Laurel, Batangas
Laurel, officially the Municipality of Laurel (Tagalog: Bayan ng Laurel), is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Batangas, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 39,444 people.[4]
Laurel | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Laurel | |
.jpg) | |
 Seal | |
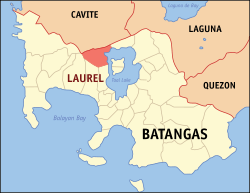 Map of Batangas with Laurel highlighted | |
OpenStreetMap 
| |
.svg.png) Laurel Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 14°03′N 120°54′E | |
| Country | |
| Region | Calabarzon (Region IV-A) |
| Province | Batangas |
| District | 3rd District |
| Founded | June 21, 1969 [1] |
| Named for | Miguel and Jose P. Laurel |
| Barangays | 23 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Joan L. Amo |
| • Vice Mayor | Rachelle B. Ogalinola |
| • Congressman | Ma. Theresa V. Collantes |
| • Electorate | 24,410 voters (2019) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 71.29 km2 (27.53 sq mi) |
| Population (2015 census)[4] | |
| • Total | 39,444 |
| • Density | 550/km2 (1,400/sq mi) |
| • Households | 8,551 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 3rd municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 25.67% (2015)[5] |
| • Revenue (₱) | 101,051,998.64 (2016) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 4221 |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)43 |
| Climate type | tropical monsoon climate |
| Native languages | Tagalog |
| Website | laurelbatangas |
Laurel had been part of Talisay, its current neighbor town. The town used to be known as Bayuyungan. On May 25, 1961, the town of Talisay was divided into two municipalities, and the new town was renamed "Laurel" after Miguel Laurel, known as the first notable Laurel in the Philippines and a longtime patriarch of the place and Jose P. Laurel, a former president.
Geography
Laurel is located at 14°03′N 120°54′E.
According to the Philippine Statistics Authority, the municipality has a land area of 71.29 square kilometres (27.53 sq mi) [3] constituting 2.29% of the 3,119.75-square-kilometre- (1,204.54 sq mi) total area of Batangas.
Barangays
Laurel is politically subdivided into 21 barangays.[6]
| PSGC | Barangay | Population | ±% p.a. | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2015[4] | 2010[7] | |||||
| 041011001 | As‑Is | 6.0% | 2,354 | 2,133 | 1.89% | |
| 041011002 | Balakilong | 10.4% | 4,118 | 3,974 | 0.68% | |
| 041011004 | Berinayan | 5.1% | 2,008 | 1,613 | 4.26% | |
| 041011006 | Bugaan East | 5.1% | 2,028 | 1,811 | 2.18% | |
| 041011007 | Bugaan West | 6.0% | 2,374 | 2,290 | 0.69% | |
| 041011008 | Buso‑buso | 6.8% | 2,692 | 2,445 | 1.85% | |
| 041011010 | Dayap Itaas | 1.9% | 752 | 494 | 8.33% | |
| 041011011 | Gulod | 7.0% | 2,746 | 2,501 | 1.80% | |
| 041011012 | Leviste | 6.0% | 2,351 | 1,884 | 4.31% | |
| 041011013 | Molinete | 3.8% | 1,480 | 1,442 | 0.50% | |
| 041011014 | Niyugan | 3.1% | 1,219 | 1,252 | −0.51% | |
| 041011015 | Paliparan | 2.2% | 887 | 760 | 2.99% | |
| 041011016 | Barangay 1 (Poblacion) | 1.4% | 570 | 507 | 2.26% | |
| 041011017 | Barangay 2 (Poblacion) | 3.6% | 1,438 | 1,265 | 2.47% | |
| 041011018 | Barangay 3 (Poblacion) | 1.7% | 663 | 759 | −2.54% | |
| 041011019 | Barangay 4 (Poblacion) | 1.5% | 610 | 593 | 0.54% | |
| 041011020 | Barangay 5 (Poblacion) | 2.0% | 790 | 674 | 3.07% | |
| 041011021 | San Gabriel | 6.5% | 2,559 | 2,340 | 1.72% | |
| 041011022 | San Gregorio | 8.7% | 3,433 | 2,931 | 3.06% | |
| 041011023 | Santa Maria | 5.6% | 2,217 | 1,986 | 2.12% | |
| 041011024 | Ticub | 5.5% | 2,155 | 2,020 | 1.24% | |
| Total | 39,444 | 35,674 | 1.93% | |||
Climate
| Climate data for Ibaan, Batangas | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 28 (82) |
29 (84) |
31 (88) |
