Kinnauri language
Kinnauri, also known as Kanauri, Kanor, Koonawur, or Kunawar, (takri: 𑚊𑚮𑚝𑚵𑚤𑚯/𑚊𑚝𑚵𑚤𑚯/𑚊𑚝𑚵𑚤/𑚊𑚱𑚝𑚭𑚦𑚰𑚤/𑚊𑚰𑚝𑚦𑚤) is a Sino-Tibetan dialect cluster centered on the Kinnaur district of the Indian state of Himachal Pradesh.
| Kinnauri | |
|---|---|
| 𑚊𑚝𑚦𑚤𑚮𑚎𑚨𑚶𑚊𑚛 Kanawaringskad | |
 | |
| Region | Himachal Pradesh |
Native speakers | 84,000 (2011 census)[1] |
Sino-Tibetan
| |
| Dialects | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | Variously:kfk – Kinnauri propercik – Chitkuli Kinnaurissk – Sunamjna – Jangshung (Thebor)scu – Shumcho |
| Glottolog | kinn1250[2] |
Kaike, once thought to be Kinnauri, is closer to Tamangic. Bhoti Kinnauri and Tukpa are Bodish (Lahauli–Spiti).
Geographical distribution
Ethnologue lists the following locations for Kinnauri proper and related languages.
Kinnauri-speaking villages are from Badhal Rampur Bushahr to Sangla and north along Satluj river to Morang. Mainly the kinnauri speaking area is located in lower parts of district Kinnaur district in Himachal Pradesh. Kinnauri is also spoken in the Shimla district and Solan District which has a fairly large kinnauri diaspora.
Chitkuli Kinnauri is spoken by a thousand people in the Baspa river area of the Sangla valley in Nichar subdivision, Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh (in Chitkul and Rakchham villages).
Jangshung is spoken in Morang tahsil, Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh (in Jangi, Lippa, and Asrang villages).
Shumcho is spoken in Puh tahsil, Kinnaur district, Himachal Pradesh (in Kanam, Labrang, Spilo, Shyaso, Taling, and Rushkaling villages).
Phonology
This description is of the Pangi dialect of Kinnauri.
Consonants
| Bilabial | Alveolar | Retroflex | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | |||
| Plosive | voiced | b | d | ɖ | ɡ | ||
| voiceless | p | t | ʈ | k | |||
| aspirated | pʰ | tʰ | ʈʰ | kʰ | |||
| Affricate | voiced | dz | dʒ | ||||
| voiceless | ts | tʃ | |||||
| aspirated | tsʰ | tʃʰ | |||||
| Fricative | s | ʃ | h | ||||
| Trill | r | ||||||
| Approximant | l | j | w | ||||
Note on palatals: /dʒ/, /tʃ/, /tʃʰ/, and /ʃ/ are post-alveolar. /ɲ/ is alveolo-palatal.
Syllables
/h/, aspirated obstruents (i.e. /pʰ/, /tʰ/, /ʈʰ/, /kʰ/, /t͡sʰ/, /t͡ʃʰ/), and glides (i.e. /w/, /j/) do not occur in syllable codas.
All consonants may occur in onsets and word-medially.
Kinnauri has the following types of syllables:
- (C)V(C)(C)(C)
- CCV(C)
- CCCVC
Grammar
Kinnauri is SOV, V-Auxiliary, Postpositional, and has head-final noun phrases. It shows case marking with an ergative alignment in the past tense, nominative-accusative elsewhere. The ergative case is identical to the instrumental. There is no distinction between accusative and dative, and a genitive is partially syncretic with the accusative/dative. An ablative case is also recognized, normally attached outside the genitive but with different allomorphs for animate and inanimate referents. There is also a locative case, normally used only with inanimate nouns.
Script
The native script of the language is a variety of Takri script.

