Herkus Monte
Herkus Monte (also Hercus; Lithuanian: Herkus Mantas; Latin: Henricus Montemin) was the most famous leader of the Great Prussian Uprising against the Teutonic Knights and Northern Crusaders. The uprising began in September 1260, following the Knights' defeat at the Battle of Durbe, and lasted for the next fourteen years.

History
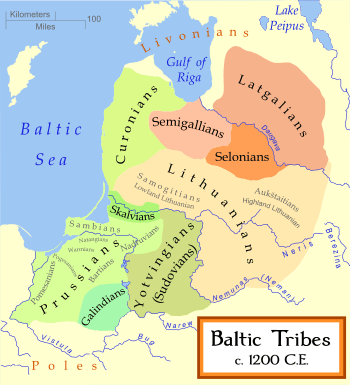
The Chronicon terrae Prussiae stated that Herkus was originally from Natangia, one of the lands of the Old Prussians. The Prussians were the first of the Baltic tribes to be conquered by the Teutonic Knights, who first arrived in Chełmno in 1226 at the request of Konrad I of Masovia, whose own struggle with the Prussians had proved unsuccessful. As part of the Northern Crusades, the Knights proceeded to attack the Prussians with the purported aim of converting them to Christianity.
As a young boy, Herkus was taken hostage by the Teutonic Knights and brought to Magdeburg, Germany. Having lived there for about ten years, and having studied at the monastery school of St. Johannes der Täufer auf dem Berge, Herkus became well-educated. He was probably baptised as Henricus, but after his release he dropped two letters from his name and called himself Hercus or Herkus. Since he was familiar with German military tactics, the Natangians elected him as a leader of their forces. At first he was successful: on 21 January 1261 he defeated the Knights in the Battle of Pokarwis. In 1262, he was severely wounded during a Siege of Königsberg. However, he soon recovered, and the following year he invaded the Chełmno Land with a large force. On his way back to Natangia, Herkus and his men were confronted by a contingent of their enemies; in the ensuing Battle of Löbau, a Master and a Marshal, together with 40 knights and a number of other soldiers, were killed.
Partially because of his victories, the Prussians were able to retake control over some of their lands. After 1263, the chronicles do not mention Herkus again until 1272. In the 1260s, the Knights, receiving support from the Pope and Western Europe, were more successful in their fight against the Prussians. The Prussian rebels, unable to capture cities and lay sieges to their enemy's castles, started losing the fight. By 1272, Herkus, with a small group of his followers, was forced to withdraw to the forests of southern Prussia. Within a year, he was captured and hanged. In 1274, the rebellion ended and the Knights proceeded to attempt to conquer the rest of the Baltic tribes.
Legacy
The Prussian hero Herkus Monte was taken by Lithuanians under the Communist Soviet regime as their symbol to regain freedom as well. The northern Prussian region, which was severed from Germany as Memelland by the Treaty of Versailles and referred to as Lithuania Minor, uses Herkus Monte references as one of its icons. The main street of the city of Memel in East Prussia, now the Lithuanian seaport of Klaipėda, was named Herkaus Manto gatvė (Herkus Monte street).
His life and dramatic resistance to the more powerful enemy became the basis for several artistic works. Juozas Grušas wrote a historical drama Herkus Mantas, portraying him as a romantic hero. The Lithuanian language movie Herkus Mantas, directed by Marijonas Giedrys, with music by Giedrius Kuprevičius, was released in 1972. It became one of the best-received Lithuanian movies during the Soviet period (1945–90), because Lithuanians under Soviet control could easily identify themselves with the Prussians under the Teutonic Knights.[1] After Lithuanian's independence, Giedrius Kuprevičius returned to Grušas's drama play about Herkus Mantus, this time writing an opera based on it and calling it The Prussians. It premiered at Klaipėda Music Theater in 1995 with Nerijus Petrokas as director and Stasys Domarkas as conductor.
Monte has also been honoured in Poland, where a primary school in Kamińsk bears his name as a patron.[2] There's a song titled "Herkus Monte" in the 2015 album Senprūsija (Old Prussia) by the Latvian folk metal band Skyforger. He is also mentioned in the song Tagad vai nekad (Now or Never) of the same album as one of the leaders who fought the Teutonic Order during the Great Prussian Uprising.[3]
References
- General
- Simas Sužiedėlis, ed. (1970–1978). "Mantas, Herkus". Encyclopedia Lituanica. III. Boston, Massachusetts: Juozas Kapočius. pp. 461–2. LCC 74-114275.
- Jasas, Rimantas (1986). "Herkus Mantas". In Jonas Zinkus; et al. (eds.). Tarybų Lietuvos enciklopedija (in Lithuanian). II. Vilnius, Lithuania: Vyriausioji enciklopedijų redakcija. pp. 24–5.
- In-line
- Arvydas Anušauskas; et al., eds. (2005). Lietuva, 1940–1990. Vilnius: Lietuvos gyventojų genocido ir rezistencijos tyrimo centras. p. 563. ISBN 9986-757-65-7.
- SZKOŁA PODSTAWOWA IM. HERKUSA MONTE W KAMIŃSKU
- New Skyforger album “Senprūsija” out soon!
External links
- "The Prussians" – an opera by the Klaipėda Music Theatre.
- Henry Monte and the Prussian Rising of 1260