Kakamigahara, Gifu
Kakamigahara (各務原市, Kakamigahara-shi) is a city located in southern Gifu Prefecture in Japan. As of 1 January 2019, the city had an estimated population of 148,225, and a population density of 1700 persons per km2, in 59,736 households.[1] The total area of the city was 87.81 square kilometres (33.90 sq mi).
Kakamigahara 各務原市 | |
|---|---|
 Kakamigahara City Hall | |
 Flag  Seal | |
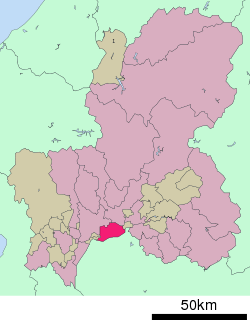 Location of Kakamigahara in Gifu Prefecture | |
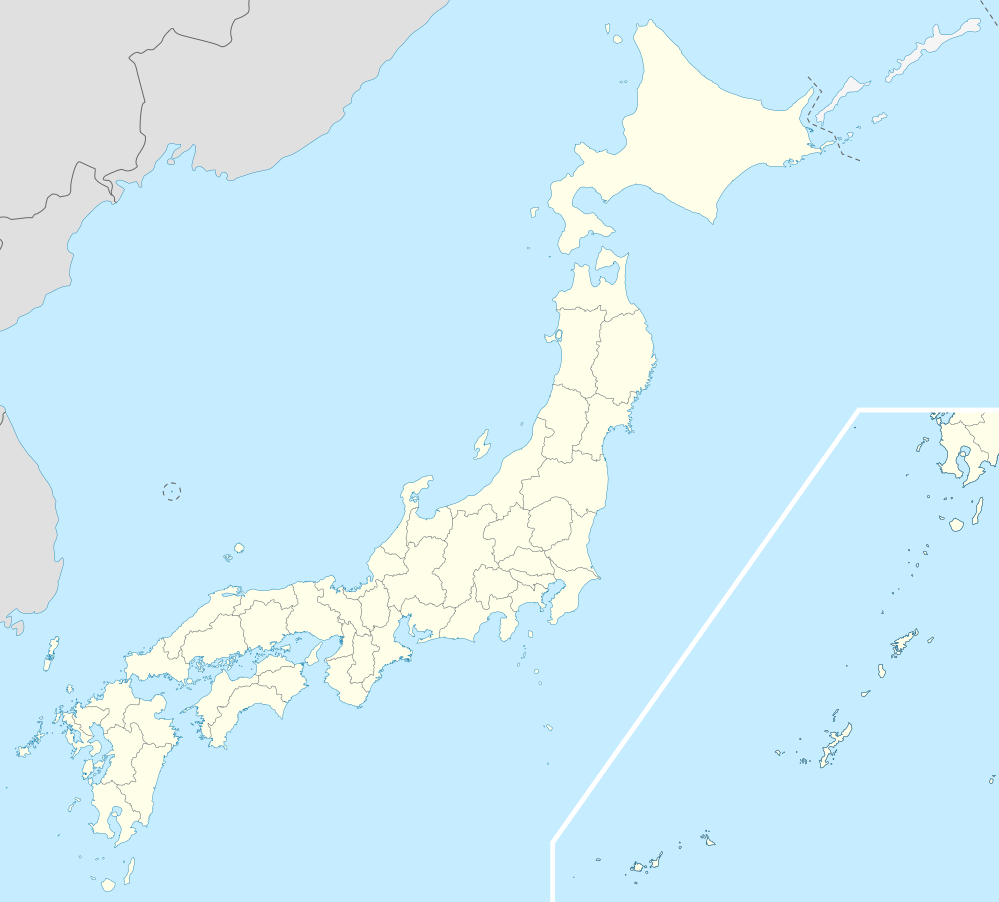 Kakamigahara | |
| Coordinates: 35°23′55.7″N 136°50′54.3″E | |
| Country | Japan |
| Region | Chūbu |
| Prefecture | Gifu |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Kenji Asano (since May 2013) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 87.81 km2 (33.90 sq mi) |
| Population (1 January 2019) | |
| • Total | 148,225 |
| • Density | 1,700/km2 (4,400/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+9 (Japan Standard Time) |
| City symbols | |
| - Tree | Pine |
| - Flower | Azalea |
| Phone number | 058-383-1111 |
| Address | 1–69 Nakasakura-machi, Kakamigahara-shi, Gifu-ken 504-8555 |
| Website | Official website |
Situated in the northern part of the Nōbi Plain, what is now Kakamigahara originally thrived as a post station on the Nakasendō highway connecting Edo with Kyoto, being called "Unuma-juku" at the time. In more recent history, the city developed thanks to the JASDF Gifu base. In addition, Kakamigahara grew as an industrial city and a commuter suburb of Gifu City and Nagoya.
