Chervonohrad
Chervonohrad (Ukrainian: Червоноград, former Polish name: Krystynopol, Ukrainian: Кристинопіль, romanized: 'Krystynopil', German: Krisnipolye) is a mining city located in Lviv Oblast of western Ukraine. Chervonohrad is designated as a city of oblast significance. It lies about 62 km north of Lviv, 7 km from Sokal, 28 km northeast of the town of Voroniv, and has a population of 67,492 (2016 est.)[1].
Chervonohrad Червоноград | |
|---|---|
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
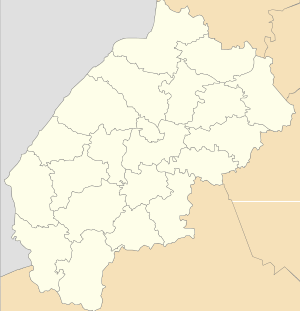 Chervonohrad Location of Chervonohrad in Ukraine 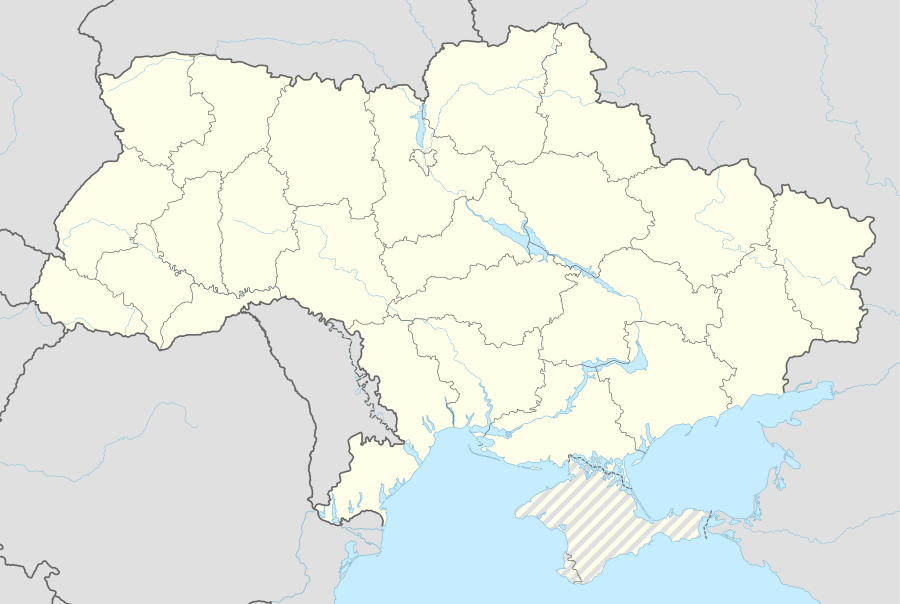 Chervonohrad Chervonohrad (Ukraine) | |
| Coordinates: 50°23′12″N 24°13′44″E | |
| Country | |
| Oblast | |
| Municipality | Chervonohrad |
| Founded | 1692 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Serhiy Chudovskiy |
| Area | |
| • Total | 37.6 km2 (14.5 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 150 m (490 ft) |
| Population (2016) | |
| • Total | 67,492 |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Sister cities | Békéscsaba |
The municipality of Chervonohrad also includes the town of Sosnivka and the urban type settlement of Hirnyk.
History
The city was part of the Polish Kingdom in the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth since its foundation in 1692 until 1772, when it was incorporated into the Habsburg Empire. During the interwar period, it belonged to the Second Polish Republic, and between 1945 and 1951 was part of the Polish People's Republic. It passed from Poland to the Ukrainian SSR after the territorial exchange in 1951 and had its name changed to Chervonohrad.
