Kalinin K-1
The Kalinin K-1 (Russian Калинин К-1), also known as RVZ-6, was a Soviet passenger plane that could carry three people.
| Kalinin K-1 | |
|---|---|
| Role | Airliner |
| National origin | Soviet Union |
| Manufacturer | RVZ-6 |
| First flight | 20 April 1925 |
| Status | Retired |
| Number built | 5 |
Development
Konstantin A. Kalinin began work on the K-1 in 1925 at the Kharkov aviation institute. Kalinin's closest collaborators included Dmitri Tomashevich , AN Grazianski and AT Rudenko. The first designs had been drawn by Kalinin as early as 1923, when the Ukrainian airline Ukrovsdukhput had demanded a cheap, robust and easy to maintain aircraft, after the opening of the first regular flight from Moscow to Nizhny Novgorod. The K-1 was a High-wing strutted monoplane with elliptical wooden wing covered with fabric. The fuselage consisted of a tubular steel frame with Aluminium sheet covering to the rear of the cabin and fabric covering the rear fuselage, constructed was carried out by RVZ-6 (RVZ - Remvozdhukozavod - factory) at Kiev. After the first flight, on 20 April 1925,[1] factory testing took place over the Summer, and in September 1925 the K-1 carried out state acceptance trials at Moscow, reaching a speed of 191 km/h (119 mph; 103 kn) with full load at 3,000 m (9,800 ft).[2]
After the K-1 was put into use, the designers came very quickly to the decision, to replace the 170 hp Salmson RB-9 engine with a more powerful and modern engine. Several engines were considered, but Kalinin and his group ultimately opted for a 240 hp BMW IV engine.
The type was mainly used as an airliner, later as an air ambulance and also as an Agricultural aircraft, as it was able to carry 400 kg (880 lb) of chemicals.
Specifications (K-1)
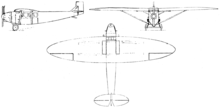
Data from The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995[3]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Capacity: 3 pax / 520 kg (1,150 lb)
- Length: 10.72 m (35 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 16.76 m (55 ft 0 in)
- Wing area: 40 m2 (430 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 7
- Empty weight: 1,452 kg (3,201 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 1,972 kg (4,348 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 170 kg (370 lb) fuel; 20 kg (44 lb) oil
- Powerplant: 1 × Salmson RB-9 9-cylinder water-cooled radial piston engine, 127 kW (170 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch wooden propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 160 km/h (99 mph, 86 kn)
- Cruise speed: 130 km/h (81 mph, 70 kn)
- Stall speed: 70 km/h (43 mph, 38 kn)
- Range: 600 km (370 mi, 320 nmi)
- Endurance: 4 hours
- Service ceiling: 3,000 m (9,800 ft)
- Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in 12.3 minutes
- Wing loading: 49.3 kg/m2 (10.1 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.061 kW/kg (0.037 hp/lb)
- Take-off distance: 120 m (390 ft)
- Landing distance: 120 m (390 ft) at70 km/h (43 mph; 38 kn)
References
- Kopenhagen, Wilfried (2007). Lexikon Sowjetluftfahrt (Reprint ed.). Klitzschen: Elbe-Dnjepr-Verl. p. 112. ISBN 978-3-933395-90-0.
- "unknown". Flieger Revue 10/1972 (10). 1972.
- Gunston, Bill (1995). The Osprey Encyclopedia of Russian Aircraft 1875–1995. London: Osprey. pp. 132–133. ISBN 1-85532-405-9.
Further reading
- Heinz A. F. Schmidt: Historische Flugzeuge Teil II. Motorbuch, Stuttgart 1970.
- Heinz A. F. Schmidt: Sowjetische Flugzeuge. Transpress, Berlin, S. 53.
- Rodionow, Iwan I.; Freytag, Jürgen (1989). "Eine sowjetische Legende – Alexandrow/Kalinin AK-1". Modellbau heute (6). ISSN 0323-312X.