Lepidobotrys
Lepidobotrys is a flowering plant genus in the family Lepidobotryaceae. It contains only one species, Lepidobotrys staudtii.[1] L. staudtii is a small African tree, ranging from Cameroon eastward to Ethiopia.[2]
| Lepidobotrys | |
|---|---|
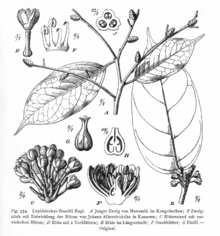 | |
| Lepidobotrys staudtii, from Vegetation der Erde (1915) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Lepidobotryaceae |
| Genus: | Lepidobotrys Engl. |
| Species: | L. staudtii |
| Binomial name | |
| Lepidobotrys staudtii Egnl. | |
The tannin 3,4,5-tri-O-galloylquinic acid is found in L. staudtii.[3]
Taxonomic history
Lepidobotrys staudtii was named and described by Adolf Engler in 1902 and placed by him in the family Linaceae.[4] It was regarded as somewhat of an anomaly and during the 20th century, was assigned to various families by different authors. Hans G. Hallier[5] and Reinhard Knuth [6] put it in Oxalidaceae. In 1950, Jean Leonard became the first to put it in a family by itself, which he thought to be close to Linaceae.[7] Arthur Cronquist, agreeing with Hallier and Knuth, put it in Oxalidaceae.[8] Adding to the confusion was the lack of any strong basis for placing these and related families into orders.
Etymology
Lepidobotrys is derived from Greek, meaning 'scale-cluster'. The name is in reference to the cone-like arrangement of its bracts, which extend under the flowers.[9]
References
- Klaus Kubitzky. "Lepidobotryaceae" In: Klaus Kubitzki (ed.). The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants vol.VI. Springer-Verlag: Berlin,Heidelberg, Germany (2004).
- Vernon H. Heywood, Richard K. Brummitt, Ole Seberg, and Alastair Culham. Flowering Plant Families of the World. Firefly Books: Ontario, Canada. (2007).
- 3,4,5-tri-O-galloylquinic acid on home.ncifcrf.gov
- Adolf Engler (May 1902). section: Linaceae africanae In: "Beitrage zur Flora von Afrika" In: Botanische Jahrbücher für Systematik, Pflanzengeschichte und Pflanzengeographie 32(1):108 (see External links below)
- Hans G. Hallier. Lepidobotrys Engl.: "Die Oxalidaceen und die Geraniaceen" Beihefte zum Botanischen Centralblatt 39(2):163.
- Reinhard G.P. Knuth. "Oxalidaceae" In: Adolf Engler and Karl Prantl. Die Naturlichen Pflanzenfamilien ed.2 volume 19a:40-41.
- Jean J.G. Leonard (Jun1950). "Lepidobotrys Engl., type d'une famille nouvelle de Spermatophytes: les Lepidobotryaceae" Bulletin du Jardin botanique de l'Etat a Bruxelles 20(1):38.
- Arthur Cronquist. An Integrated System of Classification of Flowering Plants. Columbia University Press: New York 1981.
- Gledhill, David (2008). "The Names of Plants". Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521866453 (hardback), ISBN 9780521685535 (paperback). pp 234