Fe FET
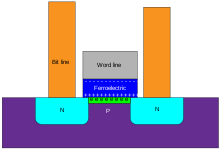
A ferroelectric field-effect transistor (Fe FET) is a type of field-effect transistor that includes a ferroelectric material sandwiched between the gate electrode and source-drain conduction region of the device. Permanent electrical field polarisation in the ferroelectric causes this type of device to retain the transistor's state (on or off) in the absence of any electrical bias.
| Computer memory types |
|---|
| Volatile |
| RAM |
| Historical |
|
| Non-volatile |
| ROM |
| NVRAM |
| Early stage NVRAM |
| Magnetic |
| Optical |
| In development |
| Historical |
|
FeFET based devices are used in FeFET memory - a type of single transistor non-volatile memory.
Description
Use of a ferroelectric (triglycine sulfate) in a solid state memory was proposed by Moll and Tarui in 1963 using a thin film transistor.[1] Further research occurred in the 1960s, but the retention characteristics of the thin film based devices was unsatisfactory.[2] Early field effect transistor based devices used bismuth titanate (Bi4Ti3O12) ferroelectric, or Pb1-xLnxTiO3 (PLT) and related mixed zironconate/titanates (PLZT).[2] In the late 1980 Ferroelectric RAM was developed, using a ferroelectric thin film as capacitor, connected to an addressing FET.[2]
FeFET based memory devices are read using voltages below the coercive voltage for the ferrolectric.[3]
Issues involved in realising a practical FeFET memory device include (as of 2006) : choice of a high permitivity, highly insulating layer between ferroelectric and gate; issues with high remanent polarisation of ferrolectrics; limited retention time (c. a few days, cf required 10 years).[4]
Provided the ferroelectric layer can be scaled accordingly FeFET based memory devices are expected to scale (shrink) as well as MOSFET devices; however a limit of ~20 nm laterally may exist (the superparaelectric limit, aka ferroelectric limit). Other challenges to feature shrinks include : reduced film thickness causing additional (undesired) polarisation effects; charge injection; and leakage currents.[4]
Research and development
In 2017 FeFET based non-volatile memory was reported as having been built at 22nm node using FDSOI CMOS (fully depleted silicon on insulator) with hafnium dioxide (HfO2) as the ferroelectric- the smallest FeFET cell size reported was 0.025 μm2, the devices were built as 32Mbit arrays, using set/reset pulses of ~10ns duration at 4.2V - the devices showed endurance of 105 cycles and data retention up to 300C.[5]
As of 2017 the startup 'Ferroelelectrc Memory Company' is attempting to develop FeFET memory into a commercial device, based on Hafnium dioxide. The company's technology is claimed to scale to modern process node sizes, and to integrate with contemporary production processes, i.e. HKMG, and is easily integrable in to conventional CMOS processes, requiring only two additional masks.[6]
See also
- Ferroelectric RAM - RAM that uses a ferrolectric material in the capacitor of a conventional DRAM structure
References
- Park et al. 2016, §1.1.1, p.3.
- Park et al. 2016, §1.1.1, p.4.
- Park et al. 2016, § 1.1.2, p.6.
- Lapedus, Mark (16 Feb 2017), "What Are FeFETs?", semiengineering.com
Sources
- Park, Byung-Eun; Ishiwara, Hiroshi; Okuyama, Masanori; Sakai, Shigeki; Yoon, Sung-Min, eds. (2016), "Ferroelectric-Gate Field Effect Transistor Memories: Device Physics and Applications", Topics in Applied Physics, Springer (131)
Further reading
- Ishiwara, Hiroshi (2012), "FeFET and ferroelectric random access memories", Multifunctional Oxide Heterostructures, doi:10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199584123.003.0012