HMS Glatton (1871)
HMS Glatton was a breastwork monitor which served in the Victorian Royal Navy.
_William_Frederick_Mitchell.jpg) Painting of HMS Glatton by William Frederick Mitchell | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | HMS Glatton |
| Builder: | Chatham Dockyard |
| Laid down: | 10 August 1868 |
| Launched: | 8 March 1871 |
| Completed: | 24 February 1872 |
| Fate: | Broken up, 1903 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Breastwork monitor |
| Displacement: | 4,912 long tons (4,991 t) |
| Length: | 245 ft 9 in (74.90 m) p/p |
| Beam: | 54 ft (16 m) |
| Draught: |
|
| Propulsion: | Two-shaft Laird, 2,870 ihp (2,140 kW) |
| Speed: | 12.11 knots (13.94 mph; 22.43 km/h) |
| Complement: | 185 |
| Armament: |
|
| Armour: |
|
Design
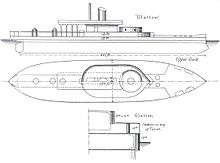
She was designed by Sir Edward Reed to a specific formula determined by the Board of Admiralty, and her purpose was never made wholly clear. Reed himself said "there is no vessel with the objects of which I am less well acquainted than the Glatton. She was designed strictly upon orders which I received and upon the object of which I was never informed". The Controller, the fourth sea lord, stated that she was to be used for "the defence of our own harbours and roadsteads, and for attacking those of the enemy". In reality, her lack of freeboard would appear to have precluded any operations whatsoever except those in calm weather and smooth water. Her freeboard was no more than three feet amidships, and 4 feet 6 inches (1.37 m) at the bow. This must, however, be viewed in the context of U.S. monitors which served at sea and weathered heavy storms, such as the USS Weehawken. Glatton's raised amidships breastwork granted improved height above the waves for both her gun turret and hatches when compared to the U.S. model and it should be further noted that the Royal Navy successfully deployed the twin-turret breastwork monitors HMS Devastation and HMS Thunderer at sea with the fleet.
The ship was designed so that, although the main armament was mounted in a single turret, there would in theory be no point on the horizon to which at least one gun could not point, whatever the orientation of the ship. To achieve this the superstructure was made to be very narrow, so that at least one of the guns in the turret could fire on targets to the after aspect of the ship. It would appear that the blast effects on the superstructure from firing abaft the beam were not regarded as important.
According to Admiral George Alexander Ballard, who served on board as a junior officer, stops were fitted to prevent the firing of the main artillery much past the beam, but not until some years after the ship was launched.
Glatton was the best protected ship of her day, with some 35% of her displacement being devoted to armour.
Service history
She was commissioned in 1872 immediately into the Dockyard reserve, as tender to the gunnery school Excellent. She was a part of the 1878 Particular Service Squadron. In July of that year she was fired upon during live firing trials.[1] In 1881 she was fitted to discharge 14-inch (360 mm) torpedoes. At the same time three QF 6 pounder Hotchkiss and 4 machine guns were added to her armament.[2] In 1887 she was specially commissioned for the manoeuvres, and with Prince Albert allocated to the defence of the Thames estuary. This is her only recorded operational sea-time. Thereafter she passed through second class reserve, fleet reserve and from April 1902 dockyard reserve status,[3] until she was sold in 1903.
References
- Paloczi-Horvath, George (1996). From Monitor to Missile Boat Coast Defence Ships and Coastal Defence since 1860. Conway Maritime Press. pp. 113–114. ISBN 0-85177-650-7.
- Paloczi-Horvath, George (1996). From Monitor to Missile Boat Coast Defence Ships and Coastal Defence since 1860. Conway Maritime Press. p. 31. ISBN 0-85177-650-7.
- "Naval & Military intelligence". The Times (36751). London. 25 April 1902. p. 8.
- Oscar Parkes British Battleships ISBN 0-85052-604-3
- Conway All the World's Fighting Ships ISBN 0-85177-133-5
External links
