Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land (Polish: Ziemia kłodzka; Czech: Kladsko; German: Glatzer Land) is a historical region in southwestern Poland.

The subject of Czech-Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with periods of rule of the Polish Piast dynasty in the Late Middle Ages. It was raised to the County of Kladsko in 1459 and was conquered by Prussia in the First Silesian War of 1740-42 and incorporated into the Province of Silesia by 1818. After World War II it fell to the Republic of Poland according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement. The region was not destroyed during World War II, thanks to which its rich historical architecture from various periods, from the Middle Ages to modern times, has been preserved.
Geography

Kłodzko Land, with an approximate area of 1,640 km2 (630 sq mi)[1] consists of the Kłodzko Valley, a basin surrounded by several Mittelgebirge ranges of the Central and Eastern Sudetes: the Owl Mountains and Golden Mountains in the east, the Śnieżnik Mountains in the south, the Bystrzyckie Mountains and Orlické Mountains in the west, and the Stołowe Mountains in the northwest. With its natural boundaries, the valley forms a significant jut into the neighbouring Czech area in the southeast. It is crossed by the Eastern Neisse (Nysa Kłodzka) river, a left tributary of the Oder.
Despite the enclosed geographical situation, Kłodzko Land since ancient times has been traversed by the Amber Road and other important trade routes connecting Bohemia with Silesia and Moravia, running over easily accessible mountain passes in the south and west, and along the Nysa water gap at Bardo. The land is named after its historic administrative capital Kłodzko (Kladsko, Glatz), formerly the administrative seat of the Bohemian governor (Zemský hejtman) and gathering place of the local estates (Landstände). The area roughly corresponds to current Kłodzko County (Powiat kłodzki) of Lower Silesian Voivodeship.
History

Historically, the area may have been part of the Great Moravia under King Svatopluk I by the late 9th century, though the extent of his realm is disputed. According to the Chronica Boëmorum (1125) by the Prague dean Cosmas, the provincia glacensis belonged to the dominions of the Bohemian nobleman Slavník, residing at the castle of Kłodzko on the road from Prague to Wrocław in Silesia until his death in 981 AD. The Slavník dynasty, among them Prince Slavník's heir Soběslav and his brother Saint Adalbert of Prague, ruled in the eastern territories of Bohemia until they were overthrown by the rivalling Přemyslid family in 995.
While the Přemyslid Dukes of Bohemia obtained the status of immediate Princes of the Holy Roman Empire, their rule was disrupted by internal dynastical struggles: during the rivalry between Duke Boleslaus III and his brother Jaromir in 1003, the Polish duke Bolesław I the Brave invaded Bohemia, but had to pull back the next year, facing the forces of King Henry II of Germany. In turn the Bohemian duke Bretislaus I campaigned the adjacent northern territory of Silesia in 1039. An armistice mediated by Emperor Henry III in 1054 demarcated the spheres of influence, leaving Kłodzko with Bohemia.
When about 1080 the Polish Piast duke Władysław I Herman married Judith Přemyslovna, daughter of Duke Vratislaus II of Bohemia, he received Kłodzko as a Bohemian fief, which upon his death in 1102 was claimed by his son Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth of Poland. However, as Bolesław became entangled in a fierce inheritance conflict with Duke Svatopluk of Bohemia and his cousin Borivoj II and campaigned the Bohemian lands several times, he finally had to renounce Kłodzko in favour of Duke Soběslav I of Bohemia in a peace treaty signed at Pentecost in 1137 under pressure from Emperor Lothair III.
Bohemian fief
Under Přemyslid rule, Kladsko became part of the Kingdom of Bohemia by 1198; it was administrated within the lands of Hradec Králové and governed by Bohemian burgraves like Witiko of Prčice (c.1120–1194), progenitor of the Vítkovci clan. From the 13th century onwards, under the rule of King Wenceslaus I and his son Ottokar II, the area was largely settled by German colonists in the course of the Ostsiedlung migration. The Kladsko estates were temporarily held by Silesian Piast dukes such as Henry IV Probus, who received it from the hands of King Rudolph I of Germany in 1280, or Henry VI the Good (in 1327) and Bolko II of Ziębice (in 1336); each time, the lands fell back to the Bohemian monarch as a reverted fief upon their death.