The city of Kakamigahara has many large parks, the most notable among them being "Kakamigahara Kōen", which was originally made from a vacant lot owned by Gifu University. A city planning policy of making Kakamigahara into a "park city" has been undertaken by the municipality, and in 2005, the city received the "Green City Prize" from the Prime Minister.
Although the city was officially named Kakamigahara, it is also called Kakamihara, Kagamihara, or Kagamigahara by tradition.
Geography
Mountainous terrain runs from the northern to the eastern part of the city. The Kiso River flows through the southern part, forming the municipal and prefectural (Aichi-Gifu) border. A large portion of the city is situated on the Kakamigahara Plateau. Because the soil is very well drained, it was not traditionally suited to rice cultivation. Therefore, with the exception of rest stops such as Unuma-juku or other roadside settlements, the area was largely wilderness until the Meiji Period. The names of the Meitetsu train stations, Rokken, Nijukken, and the Ogase Reservoir are from that era. Beginning from the Meiji period, in order to take advantage of the large amount of wilderness and well-drained soil, military bases and training grounds were established. In addition, Gifu University's agricultural and engineering departments were established in the area, leading the growth of machine and textile factories. These industries, in addition to carrot production which utilized the dry soil, became the main industries of the town. Part of the city is within the borders of the Hida-Kisogawa Quasi-National Park.
Rivers
Kiso, Sakai, Shin-Sakai, Daianji
Lakes
Ogase Reservoir
Mountains
Gongen, Igi, Mii, Kakami, Kakamigahara Alps
Adjacent cities and districts
North: Seki
East: Kamo District (Sakahogi-cho)
West: Gifu City, Hashima District (Kasamatsu-cho, Ginan-cho)
South: Ichinomiya, Konan, Inuyama, Niwa District ( Fusou-cho)
Climate
The city has a climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and mild winters (Köppen climate classification Cfa). The average annual temperature in Kakamigahara is 15.5 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1939 mm with September as the wettest month. The temperatures are highest on average in August, at around 27.9 °C, and lowest in January, at around 3.9 °C.[2]
History
The area around Kakamigahara was part of traditional Mino Province. During the post-Meiji restoration cadastral reforms, the area was organised into Inaba District, Gifu in April 1897.
1 April 1963: Kakamigahara City was founded by amalgamating Naka, Sohara, Unuma and Inaba
1968: "Line Bridge" completed. Together with the Inuyama bridge, completed in 1925, these two bridges span the Kiso river and connect Kakamigahara City with Aichi prefecture.
1969: "Aigi" bridge completed. This was the third bridge to span the Kiso river and connect the city to Aichi Prefecture. It was the first bridge to connect Kakamigahara to Konan City.
5 March 1986: The section of the Tokai-Hokoriku Expressway between Kakamigahara Junction and Mino Junction was opened. Furthermore, on 13 December 1998, the Tokai-Hokoriku Expressway was connected to the Meishin Expressway (Ichinomiya Junction).
28 March 2000: The twinning of the Inuyama Bridge was completed. Previously, Meitetsu trains had shared the bridge with automobiles, crossing the bridge in a manner similar to streetcars. After the twinning, the trains began to use the old Inuyama Bridge. This separation of trains and automobiles improved transportation across the river.
1 November 2004: Kawashima-cho (Hashima District), was incorporated in Kakamigahara City.
5 November 2006: "Shin-mei Ko-ami Bridge", connecting to Konan, is completed.
24 March 2013: Kakamigahara Bridge is completed. It connects the city hall area with Kawashima-chiku (formerly Kawashima-cho) of Konan City. With the completion of this bridge, there are now four routes from Kakamigahara City into Aichi Prefecture.