In May 1685, the Crown hetman and Kraków Voivode Feliks Kazimierz Potocki purchased land along the Bug River. In 1692, he founded a city on the lands of the village "Novyi Dvir" (literally "New Garden", Polish: Nowy Dwór) and named it "Krystynopol" after his wife Krystyna Lubomirska (the suffix "-pol" derives from Greek "polis"[2]). Potocki made the city his family center. He died here on September 22, 1702. His grandson Franciszek Salezy Potocki built a palace and in 1763 founded a monastery of Basilians (barocco church of Saint George; prior to 1946 – a place of miracles with wondrous icon of the Mother of God).[3]

In the 19th century, the "Apostolus Christinopolitanus" and famous chronicle from 1763–1779 were kept in the city. The Catholic order of Myrrh-Bearing Sisters was founded by Fr. Yulian Datsii in 1910, with the purpose of gathering funds to build a home for orphans and the poor. The first members of the congregation vowed to build two buildings: one for the people and one for the congregation. In 1913 the first convent arose, where 15 sisters lived.
Among the landmarks of the city is Count Potocki's palace, constructed by the order of Feliks Kazimierz Potocki after 1692.[3]
A local newspaper is published in the city since June 1962.[4]
On August 1, 1990, Chervonohrad became the first city in the whole Soviet Union, where a monument to Communist leader Vladimir Lenin was removed.[5]
Krystynopol Jews
Presently, there are 11–100 Jews residing in Chervonohrad. The earliest known Jewish community dates back to 1740. In 1931 the Jewish population was 2,200. The Jewish cemetery dates from 18th century with the last known Hasidic burial in 1941. Krystynopol Jews were deported to the Belzec extermination camp in September, 1942. The Jewish surname and rabbinical family Kristinopoler / Kristianpoller stem from the city's former name, Krystynopol. Jewish immigrants to America from this city founded the Krystenopoler Synagogue and First Krystenopoler Sick Benevolent Association Brith Isaac in New York. The Jewish cemetery is located in the town center, in Shevska Street.
Economics

Since 1951 the city became the center of newly emerged coal mining basin. Other enterprises, besides the mining works, include:
- Iron-Beton Foundry
- Wood Processing Plant
- Tailoring Factory
- Stockings Factory
- Mines
- Dairy
Chervonohrad Coal Mines
Chervonohrad was started as a coal mining town. Currently, there are still many functional coal mines on the outskirts around the city:
- 1) Шахта «Червоноградська»
- 2) Шахта «Великомостівська»
- 3) Шахта «Межирічанська»
- 4) Шахта «Надія»
- 5) Шахта «Степова»
- 6) Шахта «Лісова»
- 7) Шахта «Відродження»
- 8) Шахта «Зарічна»
- 9) Шахта «Візейська»
Education
- Branch of Lviv National Polytechnic University
- Mining College
Population
The population of Chervonohrad has increased significantly since 1939.
Postal codes
80100-80110
References
- "Чисельність наявного населення України (Actual population of Ukraine)" (PDF) (in Ukrainian). State Statistics Service of Ukraine. Retrieved 19 July 2016.
- Karpluk, Maria (1993). Mowa naszych przodków: podstawowe wiadomości z historii języka polskiego do końca XVIII w (in Polish). TMJP. p. 46.
- Syrtsov, Oleksandr (June 2013). "The Donbas of Halychyna" (PDF). The Ukrainian Week. № 11 (53): 34–35 – via Tyzhden.
- № 2942. «Новости Прибужья» = «Новини Прибужжя» // Летопись периодических и продолжающихся изданий СССР 1986 - 1990. Часть 2. Газеты. М., «Книжная палата», 1994. стр.386
- (in Ukrainian) The first Lenin fell in 1990: how the idol of communism was dropped, Gazeta.ua (8 December 2018)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2012-05-06. Retrieved 2010-12-01.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2015-03-17. Retrieved 2010-12-01.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Chervonohrad. |
- History of Krystynopol-Chervonograd
- Inform Agency «KRYSTYNOPIL.INFO»
- Chervonograd Night
- An extensive history of Jewish Krystynopol
- History and pictures of Chervonograd
- Short history of Rome Catholic Church in Cherwonograd (Krystynopil)
- Holy Spirit Roman Catholic Church in Chervonograd
- Chervonohrad Online
- Business of Chervonohrad