About 1300, Kladsko was governed by the Bohemian noble Arnošt (Ernest) of Hostýně, whose son Arnošt of Pardubice became the first Archbishop of Prague by appointment of Pope Clement VI in 1344. He also was a close advisor to the Luxembourg emperor Charles IV, who in 1348 separated Kladsko Land from Bohemia and raised it to an immediate Land of the Bohemian Crown. Under Charles' rule, Kladsko flourished; the development, however, ended abruptly with the beginning of the Hussite Wars in the early 15th century.
From about 1425 onwards, Hussite forces campaigned the lands and used Hummel Castle as a base for their attacks. They laid siege to Karpień Castle and devastated the towns of Bystrzyca, Radków and Nowa Ruda. A major battle with the royal Bohemian forces led by the Kladsko governor Půta III of Častolovice and the Silesian duke John I of Münsterberg was fought at Stary Wielisław on 27 December 1428. Duke John was killed in action and Půta received his Duchy of Münsterberg as well as Kladsko and the adjacent Silesian lands of Ząbkowice as a pledge from the hands of Emperor Sigismund. After Půta's death, his widow Anne of Colditz sold Kladsko Land to the former Hussite leader Hynek Krušina of Lichtenburg in September 1440, and married him three weeks later.
County of Kladsko
In 1454 the Utraquist Bohemian regent, and later king, George of Poděbrady re-acquired Kladsko Land from the heirs of the late Hynek Krušina; together with the adjacent Náchod lordship and the Silesian Duchy of Münsterberg, it became his powerbase to assume the Bohemian Crown. Once elected king by the Bohemian estates, in 1458, he raised Kladsko to a county in its own right and conveyed the title of an Imperial count (Reichsgraf) to his second son Victor, for which he obtained the confirmation by Emperor Frederick III the next year.

The comital title became hereditary in 1462 and could also be bequeathed by Victor's brothers Henry of the Elder Münsterberg and Henry the Younger of Poděbrady. Henry the Elder ruled Kladsko upon King George's death in 1471; he attached the Lordship of Hummel to his comital lands by 1477 and had Kladsko Castle rebuilt as his permanent residence. His overindebted sons and heirs Albert, George and Charles, however, had to sell the estates to their brother-in-law, the Austrian noble Ulrich of Hardegg. Nevertheless, their descendants retained the comital title until the extinction of the line in 1647.
When the Bohemian Crown fell to the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in 1526, the rights of the Hardegg family were confirmed by King Ferdinand I. Johann von Hardegg finally sold Kladsko to Ferdinand in 1534/37; from that time on, the Habsburg rulers pledged the county several times: first to the Bohemian noble and former governor John III of Pernstein, later to the Salzburg administrator Ernest of Bavaria, who implemented stern measures of Counter-Reformation. After Ernest's death in 1560, his heir Duke Albert V of Bavaria sold Kladsko back to Emperor Maximilian II. The Habsburg rulers raised the pledge sum with the support of the local estates, and the Counter-Reformation efforts ended.
When the Thirty Years' War broke out, Kladsko became a centre of the Protestant revolt in Bohemia. Even after the lost Battle of White Mountain, the estates refused to submit to Emperor Ferdinand II, who had their lands occupied and numerous punitive measures enacted. His son and successor Ferdinand III commissioned the Jesuits to continue the recatholization policies.
