682) and fought with distinction against the Turks, by whom he was wounded and captured in an action on the River Rába; sold to a pasha who met him after the Battle of Vienna, his release was secured in 1684. He returned to the Imperial Army deploying his skills as a talented military engineer. Marsigli contributed to the successful siege of Buda in 1686 and in the following years in the military operations of the liberation war against the Turks.
After the Treaty of Karlowitz he was commissioned to lead the Habsburg border demarcation commission. Marsigli mapped the 850 km-long Habsburg-Ottoman border in the former Kingdom of Hungary (today including Croatia, Serbia, Romania). During the twenty years he spent in Hungary he collected scientific information, specimens, antiques, took measurements and observations for his work on the Danube. He was assisted by Dr Johann Christoph Müller who prepared manuscripts for printing and commissioned the engravers in his home town of Nuremberg. The sample of the work, Prodromus, was published in 1700 and the large work was expected by 1704. His scholarship was well received in England, and was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in November 1691.[2]
During the War of the Spanish Succession Marsigli was second-in-command under the Count d'Arco at the Imperial fortress of Breisach on the Rhine, which was surrendered in 1703. Count d'Arco was beheaded because he was found guilty of capitulating before necessary, while Marsigli was stripped of his titles and honours by the Holy Roman Emperor, and his chivalric sword was broken over him. His appeals to the Emperor were in vain, but public opinion, however, acquitted him later of the charge of neglect or ignorance.
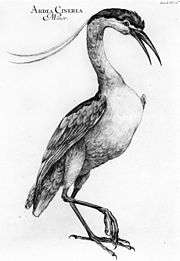
After he had left the Habsburg Army he made journeys to Switzerland and then France, spending a considerable time at Marseilles undertaking studies about the nature of the sea. He drew plans, made astronomical observations, measured the speed and size of rivers, studied the products, the mines, the birds, fishes, and fossils of every land he visited, and also collected specimens of every kind, instruments, models, antiquities, etc. Finally he returned to Bologna and presented his entire collection to the Senate of Bologna University in 1712. There he founded his "Institute of Sciences and Arts", which was formally opened in 1715. Six professors were put in charge of the different divisions of the Institute. Later he established a printing-house furnished with the best type sets for Latin, Greek, Hebrew, and Arabic. This was put in charge of the Dominicans under the patronage of St. Thomas Aquinas.
His major work on the Danube was published, after twenty years of delay, in 1726 in Amsterdam and The Hague. The maps of the work were published as an atlas in 1744. His treatise of oceans, published in 1725, renders Marsigli to be considered the founding father of modern oceanography.[3]
In 1727 he added to his other collections East India material which he collected in England and Holland. A formal procession of the Institute he founded was established to take place every twenty-five years on the Feast of the Annunciation. In 1715 he was named a Foreign Associate of the Paris Academy of Sciences; he was also a Fellow of the Royal Society of London,[4] and of Montpellier.
Works
A list of his works, over twenty in number, is given in Niceron's Mémoirs. His principal works are the following: Osservazioni interne al Bosforo Tracio (Rome, 1681); Histoire physique de la mer, translated by Leclerc (Amsterdam, 1725); Danubius Pannonico-Mysicus, richly illustrated work in six volumes containing much valuable historic and scientific information on the river Danubius, (6 vols., The Hague, 1726); and L'Etat militaire de l'empire ottoman (Amsterdam, 1732).
References
- Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). . Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- "Lists of Royal Society Fellows 1660–2007". London: The Royal Society. Archived from the original on 24 March 2010. Retrieved 14 July 2010.
- Sartori, Renzo. “Luigi Ferdinando Marsili, Founding Father of Oceanography.” In Four Centuries of the Word Geology. Ulisse Aldrovandi 1603 in Bologna, edited by Gian Battista Vai and William Cavazza. Bologna, Italy: Minerva Edizioni, 2003.
- royalsocietypublishing.org
![]()
![]()
Sources
- John Stoye: Marsigli's Europe. The life and times of Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli, soldier and virtuoso. Yale University Press, New Haven, N.J. 1994, ISBN 0-300-05542-0
- Giuseppe Olmi, L'illustrazione naturalistica nelle opere di Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli, in Natura-Cultura. L'interpretazione del mondo fisico nei testi e nelle immagini, edited by G. Olmi, L. Tongiorgi Tomasi, A. Zanca, Firenze: Olschki, 2000, pp. 255–303.
- Dimitar Vesselinov, Anna Angelova Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli şi Balcanii, in Revista Romana de Istorie a Cartii /Revue Roumaine de l’Histoire du Livre / Biblioteca Academiei Romane, Biblioteca Centrala Universitara, Biblioteca Nationala a Romaniei, edited by Bucureşti : Editura Bibliotecii Naţionale a României, 2010, pp. 121–124.
External links

- Marsili at encyclopedia.com
- Works and collections of Count Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli at kunstkammer.at/
- www.bub.unibo.it
- Brieve ristretto del saggio fisico intorno alla storia del mare (1711) – full digital facsimile at Linda Hall Library
- Engraved figures on the book published after being in Turkish captivity (1737)
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli. |