Kipunada
Kipunada (Brahmi script: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
| Kipunada | |
|---|---|
| Kushan Ruler | |
 Coin of Kipunada. Circa 335-350 CE. Obverse: Kipunada standing left, sacrificing over altar. To the right, name vertically in Brahmi script in monogrammic form: Ki-pu-ṇa Reverse: Ardoxsho enthroned facing, holding investiture garland and cornucopia.[1] | |
| Reign | 335-350 CE[2] |
| Predecessor | Shaka I |
| Successor | Kidarites |
| Kushan Empire 30 CE–350 CE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Gupta and Kidarite successors
The coins of Kipunada in Central and Western Punjab were followed by peculiar coins minted locally in Punjab, with the name "Samudra" on them (Gupta script:![]()
![]()
![]()
 Local coin minted in the Punjab area with the name "Samudra" (
Local coin minted in the Punjab area with the name "Samudra" (
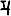
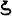

| Preceded by Shaka I |
Kushan Ruler c.335-350 CE[2] |
Succeeded by Gupta Empire/ Kidarites (Kirada) |
Notes
- CNG Coins
- Cribb, Joe; Donovan, Peter (2014). Kushan, Kushano-Sasanian, and Kidarite Coins A Catalogue of Coins From the American Numismatic Society by David Jongeward and Joe Cribb with Peter Donovan. p. 4.
- Heritage World Coin Auctions Long Beach Signature Auction Catalog #378. Ivy Press. May 2005. p. 15. ISBN 978-1-932899-79-5.
- Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017). From the Kushans to the Western Turks. p. 203.
- Cribb, Joe. "The Kidarites, the numismatic evidence.pdf". Coins, Art and Chronology II, Edited by M. Alram et Al.: 101.
- "In the Punjab the stylistic progression of the gold series from Kushan to Kidarite is clear: imitation staters were issued first in the name of Samudragupta, then by Kirada, 'Peroz' and finally Kidara" in Errington, Elizabeth; Curtis, Vesta Sarkhosh (2007). From Persepolis to the Punjab: Exploring Ancient Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan. British Museum Press. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-7141-1165-0.
- Rezakhani, Khodadad (2017). ReOrienting the Sasanians: East Iran in Late Antiquity. Edinburgh University Press. p. 85. ISBN 978-1-4744-0030-5.
- From the dated inscription on the Rukhana reliquary
- An Inscribed Silver Buddhist Reliquary of the Time of King Kharaosta and Prince Indravarman, Richard Salomon, Journal of the American Oriental Society, Vol. 116, No. 3 (Jul. - Sep., 1996), pp. 442
- A Kharosthī Reliquary Inscription of the Time of the Apraca Prince Visnuvarma, by Richard Salomon, South Asian Studies 11 1995, Pages 27-32, Published online: 09 Aug 2010
gollark: I REQUIRE TESTCASES, BOI OF HELLO.
gollark: In my experimental program.
gollark: iii infinite loops, ii terminates.
gollark: I see.
gollark: What do you mean "increment infinitely"?
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.

