Guion Line
The Liverpool and Great Western Steamship Company, known commonly as the Guion Line, was a British passenger service that operated the Liverpool-Queenstown-New York route from 1866 to 1894.[1] While incorporated in Great Britain, 52% of the company's capital was from the American firm, Williams and Guion of New York.[2] Known primarily for transporting immigrants, in 1879 the line started commissioning Blue Riband record breakers to compete against Cunard, White Star and Inman for first class passengers.[1] The financial troubles of one of the company's major partners in 1884 forced the firm to return its latest record breaker, the Oregon, to her builders and focus again on the immigrant trade.[3] The company suspended sailings in 1894 because of new American restrictions on immigrant traffic.[4]
History
Steerage trade
In 1848, John Stanton Williams (c. 1810-1876) and Stephen Barker Guion (1820-1885) formed the New York firm of Williams and Guion to operate the Black Star Line of sailing packets on the Liverpool-Queenstown-New York route.[5] In 1852, Guion relocated to Liverpool as the firm's agent while Williams remained in New York.[5] The next year, Guion's older brother, William H. Guion joined the firm's New York office.[5] The Black Star Line concentrated on the steerage trade[6] and ultimately owned 18 sailing ships.[5] Black Star was shut down in 1863 because of the success of iron-screw liners in attracting steerage passengers and the danger of Confederate commerce raiders during the Civil War.[1] Stephen Guion, by now a naturalized British citizen, contracted with the Cunard Line and the National Line to provide steerage passengers.[3]
In 1866, Stephen Guion incorporated the Liverpool and Great Western Steamship Company in Great Britain to operate a quartet of 2,900 GRT liners for a weekly service to New York.[1] Although 52% of the capital came from the Williams and Guion partnership,[5] the Guion Line was formed as a British company because American law only allowed U.S.-built ships to be registered in the U.S., and American shipyards were incapable at that time of building the iron-hulled screw steamers required to compete on this route.[3] Guion took advantage of an 1846 legal decision that considered a British corporation as a British citizen even if its shareholders were largely foreigners.[3]
By 1870, the Guion Line ranked third in the delivery of immigrants to New York, with 27,054 steerage passengers, but only 1,115 first class.[3] The line's eight ships were known as good sea-boats and had a reputation for innovative engineering.[6] Guion's Wisconsin and Wyoming were the first liners on the Atlantic built with compound engines.[1] Unfortunately, Guion's ships also had a reputation for being slow.[7] In 1873, the New York Times urged the U.S. Post Office to contract with another line because of the long passage times of Guion ships.[7]
Ocean greyhounds

The five-year shipping depression beginning in 1873 changed the character of the Guion Line. By 1875, the fleet was reduced to the four newest ships.[1] The directors decided that they needed record breakers to change the company's image and ordered two 17 knot steamers, the Montana and the Dakota, to win the Blue Riband. However, both ships proved to be major failures and only achieved 11.5 knots in service.[1] In 1877, Dakota became a total loss after stranding off Anglesey, and in 1880 Montana was lost after she also stranded only a few miles away from her sister.[1] Guion purchased Cunard's ten-year-old Abyssinia to take her place in the schedule.[1]
William Pearce, the controlling partner of the John Elder shipyard, was convinced that a crack steamer that carried only passengers and light freight could be profitable because she would attract more passengers and spend less time in port.[6] He proposed a ship that crammed the most powerful machinery possible into the hull, sacrificing everything to speed.[1] When Cunard rejected his proposal, Pearce offered his idea to Guion at a bargain price of £140,000 at a time when express liners typically cost £200,000.[6] He also agreed to share the initial costs. Financially stressed after a series of shipwrecks, Guion was pleased with the arrangement.[6] Stephen Guion personally owned the new vessel.[5]


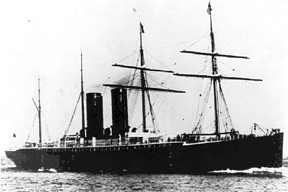
Guion's 16-knot Arizona took the eastbound record, but not the Blue Riband (i.e. the westbound record). Arizona also won considerable publicity when on an early voyage she hit an iceberg head-on, telescoping 25 feet of her bow.[3] She returned to St. John's, where a temporary wooden bow was fitted until permanent repairs were made in Scotland. Guion advertised this incident as proof of the ship's strength.[1]
Two years later, Guion took delivery of an even faster Blue Riband winner, the 17-knot Alaska, also personally owned by Guion.[5] To continue the program, Pearce offered Guion favorable terms on a third unit, the 18-knot Oregon of 1883.[1] While these ships were uncomfortable, they proved popular with American clients because of their American ownership.[3]