Population
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 76,595 | — |
| 1975 | 91,991 | +3.73% |
| 1980 | 114,036 | +4.39% |
| 1985 | 123,446 | +1.60% |
| 1990 | 129,852 | +1.02% |
| 1995 | 133,933 | +0.62% |
| 2000 | 135,044 | +0.17% |
| 2005 | 148,315 | +1.89% |
| 2010 | 149,704 | +0.19% |
| 2016 | 148,490 | −0.14% |
| Source: city's official website | ||
As of December 2013, about 3,000 residents of foreign nationality were registered in Kakamigahara City. The largest numbers are, in descending order, from Brazil, China, and the Philippines.[3]
Politics
Kakamigahara has a mayor-council form of government with a directly elected mayor and a unicameral city legislature of 24 members.
Current Mayor: Kenji Asano (inaugurated 20 May 2013, first term)
Previous Mayors:
Kaichi Mutou: 1963–1968. Resigned during second term due to illness
Keikichi Matsubara 1968–1973. Resigned during second term due to corruption scandal.
Kihachirou Hirano: 1973–1997. Served six terms.
Shin Mori: May 1997-May 2013. Served four terms.
Economy
Kakamigahara City is second in Gifu Prefecture in terms of industrial production. The city has an aircraft factory operated by Kawasaki Heavy Industries Aerospace Company, located next to the JASDF Gifu Air Base, and Mitsubishi Heavy Industries also produces aircraft parts. The city also has many automobile-related factories including parts makers, and metalworking industries. In Sue-cho in the north of Kakamigahara City, there is an industrial park called "Techno Plaza", which was established by the Gifu Prefectural government as a focal point for the research and development of robotics and virtual reality. With Waseda University's WABOT-HOUSE laboratory and Gifu University's Science and Technology Promotion Center as a nucleus, Techno Plaza is structured as an industrial and R&D center. Many ventures have moved into the park, including some companies which have made IPOs, such as Nippon Ichi Software, Inc.
Major employers
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries Aerospace Company
- Calbee (Kakamigahara factory). This factory produces Kakamigahara kimchi flavored potato chips, which are exclusive to this region.
- Nippon Ichi Software, Inc.
- Gifu Auto Body Industries Co., Ltd.
- Nakanihon Diecast Co., Ltd.
- Tenryu Industries Co., Ltd.
- Eisai Co., Ltd.
- Taikou Seikou Co., Ltd.
- Zero Sports (Zero Max).
Educational institutions
Universities and colleges
High schools
The city has three public high schools operated by the Gifu Prefectural Board of Education.
- Gifu Prefectural Kakamihara Senior High School (岐阜県立各務原高等学校) (Academic)
- Gifu Prefectural Kakamigahara Nishi Senior High School (岐阜県立各務原西高等学校) (Academic)
- Gifu Prefectural Gifu-Kakamino High School (岐阜県立岐阜各務野高等学校) (Technical)
Primary and secondary schools
Kakimigahara has 16 public elementary schools and eight public junior high schools operated by the city government. The city also operates one special education school.
International schools
- Centro Educacional Nova Etapa - CENE (セントロ・エドカショナル・ノヴァ・エターパ) - Brazilian school[4]
Transportation
Railways
Highways
- Tōkai-Hokuriku Expressway Gifu-Kakamigahara IC

Bridges
- Aigi Ohashi Bridge, crossing the Kiso River into Inuyama in Aichi Prefecture
Other
- JASDF Gifu Air Base was established as an army airfield in 1917 and is currently used by the JSDF for aircraft and flight testing. From 1945 to 1958 it was occupied by the U.S. military and known as "Camp Gifu".
Local attractions
- Kakamigahara Aerospace Science Museum - A museum featuring a number of indoor and outdoor exhibits including aircraft and displays covering the history of aircraft development and Gifu prefecture's role in it.
- ÆON Kakamigahara Shopping Center - Opened in July 2007, ÆON Kakamigahara Shopping Center houses 186 specialty shops and a JUSCO department store. The center includes a 10-screen multiplex cinema and a parking lot for approximately 4,000 cars.
Sister/friendship cities
- Domestic
- Tsuruga, Fukui Prefecture (friendship city as of 2 October 1989)
- International
.svg.png)
References
- Kakamigahara city official home statistics(in Japanese)
- Kakamigahara climate data
- https://www.city.kakamigahara.lg.jp/shisei/toukei/003317.html
- "Escolas Brasileiras Homologadas no Japão" (Archive). Embassy of Brazil in Tokyo. Retrieved on 13 October 2015.
External links

- Official website (in Japanese)