Prussian rule
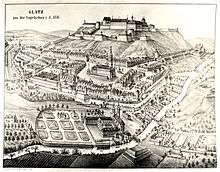
In December 1740 the Prussian Army under King Frederick the Great invaded Habsburg Silesia and also occupied the County of Kladsko; while they were largely welcomed by the Protestant population of Silesia, Kladsko remained a suspiciously eyed Catholic area. By the 1742 Treaty of Berlin, again confirmed by the 1763 Peace of Hubertusburg, the Habsburg empress Maria Theresa ceded Kladsko to the Kingdom of Prussia.
During the Napoleonic War, in 1807, Kladsko Castle was besieged by Confederation troops led by Jérôme Bonaparte, but successfully defended by the Prussian garrison under General Friedrich Wilhelm von Götzen the Younger. In the same year, manoralism was finally abolished in the course of the Stein-Hardenberg Reforms. By 1818 the county was finally abolished, and the territory was reformed into the three Landkreise of Glatz, Habelschwerdt and Neurode within the Silesian province. During the Austro-Prussian War of 1866 the area again became a deployment zone of Prussian troops on the eve of the Battle of Nachod. From 1871 it was part of Germany, until the country's defeat in World War II in 1945.
Czech claims
From a traditional Czech perspective, Kladsko was culturally and traditionally a part of Bohemia, although the region has been a part of the Lower Silesia region since its conquest by the Kingdom of Prussia in 1742/63. Referred to as "Little Prague" (German: Klein-Prag), the Kłodzko Valley region on the Nysa Kłodzka river was the focus of several attempts to reincorporate the area into Czechoslovakia, one of several Polish–Czechoslovak border conflicts.[2]
- Proposals by the Czechoslovak Delegation on incorporating Kłodzko Land into Czechoslovakia during the Paris Peace Conference, 1919
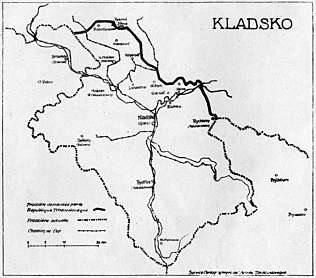 The maximalist variant
The maximalist variant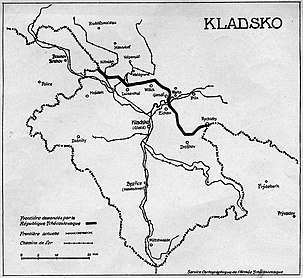 The intermediate variant
The intermediate variant The minimalist variant
The minimalist variant
After the defeat of the German Empire in World War I, the newly established First Czechoslovak Republic raised claims to Kladsko Land, that were however rejected in the 1919 Treaty of Versailles. While the area remained with the Free State of Prussia and the Weimar Republic, the Czechoslovak government had extended border fortifications erected around the Kladsko just after the Nazi seizure of power in 1933. With the 1938 Munich Agreement, however, these security measures became obsolete.
The last attempt occurred at the end of World War II, when Czechoslovak forces tried to annex the area on behalf of the Czech minority present in the western part of the Kłodzko Valley known as the "Czech Corner". Pressure brought on by the Soviet Union led to a ceasing of military operations, with the remaining German population and the Czech minority being expelled to Germany and Czechoslovakia. With most of the former Silesia province, Kladsko passed to Poland in 1945. Most Germans in the region who had not already fled were expelled.
According to canon law of the Roman Catholic Church, the area remained part of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Prague until 1972.
The region suffered during the 1997 Central European flood.
Towns
The region is currently inhabited by around 160,000 people. There are 11 towns in the region. The largest is the historical capital, Kłodzko.
|
|
|
|
See also
References
- Semotanová, Eva; Felcman, Ondřej (2005). Kladsko. Proměny středoevropského regionu : historický atlas [Kladsko Region. The Transformations of the Central European Region : A Historical Atlas] (in Czech). Hradec Králové; Prague: Univerzita Hradec Králové; Historický ústav AV ČR. p. 15. ISBN 80-7286-066-6.
- "Konflikt graniczny polsko-czechosłowacki w latach 1945-1947 - Inne Oblicza Historii". ioh.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 2017-11-30.