In 1876, John Williams died and the firm was restructured in 1883 to settle his estate.[5] Then in January 1884, Stephen Guion's older brother, William, resigned from the firm because of bad investments unrelated to the steamship line.[8] Unable to make payments to the shipbuilder, Stephen Guion returned the current Blue Riband holder, Oregon, to the Elders, who sold her to Cunard. Stephen himself died in December 1885,[5] and his 37-year-old nephew, William H. Guion Jr., died a month later, forcing a liquidation of the now named Guion and Company. The line was reorganized as a public stock corporation to settle the estates.[1]
Final chapter
The new directors, chaired by Sir William Pearce himself, continued a weekly schedule with the old Nevada, Wisconsin and Wyoming along with the relatively new Arizona and Alaska, while Abyssinia was put on long-term charter to the Canadian Pacific Line. In 1886, the line was granted a share of the British transatlantic mail contract. However, the company's reputation was hurt in 1891 when the recently returned Abyssinia burned at sea, fortunately without loss of life.[9] In 1892, the cholera scare caused New York officials to quarantine vessels arriving with steerage passengers.[10] The Wyoming was one of the ships detained and a crewman on the ship died of cholera.[10] Immigration regulation was taken over by the Federal Government and steamship lines were made responsible for returning any immigrants found unfit. In December 1892, Guion directors decided to retire the three oldest steamers, which were primarily in the steerage trade.[4] In 1894, outpaced by the latest twin-screw liners from Cunard, White Star and Inman, the directors also withdrew the two former record breakers and liquidated the remaining assets.[1]
Guion fleet
All built for Guion unless otherwise indicated—presented in order of acquisition.[1]
| Ship | Built | In service for Guion | Type | Tonnage | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manhattan | 1866 | 1866-1875 | intermediate | 2,900 | Sold to Warren Line 1875 |
| Chicago | 1866 | 1866-1868 | intermediate | 2,900 | Wrecked near Queenstown, Southern Ireland in 1868 with no loss of life |
| Minnesota | 1867 | 1867-1875 | intermediate | 2,900 | sold to Warren Line 1875 |
| Nebraska | 1867 | 1867-1874 | intermediate | 3,900 | sold 1874 |
| Colorado | 1868 | 1868-1873 | intermediate | 2,900 | Sunk in Mersey 1873 with 6 lost |
| Nevada | 1869 | 1869-1893 | intermediate | 3,150 | sold to Dominion Line. A notable passenger was Annie Moore, from Ireland, the first passenger to cross the threshold of Ellis Island in January 1892. |
| Idaho | 1869 | 1869-1878 | intermediate | 3,150 | Wrecked near Queenstown, Southern Ireland on 1 June 1878 with no loss of life |
| Wisconsin | 1870 | 1870-1893 | intermediate | 3,250 | sold 1893 |
| Wyoming | 1870 | 1870-1893 | intermediate | 3,250 | sold 1893 |
| Montana | 1875 | 1875-1880 | intermediate | 4,300 | Wrecked off Anglesey on 14 March 1880 with no loss of life |
| Dakota | 1875 | 1875-1877 | intermediate | 4,300 | Wrecked off Anglesey on 9 May 1877 with no loss of life |
| Arizona | 1879 | 1879-1894 | express | 5,150 | Eastbound record holder, sold 1898 to the U.S. Government |
| Abyssinia | 1870 | 1880-1891 | express | 3,250 | Purchased from Cunard, burned at sea 1891 with no loss of life |
| Alaska | 1881 | 1881-1894 | express | 6,950 | Blue Riband, sold 1899 |
| Oregon | 1883 | 1883-1884 | express | 7,400 | Blue Riband, returned to builder and resold to Cunard 1884, sunk 1886 without loss of life |
| Parthia[11] | 1870 | 1885-1887 | intermediate | 3,200 | Purchased from Cunard, sold in 1892 to the North American Mail Steamship Company as Victoria. |
References
- Gibbs, Charles Robert Vernon (1957). Passenger Liners of the Western Ocean: A Record of Atlantic Steam and Motor Passenger Vessels from 1838 to the Present Day. John De Graff. pp. 52–92.
- New York Times (2 August 1873). Williams and Guion, A Thoroughly English Line.
- Fry, Henry (1896). The History of North Atlantic Steam Navigation with Some Account of Early Ships and Shipowners. London: Sampson, Low & Marston. OCLC 271397492.
- New York Times (25 December 1892). Going Out of Business.
- New York Times (20 December 1885). Obituary: Stephen Baker Guion.
- Fox, Stephen. Transatlantic: Samuel Cunard, Isambard Brunel and the Great Atlantic Streamships.
- New York Times (29 July 1873). Transatlantic Mails, Is there more than one mail a week to England?.
- New York Times (21 January 1884). William H. Guion, Ruined by loans to friends.
- New York Times (1892). The burning of the Abyssinia, Second officer censored by London Board of Trade.
- Harper's Weekly (17 September 1892). Cholera in New York Bay.
- Ljungstrom, Henrik. "Parthia (I)/Victoria". Original. The Great Ocean Liners. Retrieved 5 October 2013.