Foramen ovale (skull)
At the base of the skull, the foramen ovale (Latin: oval window) is one of the larger of the several holes (the foramina) that transmit nerves through the skull. The foramen ovale is situated in the posterior part of the sphenoid bone, posterolateral to the foramen rotundum.
| Foramen ovale of Sphenoid | |
|---|---|
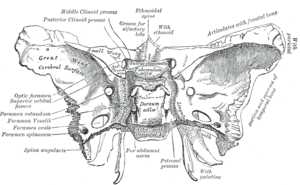 Sphenoid bone. Upper surface. (foramen ovale labeled at left, third from bottom) | |
 Horizontal section of nasal and orbital cavities. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | foramen ovale ossis sphenoidalis |
| TA | A02.1.05.036 |
| FMA | 53155 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structure

The foramen ovale is an opening in the greater wing of the sphenoid bone. The foramen ovale is one of two cranial foramina in the greater wing, the other being the foramen spinosum. [1] :771 The foramen ovale is posterolateral to the foramen rotundum and anteromedial to the foramen spinosum. Posterior and medial to the foramen is the opening for the carotid canal.[1] :776
Variation
Similar to other foramina, the foramen ovale differs in shape and size throughout the natural life. The earliest perfect ring-shaped formation of the foramen ovale was observed in the 7th fetal month and the latest in 3 years after birth, in a study using over 350 skulls.[2]
In a study conducted on 100 skulls, the foramen ovale was divided into 2 or 3 components in 4.5% of the cases. The borders of the foramen in some skulls were also irregular and rough. This may suggest, based on radiological images, the presence of morbid changes, which might be the sole anatomical variation in the foramina ovalia of humans.[3]
In newborn, the foramen ovale is about 3.85 mm and in the adults about 7.2 mm in length. The average maximal length is about 7.48 mm and its average minimal length is 4.17 mm in the adult. The width extends from 1.81 mm in the newborn to 3.7 mm in adults.[2][4]
Structures passing through it
The following structures pass through foramen ovale:
- mandibular nerve, a branch of the trigeminal nerve
- accessory meningeal artery
- lesser petrosal nerve, a branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve[1]
- an emissary vein connecting the cavernous sinus with the pterygoid plexus of veins
Clinical significance
The foramen ovale is used as the entry point into the skull when conducting a Percutaneous Stereotactic Rhizotomy, a type of radiofrequency ablation performed to treat trigeminal neuralgia. In the procedure, the electrode is introduced through the cheek of an anesthetized patient and radiologically guided into the foramen ovale, with the intention of partially or fully ablating one or more of the divisions (typically the Mandibular) to relieve pain.[5]
This entry point is also used to surgically place local electrodes directly on the surface of the mesial temporal lobe, in order to observe neural activity of patients with suspected focal epilepsy.[6]
See also
- Foramina of the skull
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 150 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- Yanagi S (1987). "Developmental studies on the foramen rotundum, foramen ovale and foramen spinosum of the human sphenoid bone". The Hokkaido Journal of Medical Science. 62 (3): 485–96. PMID 3610040.
- Reymond J, Charuta A, Wysocki J (2005). "The morphology and morphometry of the foramina of the greater wing of the human sphenoid bone". Folia Morphologica. 64 (3): 188–93. PMID 16228954.
- Lang J, Maier R, Schafhauser O (1984). "Postnatal enlargement of the foramina rotundum, ovale et spinosum and their topographical changes". Anatomischer Anzeiger. 156 (5): 351–87. PMID 6486466.
- Tew, John. "Percutaneous stereotactic rhizotomy (PSR) for facial pain". Mayfield Brain & Spine. Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- Velasco, TR; Sakamoto, AC; Alexandre, V Jr; Walz, R; Dalmagro, CL; Bianchin, MM; Araújo, D; Santos, AC; Leite, JP; Assirati, JA; Carlotti, C Jr. "Foramen ovale electrodes can identify a focal seizure onset when surface EEG fails in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy". Epilepsia. 47: 1300–7. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2006.00547.x. PMID 16922874.
External links
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0904 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (IX)
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-1". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Adult skull as seen from beneath at uiuc.edu