Fluorodopa
Fluorodopa, also known as FDOPA, is a fluorinated form of L-DOPA primarily synthesized as its fluorine-18 isotopologue for use as a radiotracer in positron emission tomography (PET).[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Fluorodopa F18 |
| Other names | 6-fluoro-L-DOPA, FDOPA |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
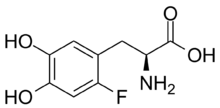
| Formula | C9H10FNO4 |
| Molar mass | 214.18 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The most common side effects are injection site pain.[2]
Medical uses
Fluorodopa is indicated for use in positron emission tomography (PET) to visualize dopaminergic nerve terminals in the striatum for the evaluation of adults with suspected Parkinsonian syndromes (PS).[2]
History
In October 2019, Fluorodopa was approved in the United States for the visual detection of certain nerve cells in adult patients with suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes (PS).[3][4]
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Fluorodopa F 18 based on evidence from one clinical trial of 56 patients with suspected PS.[3] The trial was conducted at one clinical site in the United States.[3]
References
- Deng WP, Wong KA, Kirk KL (June 2002). "Convenient syntheses of 2-, 5- and 6-fluoro- and 2,6-difluoro-L-DOPA". Tetrahedron: Asymmetry. 13 (11): 1135–1140. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(02)00321-X.
- "Fluorodopa F18 injection". DailyMed. 12 October 2019. Retrieved 26 April 2020.
- "Drug Trials Snapshots: Fluorodopa F 18". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 27 November 2019. Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 27 November 2019.

- "Drug Approval Package: Fluorodopa F18". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 November 2019. Archived from the original on 27 November 2019. Retrieved 26 November 2019.

External links
- "Fluorodopa F 18". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.