Inogatran
Inogatran (INN)[1] is a low molecular weight peptidomimetic thrombin inhibitor. Inogatran was developed for the potential treatment of arterial and venous thrombotic diseases.[2]
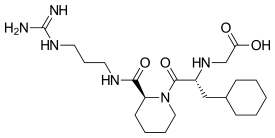 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-{[(2R)-1-[(2S)-2-[(4-Carbamimidamidopropyl)carbamoyl]piperidin-1-yl]-3-cyclohexyl-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino}acetic acid | |
| Other names
N-[(1R)-2-Cyclohexyl-1-[[(2S)-2-[(3-guanidinopropyl)carbamoyl]piperidino]carbonyl] ethyl]glycine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H38N6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 438.6 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- "International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN). Recommended International Nonproprietary Names (Rec. INN): List 35" (PDF). World Health Organization. p. 13. Retrieved 2 December 2016.
- Teger-Nilsson, AC; Bylund, R; Gustafsson, D; Gyzander, E; Eriksson, U (January 1997). "In Vitro Effects of Inogatran, a Selective Low Molecular Weight Thrombin Inhibitor". Thrombosis Research. 85 (2): 133–45. doi:10.1016/s0049-3848(96)00230-7. PMID 9058487.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.