Fort Reynolds (Virginia)
Fort Reynolds was a Union Army redoubt built as part of the defenses of Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War.
| Fort Reynolds | |
|---|---|
| Part of the Civil War defenses of Washington, D.C. | |
| Arlington, Virginia, USA | |
Fort Reynolds historical marker | |
 Fort Reynolds | |
| Coordinates | 38.8376°N 77.0948°W |
| Type | Earthwork fort |
| Site information | |
| Controlled by | Union Army |
| Condition | Stabilized |
| Site history | |
| Built | 1861 |
| Built by | U.S. Army Corps of Engineers |
| In use | 1861–1865 |
| Materials | Earth, timber |
| Demolished | 1865 |
| Battles/wars | American Civil War |
The fort was located in Fairlington, Arlington County, Virginia. It was constructed in September 1861 to command the approach to Alexandria by the Four Mile Run valley and was itself protected by nearby Battery Garesche. It had a perimeter of 360 yards (329 m) and emplacements for 12 guns.
The fort was originally called Fort Blenker after Colonel Louis Blenker's brigade stationed nearby. In late 1863, the fort was renamed after Major General John F. Reynolds, who was killed on 1 July at the Battle of Gettysburg in Pennsylvania.
Occupation of Arlington
Before the outbreak of the Civil War, Alexandria County (renamed Arlington County in 1920), the northernmost county in Virginia and the closest to Washington, D.C., was a predominantly rural area. Originally part of the District of Columbia, the land now comprising the county was retroceded to Virginia in a July 9, 1846 act of Congress that took effect in 1847.[1] Most of the county is hilly, and at the time, most of the county's population was concentrated in the city of Alexandria, at the far southeastern corner of the county. In 1861, the rest of the county largely consisted of scattered farms, the occasional house, fields for grazing livestock, and Arlington House, owned by Mary Custis, wife of Robert E. Lee.[2]
Following the surrender of Fort Sumter in Charleston, South Carolina, on April 14, 1861, new American president Abraham Lincoln declared that "an insurrection existed," and called for 75,000 troops to be called up to quash the rebellion.[3] The move sparked resentment in many other southern states, which promptly moved to convene discussions of secession. The Virginia State Convention passed "an ordinance of secession" and ordered a May 23 referendum to decide whether or not the state should secede from the Union. The U.S. Army responded by creating the Department of Washington, which united all Union troops in the District of Columbia and Maryland under one command.[4]
Brigadier General J.F.K. Mansfield, commander of the Department of Washington, argued that Northern Virginia should be occupied as soon as possible in order to prevent the possibility of the Confederate Army mounting artillery on the hills of Arlington and shelling government buildings in Washington. He also urged the erection of fortifications on the Virginia side of the Potomac River to protect the southern terminuses of the Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge. His superiors approved these recommendations, but decided to wait until after Virginia voted for or against secession.[5]
On May 23, 1861, Virginia voted by a margin of 3 to 1 in favor of leaving the Union. That night, U.S. Army troops began crossing the bridges linking Washington, D.C. to Virginia. The march, which began at 10 p.m. on the night of the 23rd, was described in colorful terms by the New York Herald two days later:

There can be no more complaints of inactivity of the government. The forward march movement into Virginia, indicated in my despatches last night, took place at the precise time this morning that I named, but in much more imposing and powerful numbers.
About ten o'clock last night four companies of picked men moved over the Long Bridge, as an advance guard. They were sent to reconnoitre, and if assailed were ordered to signal, when they would have been reinforced by a corps of regular infantry and a battery....
At twelve o'clock the infantry regiment, artillery and cavalry corps began to muster and assume marching order. As fast as the several regiments were ready they proceeded to the Long Bridge, those in Washington being directed to take that route.
The troops quartered at Georgetown, the Sixty-ninth, Fifth, Eighth and Twenty-eighth New York regiments, proceeded across what is known as the chain bridge, above the mouth of the Potomac Aqueduct, under the command of General McDowell. They took possession of the heights in that direction.
The imposing scene was at the Long Bridge, where the main body of the troops crossed. Eight thousand infantry, two regular cavalry companies and two sections of Sherman's artillery battalion, consisting of two batteries, were in line this side of the Long Bridge at two o'clock.[6]
The occupation of Northern Virginia was peaceful, with the sole exception of the town of Alexandria. There, as Colonel Elmer E. Ellsworth, commander of the New York Fire Zouaves (11th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment), entered a local hotel to remove the Confederate flag flying above it, he was shot and killed by James Jackson, the proprietor. Ellsworth was one of the first men killed in the American Civil War.[7] Throughout the remainder of the war, Alexandria would lean strongly towards the Confederate government, necessitating continued occupation by a Union garrison.[8]
Battle of Bull Run
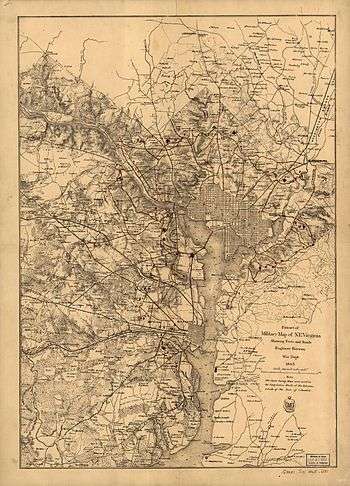
Over the seven weeks that followed the occupation of northern Virginia, forts were constructed along the banks of the Potomac River and at the approaches to each of the three major bridges (Chain Bridge, Long Bridge, and Aqueduct Bridge) connecting Virginia to Washington and Georgetown.[9]
While the Potomac River forts were being built, planning and surveying was ordered for an enormous new ring of forts to protect the city. Unlike the fortifications under construction, the new forts would defend the city in all directions, not just the most direct route through Arlington. In mid-July, this work was interrupted by the First Battle of Bull Run. As the Army of Northeastern Virginia marched south to Manassas, the soldiers previously assigned to construction duties marched instead to battle. In the days that followed the Union defeat at Bull Run, panicked efforts were made to defend Washington from what was perceived as an imminent Confederate attack.[10] The makeshift trenches and earthworks that resulted were largely confined to Arlington and the direct approaches to Washington.
