Labyrinthine artery
The labyrinthine artery (auditory artery, internal auditory artery) is a branch of the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (85–100% cases) or basilar artery (<15% cases). It accompanies the vestibulocochlear nerve through the internal acoustic meatus, and supplies blood to the internal ear.[1]
| Labyrinthine artery | |
|---|---|
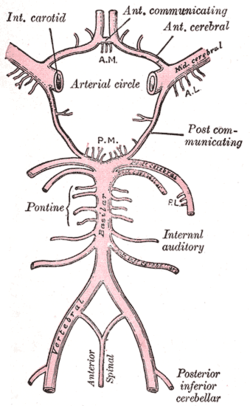 Diagram of the arterial circulation at the base of the brain. (Internal auditory artery labeled at center right.) | |
| Details | |
| Source | anterior inferior cerebellar artery or less commonly the basilar artery |
| Vein | internal auditory veins |
| Supplies | internal ear |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | arteria labyrinthi, arteria auditiva interna |
| TA | A12.2.08.020 |
| FMA | 50548 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
References
- Refer to diagram.
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 580 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.