Hanriot H.41
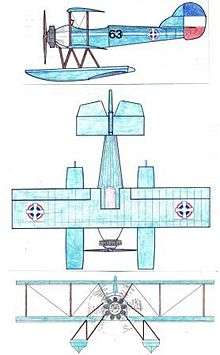
The Hanriot H.41 was a military trainer aircraft produced in France in the 1920s. It was a further development in the family of aircraft that had commenced with the HD.14 in 1920, and incorporated a number of design features that had been developed for other members of that family. Like those other aircraft, however, it was a conventional, two-bay biplane with unstaggered wings of equal span.
| H.41 | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Role | Trainer |
| National origin | France |
| Manufacturer | Hanriot |
| First flight | 1925 |
The H.41 used the modern engine and mixed construction developed for the HD.40 air ambulance and used them in a new design for a military trainer. The design did not prove a success, however, and only eleven were built, with three different engine types. A floatplane variant based on the HD.17 was slightly more successful, with twelve examples exported to Greece and Portugal.
Variants
- H.41
- Two-seat training aircraft.
- H.410
- version with Lorraine 5Pa engine (5 built)
- H.411
- version with Salmson 7Ac engine (2 built)
- LH.412
- version with Lorraine 5Pb engine (4 built, plus 3 converted from H.410)
- HD.41H
- :(Hydro) - floatplane with Salmson 9Ac engine (12 built)+ (10 built in Yugoslav Aircraft factory "Zmaj" Zemun)
Operators
- Yugoslav Royal Navy
Specifications (variant)
Data from Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928[1]
General characteristics
- Crew: 2
- Length: 7.25 m (23 ft 9 in)
- Wingspan: 10.26 m (33 ft 8 in)
- Height: 3.13 m (10 ft 3 in)
- Wing area: 34.9 m2 (376 sq ft)
- Empty weight: 625 kg (1,378 lb)
- Gross weight: 900 kg (1,984 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Lorraine 5P 5-cylinder air-cooled radial piston engine, 75 kW (100 hp)
- Propellers: 2-bladed fixed pitch propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 185 km/h (115 mph, 100 kn)
- Landing speed: 50 km/h (31 mph; 27 kn)
- Range: 400 km (250 mi, 220 nmi)
- Service ceiling: 3,500 m (11,500 ft)
- Time to altitude: 1,000 m (3,300 ft) in 13 minutes
- Wing loading: 25.8 kg/m2 (5.3 lb/sq ft)
- Power/mass: 0.0830 kW/kg (0.0505 hp/lb)
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hanriot HD.41. |
- Grey, C.G., ed. (1928). Jane's all the World's Aircraft 1928. London: Sampson Low, Marston & company, ltd. p. 104c.
Further reading
- Taylor, Michael J. H. (1989). Jane's Encyclopedia of Aviation. London: Studio Editions. p. 470.
- World Aircraft Information Files. London: Bright Star Publishing. pp. File 896 Sheet 11.
- Janić, Čedomir; O. Petrović (2011). Short History of Aviation in Serbia. Beograd: Aerokomunikacije. ISBN 978-86-913973-2-6.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)