On July 26, 1861, five days after the battle, Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan was named commander of the military district of Washington and the subsequently renamed Army of the Potomac. Upon arriving in Washington, McClellan was appalled by the condition of the city's defenses.
In no quarter were the dispositions for defense such as to offer a vigorous resistance to a respectable body of the enemy, either in the position and numbers of the troops or the number and character of the defensive works... not a single defensive work had been commenced on the Maryland side. There was nothing to prevent the enemy shelling the city from heights within easy range, which could be occupied by a hostile column almost without resistance.[11]
To remedy the situation, one of McClellan's first orders upon taking command was to greatly expand the defenses of Washington. At all points of the compass, forts and entrenchments would be constructed in sufficient strength to defeat any attack.[12] Alexandria, which contained the southern terminus of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal and one of the largest ports in the Chesapeake Bay, was an object of "anxious study."[13]
Planning and construction
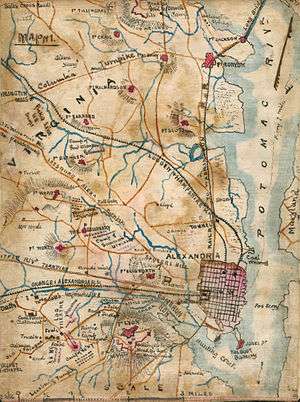
Gen. John Newton, who was in charge of the forts south of Four Mile Run, supervised the construction and managed the flow of men and material.[14]
Fort Blenker was built by the troops of Gen. Louis Blenker, to the North of Fort Ward across the Leesburg and Alexandria Turnpike, now Route 7.
On Friday January 17, 1862, Col. J. Howard Kitching marched with the 6th New York Artillery to occupy the Fort, and complete construction,
Fort Blenker, January 19, 1862.
.... On Friday morning, while we were all hard at work in Fort Worth, Major Doull received orders to march, immediately to this post with two companies. In less than two hours' time, we had torn down our nice winter quarters, which we had built with so much trouble; left our nice log cook-houses and stables, and were on the march; I, in command of the troops, Doull having gone ahead to arrange for our relieving the troops at Blenker.[15]
It had a perimeter of 360 yards, and places for 12 guns.[16]
In 1954, the fort was demolished to construct an apartment complex. It still lends its name to nearby Fort Reynolds Park and is noted with a historical marker.
References
- "Frequently Asked Questions About Washington, D.C., The Historical Society of Washington, D.C." Archived from the original on February 6, 2007. Retrieved September 13, 2007.
- "Evacuation of Arlington House, U.S. National Park Service". Retrieved September 13, 2007.
- E.B. Long with Barbara Long, The Civil War Day by Day: An Almanac 1861-1865 (Garden City, NY: Doubleday & Company, Inc., 1971), pp. 47-50
- Long 1971, p. 67
- Cooling, Benjamin Franklin, III, Symbol, Sword, and Shield: Defending Washington During the Civil War Second Edition Revised (Shippensburg, PA: White Mane Publishing Company, 1991), pp. 32-26, 41.
- New York Herald. "THE INSURRECTION. ADVANCE OF THE FEDERAL TROOPS INTO VIRGINIA," Washington, D.C., May 24, 1861.
- Ames W. Williams, "The Occupation of Alexandria," Virginia Cavalcade, Volume 11, (Winter 1961-62), pp. 33-34.
- "Alexandria Library, Diary of Henry B. Whittington, May 31, 1861".
- J.G. Barnard and W.F. Barry, "Report of the Engineer and Artillery Operations of the Army of the Potomac from Its Organization to the Close of the Peninsular Campaign," (New York: D. Van Nostrand, 1863), pp. 9-10.
- Margaret Leech, Reveille in Washington (New York: Harper & Brothers Publishers, 1941), pp. 101-110.
- U.S., War Department, The War of the Rebellion: A Compilation of the Official Records of the Union and Confederate Armies, 70 Volumes (Washington, DC: The Government Printing Office, 1880-1901) I, Volume 5, p. 11.
- Official Records, Series I, Volume 5, Chapter 14, p. 679.
- Official Records, Series I, Volume 5, Chapter 14, p. 680.
- Official Records, Series I, Volume 5, Chapter 14, p. 684.
- Kitching, J. Howard. "More than a Conqueror". p. 39.
- Cooling III, Benjamin Franklin; Owen II, Walton H. (6 October 2009). Mr. Lincoln's Forts: A Guide to the Civil War Defenses of Washington. Scarecrow Press. pp. 76–77. ISBN 978-0-8108-6307-1.