32 (90) |
31 (88) |
30 (86) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
28 (82) |
29 (84) |
29 (84) |
28 (82) |
29 (85) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 19 (66) |
19 (66) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
24 (75) |
23 (73) |
21 (70) |
20 (68) |
22 (72) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 11 (0.4) |
13 (0.5) |
14 (0.6) |
32 (1.3) |
101 (4.0) |
142 (5.6) |
208 (8.2) |
187 (7.4) |
175 (6.9) |
131 (5.2) |
68 (2.7) |
39 (1.5) |
1,121 (44.3) |
| Average rainy days | 5.2 | 5.0 | 7.4 | 11.5 | 19.8 | 23.5 | 27.0 | 25.9 | 25.2 | 23.2 | 15.5 | 8.3 | 197.5 |
| Source: Meteoblue [8] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 13,137 | — |
| 1975 | 15,143 | +2.89% |
| 1980 | 17,889 | +3.39% |
| 1990 | 22,099 | +2.14% |
| 1995 | 23,781 | +1.38% |
| 2000 | 27,604 | +3.25% |
| 2007 | 34,953 | +3.31% |
| 2010 | 35,674 | +0.75% |
| 2015 | 39,444 | +1.93% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[4][7][9][10] | ||
In the 2015 census, Laurel had a population of 39,444.[4] The population density was 550 inhabitants per square kilometre (1,400/sq mi).
Economy
- Fishing – Laurel's main economical source is fish culture in Taal Lake where most of local residents base their trade.
- Farming – Small rice paddies on the foothills of Taal canyon ridge provide for ricefields to farmers.
- Real estate – The town's vast land resource provide ideal location for real estate developers such as Megaworld and Fil-Estate which are mostly based in Metro Manila. Among the major real estate subdivisions located in Barangay San Gregorio are Canyon Woods and Twin Lakes.[11]
Government
Elected municipal officials:
- Mayor: RANDY JAMES E. AMO (LP) (2010–present)
- Vice Mayor: FELIMON P. AUSTRIA (LP) (2013–present)
- Councilors:
- Angelito Rodriguez (LP) (2013–present)
- Rachelle Balba-Ogalinola (LP) (2013–present)
- Regina Landicho (LP) (2010–present)
- Andreo Landicho (LP) (2004–present)
- Junie Ulitin (LP) (2016–present)
- Domingo Tenorio (LP) (2016–present)
- Luciano Gardiola (LP) (2016–present)
- Hon. Romulo Macaraig (PDP-Laban) (2013–present)
Former mayors
- Placido Amo: (1972-1986) (1988-1992), 18 years in service
- Joven De Grano: (1992-1995), three years in service
- Natalio Panganiban: (1986-1988) and (1995-2004), 11 years in service
- John Benedict Panganiban: (2004-2010), six years in service
Gallery
- Laurel Municipal Hall
- Laurel Police Station
- Street in Poblacion Laurel
- Laurel welcome arch
- Laurel Church
References
- http://laurelbatangas.gov.ph/49th-founding-anniversary-of-the-municipality-of-laurel-schedule-of-activities/
- "Municipality". Quezon City, Philippines: Department of the Interior and Local Government. Retrieved 31 May 2013.
- "Province: Batangas". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- Census of Population (2015). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. PSA. Retrieved 20 June 2016.
- "PSA releases the 2015 Municipal and City Level Poverty Estimates". Quezon City, Philippines. Retrieved 1 January 2020.
- "Municipal: Laurel, Batangas". PSGC Interactive. Quezon City, Philippines: Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved 8 January 2016.
- Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. NSO. Retrieved 29 June 2016.
- "Laurel: Average Temperatures and Rainfall". Meteoblue. Retrieved 5 May 2020.
- Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Region IV-A (Calabarzon)". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. NSO.
- "Province of Batangas". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved 17 December 2016.
- "Twin Lakes : Tagaytay Philippines". Twinlakestagaytay.com.ph. Retrieved 2016-11-26.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Laurel, Batangas. |