Lorraine 14A Antarès
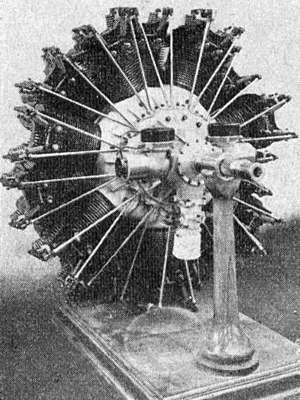
The Lorraine 14A Antarès was a French 14-cylinder radial aero engine built and used in the 1930s. It was rated in the 370 kW (500 hp) range.
| 14A Antarès | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 14E | |
| Type | 14-cylinder air-cooled radial aircraft engine |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Société Lorraine, Argenteuil, Paris |
| Variants | Lorraine Sirius |
Design and development
The Antarès was a conventionally laid out radial engine, with 14 cylinders in two rows. The crankcase was a barrel-shaped aluminium alloy casting, with an internal integral diaphragm which held the front crankshaft bearing. Forward of the diaphragm there was an integrally cast cam-gear case for the double track cam-rings. The reduction gear was housed under a domed casing attached to the front of the crankcase.
Flange-mounted steel barrels were bolted to the crankcase and enclosed with cast aluminium alloy, screwed-on, cylinder heads with integral cooling fins. The pistons were also made of aluminium alloy and had floating gudgeon pins. The fourteen pistons drove the double throw crankshaft via two channel-section master rods and twelve circular section auxiliary rods. The master rod had an integral, split type big-end. The crankshaft was machined from a single forging, with bolt-on balance weights.
The Antarès had a single pair of overhead inlet and exhaust valves per cylinder. The cam-rings drove roller tappets, mounted in the cam-case, which in turn operated rocker arms, fitted with ball bearings, via pushrods. The cam-rings were concentric with the crankshaft and driven via epicyclic gears. Most Antarès were conventionally aspirated via a single carburettor.
Variants
- 14A
- 14Ac
- 14E
- 14L
Specifications
Data from Societe Generale Aeronautique[1]
General characteristics
- Type: 14-cylinder two-row radial piston engine
- Bore: 140 mm (5.51 in)
- Stroke: 150 mm (5.91 in)
- Displacement: 32.326 l (1,972.7 cu in)
- Length: 1,424 mm (56.06 in) - direct drive, 1,552 mm (61.10 in) - reduction gear
- Diameter: 1,240 mm (48.82 in)
- Dry weight: complete 448 kg (988 lb) - direct drive, 487 kg (1,074 lb) - reduction gear
Components
- Valvetrain: one inlet and one exhaust overhead valve per cylinder, operated with rocker arms, pushrod driven via roller tappets bearing on a double track cam-ring
- Fuel system: dual 75 mm (2.95 in) Zenith carburettors
- Fuel type: petrol
- Cooling system: air-cooled
- Reduction gear: 0.647:1
Performance
- Power output: 370 kW (500 hp) at 1900 rpm
- Compression ratio: 5:1
- Specific fuel consumption: 0.311 kg/kW/hr (0.511 lb/hp/hr)
- Oil consumption: 0.016 kg/kW/hr (0.026 lb/hp/hr)
References
- Revue de la Societe Generale Aeronautique (PDF) (in French). Paris: Societe Generale Aeronautique. November 1932. pp. 28–30. Retrieved 12 October 2014.
- Revue de la Societe Generale Aeronautique (PDF) (in French). Paris: Societe Generale Aeronautique. November 1932. pp. 28–30. Retrieved 12 October 2014.