Janowski Don Kichot
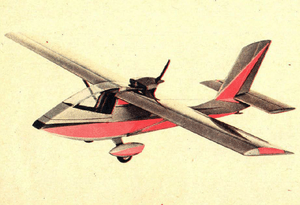
The Janowski J1 Prząśniczka ("Distaff"), later named the Don Kichot ("Don Quixote") was an ultralight aircraft designed in Poland and marketed for homebuilding in the 1970s. Designed by Jarosław Janowski in 1967 and built with the help of some friends, it flew three years later. It had an unusual design, with a high, strut-braced wing and a pusher propeller mounted behind it. The pilot had a fully enclosed cabin, and the undercarriage was of fixed, tailwheel type. Original prototype was flown with Saturn engine design by Mr Janowski. This engine was made out of two motorcycle engines (MZ250). J1 was also flown with Trabant engine (29HP) and VW conversion (48BPH) made by Christine Aero Engines in Donlands - California.
| J1 Prząśniczka, Don Kichot | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Recreational ultralight |
| Manufacturer | Homebuilt |
| Designer | Jarosław Janowski |
| First flight | 30 July 1970 |
Later versions such as J1B were flown with Hirth and Rotax engines. Mr Janowski restricted maximum engine power for his design to maximum of 50BHP. There were several articles in worldwide press in regards of this design and many successfully build all around the world.
Derived from it was the J2 Polonez with a T-tail and a shoulder-mounted cantilever wing, being otherwise quite similar.[1] Neither model was built in numbers. Further developments included the J3, J5 and J6.
Specifications (variant)
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1975-76[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 4.88 m (16 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 7.6 m (24 ft 11 in)
- Height: 1.4 m (4 ft 7 in)
- Wing area: 7.5 m2 (81 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 7.7
- Empty weight: 163 kg (359 lb)
- Gross weight: 270 kg (595 lb) or 293 kg (646 lb) with 37 kW (50 hp) engine
- Fuel capacity: 18.2 litres (4.8 US gal; 4.0 imp gal)
- Powerplant: 1 × Janowski Saturn 500B 2-stroke 2-cyl. horizontally-opposed air-cooled piston engine, 17 kW (23 hp) or 37 kW (50 hp) VW conversion
- Propellers: 2-bladed Janowski wooden fixed pitch pusher propeller, 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 135 km/h (84 mph, 73 kn) or 207 km/h (129 mph; 112 kn) with 37 kW (50 hp) engine
- Cruise speed: 120 km/h (75 mph, 65 kn)
- Stall speed: 58 km/h (36 mph, 31 kn)
- Never exceed speed: 180 km/h (110 mph, 97 kn)
- Range: 250 km (160 mi, 130 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 2,500 m (8,200 ft)
- g limits: +4 -1.5
- Rate of climb: 2.0 m/s (390 ft/min) 3.99 m/s (785 ft/min) with 37 kW (50 hp) VW conversion
- Wing loading: 36 kg/m2 (7.4 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.083 kW/kg (0.05 hp/lb)
- Take-off run: 200 m (660 ft)
- Landing run: 150 m (490 ft)
References
- "Janowski Aircraft Home Pages". Retrieved 21 October 2017.
- Taylor, John W.R., ed. (1975). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1975-76 (66th annual ed.). New York: Franklin Watts Inc. p. 170. ISBN 978-0531032503.
Further reading
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 535.
- Jane's All the World's Aircraft 1977-78. London: Jane's Yearbooks. p. 502.