French destroyer Épée (1900)
Epée was one of four Framée-class destroyers built for the French Navy around the beginning of the 20th century. During the First World War, the ship saw service in the Mediterranean Sea and survived the war to be stricken from the naval register on 1 October 1920.
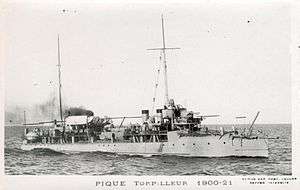 Sister ship Pique | |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Epée |
| Namesake: | Épée |
| Builder: | Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, Le Havre |
| Laid down: | 1897 |
| Launched: | 27 July 1900 |
| Stricken: | 1 October 1920 |
| Fate: | Sold for scrap, 8 January 1921 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type: | Framée-class destroyer |
| Displacement: | 319 t (314 long tons) |
| Length: | 58.2 m (190 ft 11 in) o/a |
| Beam: | 6.31 m (20 ft 8 in) |
| Draft: | 3.03 m (9 ft 11 in) |
| Installed power: |
|
| Propulsion: | 2 shafts; 2 triple-expansion steam engines |
| Speed: | 26 knots (48 km/h; 30 mph) |
| Range: | 2,055 nmi (3,806 km; 2,365 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph) |
| Complement: | 48 |
| Armament: |
|
Design and description
The Framées had an overall length of 58.2 meters (190 ft 11 in), a beam of 6.31 meters (20 ft 8 in), and a maximum draft of 3.03 meters (9 ft 11 in). They displaced 319 metric tons (314 long tons) at deep load. The two triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one propeller shaft, produced a total of 4,200–5,200 indicated horsepower (3,132–3,878 kW), using steam provided by four water-tube boilers. The ships had a designed speed of 26 knots (48 km/h; 30 mph) and Épée reached a speed of 26.19 knots (48.50 km/h; 30.14 mph) during her sea trials on 1 July 1901. The ships carried enough coal to give them a range of 2,055 nautical miles (3,806 km; 2,365 mi) at 10 knots (19 km/h; 12 mph). Their complement consisted of four officers and forty-four enlisted men.[1]
The Framée-class ships were armed with a single 65-millimeter (2.6 in) gun forward of the bridge and six 47-millimeter (1.9 in) Hotchkiss guns, three on each broadside. They were fitted with two single 381-millimeter (15 in) torpedo tubes, one between the funnels and the other on the stern.[2] Two reload torpedoes were also carried.[3]
Construction and career
Épée was ordered from Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée and the ship was laid down in 1897 at its shipyard in Granville-Le Havre.[1] She was launched on 27 July 1900.[2]
References
- Couhat, p. 83
- Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 326
- Couhat, p. 81
Bibliography
- Chesneau, Roger & Kolesnik, Eugene M. (1979). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-133-5.
- Couhat, Jean Labayle (1974). French Warships of World War I. London: Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-0445-5.
- Gardiner, Robert & Gray, Randal (1985). Conway's All The World's Fighting Ships 1906–1921. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 0-85177-245-5.