HYDIA
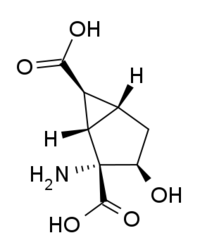
HYDIA is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3). It has been useful in the mapping of the group II mGluR receptor proteins and their molecular modeling.[1] HYDIA is similar in structure to group II mGluR agonists such as eglumegad and LY-404,039, but the addition of the 3-hydroxy group reverses the activity to a competitive antagonist. Other derivatives such as the 3-benzyloxy ether are more potent antagonists than HYDIA itself.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C8H11NO5 |
| Molar mass | 201.178 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- Lundström L, Kuhn B, Beck J, Borroni E, Wettstein JG, Woltering TJ, Gatti S (July 2009). "Mutagenesis and molecular modeling of the orthosteric binding site of the mGlu2 receptor determining interactions of the group II receptor antagonist (3)H-HYDIA". ChemMedChem. 4 (7): 1086–94. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200900028. PMID 19402024.
- Woltering TJ, Adam G, Huguenin P, Wichmann J, Kolczewski S, Gatti S, Bourson A, Kew JN, Richards G, Kemp JA, Mutel V, Knoflach F (February 2008). "Asymmetric synthesis and receptor pharmacology of the group II mGlu receptor ligand (1S,2R,3R,5R,6S)-2-amino-3-hydroxy-bicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,6-dicarboxylic acid-HYDIA". ChemMedChem. 3 (2): 323–35. doi:10.1002/cmdc.200700226. PMID 18058780.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.