Jalpa de Méndez Municipality
Jalpa de Méndez Municipality is a municipality in Tabasco in south-eastern Mexico.[1]
Jalpa de Méndez Municipality | |
|---|---|
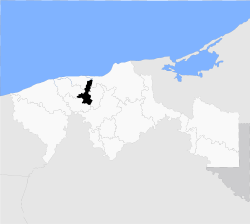 Location of the municipality in Tabasco. | |
| Country | |
| State | Tabasco |
| Time zone | UTC-6 (Central Standard Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-5 (Central Daylight Time) |
The seat is at Jalpa de Méndez.
The municipality of Jalpa de Méndez makes up part of the Grijalva River region of the state and the Chontalpa sub-region.[2][3] It borders the municipalities of Paraíso, Centla, Cunduacán, Nacajuca and Comalcalco.[3] There are 64 active communities in the municipality, with a population of 83,356 in 2010, up from 72,969 in 2005, with a count of 19,630 residences in 2010.[4] It is considered to be one of the Chontal Maya areas of the state of Tabasco,[5] but only 396 people speak an indigenous language,[4] and about half of those speak Zapotec.[2]
The municipal government consists of a municipal president, a treasury official and 12 community representatives called “regidors.”[6]
All schools are directed at the municipal level. There are 155 scholastic centers with 62 primary schools, 22 middle schools, six high schools, two vocational centers, three centers for special education with ten laboratories, 26 workshops, and forty four public libraries. These serve about 21,500 students.[6]
Various state highways and municipal roads cross the municipality. Important roads include the Villahermosa-Comalcalco highway, which connects Jalpa with Comalcalco and Nacajuca. The Samaria-Jalpa de Méndez highway connects the municipality with Cunduacán. The Tulipán-Jalpa de Méndez highway connects it with federal highway 187 and the Jalpa de Méndez-Chiltepec connects it with the Paraíso municipality.[2] There is one intercity bus terminal.[6]
Aside from the municipal seat, there are a number of other important communities. There are two mostly indigenous communities called Ayapa and Mecoacán. Both have churches painted in bright colors called San Miguel Arcángel and San Mateo, respectively.[2] Ayapa is 35 km from the municipal seat with a population of about 4,600. Its main economic activities are livestock and the production of decorated gourds even though three oil wells of the Ayapa field are in its jurisdiction. Mecoacán is located eight km from the municipal seat with a population of about 3,200 people. It main economic activities are agriculture, the raising of pigs and domestic fowl and petroleum production. Iquinuapa is located four km from the municipal seat with a population of about 3,500 people. Its main economic activities are agriculture and handcrafts. Villa Jalupa is six km from the municipal seat with a population of about 3,400. Its main economic activity is agriculture. Soyataco is four km from the municipal seat with a population of about 3,250. Its main economic activity is agriculture. Hermenegildo Galeana 2ª is located six km from the municipal seat with a population of about 1,250 people. Its main economic activity is the production of cacao and coconut.[2]
References
- "-". Enciclopedia de los Municipios de México. Instituto Nacional para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal. Archived from the original on March 2, 2007. Retrieved January 4, 2010.
- "Conoce Jalpa" [Get to know Jalpa] (in Spanish). Tabasco: Municipality of Jalpa de Méndez. Archived from the original on August 14, 2011. Retrieved January 14, 2012.
- "Historia de Jalpa de Méndez" [History of Jalpa de Méndez] (in Spanish). Tabasco: Municipality of Jalpa de Méndez. Archived from the original on August 14, 2011. Retrieved January 14, 2012.
- "Resumen municipal Jalpa de Méndez" [Municipality summary Jalpa de Méndez] (in Spanish). Mexico: SEDESOL. Retrieved January 14, 2012.
- Jiménez González, Victor Manuel, ed. (2010). Tabasco: Guía para descubrir los encantos del estado [Tabasco: Guide to discover the charms of the state] (in Spanish). Mexico City: Editorial Océano de México SA de CV. pp. 110–112. ISBN 978-607-400-320-8.
- "Jalpa de Méndez". Enciclopedia de los Municipios y Delegaciones de México (in Spanish). Mexico: INAFED Instituto para el Federalismo y el Desarrollo Municipal. SEGOB Secretaría de Gobernación. 2010. Archived from the original on February 21, 2013. Retrieved January 14, 2012.