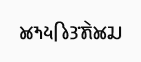
Language Vitality
Kinnaura people are bilinguals who speak Hindi along with their mother tongue. Hindi is the main lingua franca for people from different language groups in Kinnaur. It is also the main language in schools, colleges, government offices, market place, banks and more such domains. Younger generation is exposed to entertainment media like movies,music, mobile phone, newspapers etc., in Hindi. Kinnauri songs beings produced show heavy influence of Hindi. Young learners are encouraged to learn and speak Hindi in order to benefit in education and employment in future. Fluent speakers of Kinnauri are only the elders or the mid aged people who have little exposure to the outer world or are still unaffected by the modernity. But whether the next generation will inherit the cultural knowledge or the legacy of ancestors is doubted. From UNESCO factors study, all languages in Kinnaur region are definitely endangered, inter-generational transmission is unsafe, number of speakers using Kinnauri as first language is very low, domains are shifting, Hindi is replacing Kinnauri in most domains, there is lack of literary traditions, government support towards the protection and promotion of Kinnaur language or culture is absent, very little is known about the linguistic structure of the languages in the region. Like other tribal languages, Kinnauri too may lose much of its linguistic characteristics due to lack of proper documentation and government support and community apathy as well. Among urgent measures, Kinnauri languages need community collaborative efforts to document and discuss among the locals, scholars, linguists and researchers.
References
- "Statement 1: Abstract of speakers' strength of languages and mother tongues - 2011". www.censusindia.gov.in. Office of the Registrar General & Census Commissioner, India. Retrieved 7 July 2018.
- Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Kinnauric". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
Bibliography
- Nagano, Yasuhiko; & LaPolla, Randy J. (Eds.). (2001). New research on Zhangzhung and related Himalayan languages. Bon studies 3, Senri ethnological reports 19. Osaka: National Museum of Ethnology.
- Negi, Harvinder. 2012. A Sociolinguistic profile of the Kinnaura tribe. Nepalese Linguistics. Vol. 27, pp 101-105 http://himalaya.socanth.cam.ac.uk/collections/journals/nepling/pdf/Nep_Ling_27.pdf
- Nishi 西, Yoshio 義郎 (1993a). "カナウル語" [Kanaur, Kănaur, Kănāwăr, Kanor, Koonawur, Kunáwar, Kunawar, Kanâr, (LSI), Kanawar; Kanauri, Kănaurī, (LSI) Kanāwᵃrī; Kanâwari, Kunawaree]. In 亀井 Kamei, 孝 Takashi; 河野 Kōno, 六郎 Rokurō; 千野 Chino, 栄一 Eichi (eds.). 三省堂言語学大辞典 The Sanseido Encyclopaedia of Linguistics (in Japanese). 5. Tokyo: 三省堂 Sanseido Press. pp. 75b–86b. ISBN 4385152144.
- Takahashi, Yoshiharu (2001). "A descriptive study of Kinnauri (Pangi dialect): A preliminary report". In Nagano, Yasuhiko; LaPolla, Randy J. (eds.). New research on Zhangzhung and related Himalayan languages. Osaka: National Museum of Ethnology. pp. 97–119. doi:10.15021/00002143.
- Takahashi, Yoshiharu. 2007. On the deictic patterns in Kinnauri (Pangi dialect). In Roland Bielmeier and Felix Haller (eds.). Linguistics of the Himalayas and beyond, 341-354. Berlin, New York: Mouton de Gruyter.
- Takahashi, Yoshiharu (2009) “On the Verbal Affixes in West Himalayan”. Issues in Tibeto-Burman Historical Linguistics, Yasuhiko Nagano, ed. special issue of Senri Ethnological Studies 75: 21–49.
- Takahashi, Yoshiharu (2012). "On a Middle Voice Suffix in Kinnauri (Pangi dialect) Yoshiharu". Objectivization and Subjectivization: A Typology of Voice Systems Edited by Wataru Nakamura and Ritsuko Kikusawa, eds., special issue of Senri Ethnological Studies 77: 157–175.