European Plain
The European Plain or Great European Plain is a plain in Europe and is a major feature of one of four major topographical units of Europe - the Central and Interior Lowlands.[1] It is the largest mountain-free landform in Europe, although a number of highlands are identified within it.

.svg.png)
Location
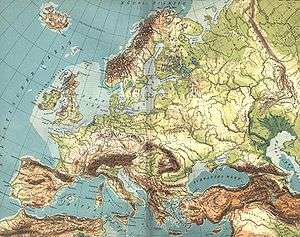
The plain stretches from the Pyrenees mountains and the French coast of the Bay of Biscay in the west to the Russian Ural Mountains in the east.[2] Its shores are washed to the west and northwest by waters of the Atlantic basin, to the northeast - the Arctic basin, and to the southeast - the Mediterranean basin, including the Black Sea. To the south of the Middle European Plain stretch the central uplands and plateaus of Europe elevating to the peaks of the Alps, the Carpathian Mountains and the Balkan Mountains. To the northwest across the English Channel lie the British Isles and their lowlands, while across several straits north of the Jutland Peninsula lies the Central Swedish lowland in the Scandinavian Peninsula, which is part of the Fennoscandia ecoregion.
Most of the plain lies in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forest biome, while its far eastern portion extends into steppe of the ecoregion Eurasian Steppe.
Beside the Great European Plain there are other, smaller European plains such as the Pannonian Basin or Mid-Danube Plain, which lies in Central Europe, Padana Plain which is located in the valley of the Po river, the Thracian Plain with Maritsa river, and lowlands of the British Isles.
The Great European Plain is divided into the North European Plain (Central/Middle European Plain) and the East European Plain. The subdivision is a historical one, rather than geomorphological: the Russian portion of the East European Plain is also known as the Russian Plain which covers almost entirely the European portion of the Russian Federation (European Russia).
In Western Europe, the plain is relatively narrow (mostly within 200 miles or 320 kilometres in width) in the northern part of Europe, but it broadens significantly toward its eastern part in Western Russia.[2]
Hydrology
The plains are cut by many important rivers like the Loire, Rhine and Vistula in the west; the Northern Dvina and Daugava flowing northwards in East Europe and Russia and the Volga, the Don and the Dnieper flowing southwards of the European Russia.
List of large bodies of water
Bio-system
The European plain was once largely covered by forest, before human settlement and the resulting deforestation that occurred. One of the last (and largest) remnants of this primeval forest is Białowieża Forest, which straddles the border between Belarus and Poland. Now the European Plain is the most agriculturally productive region of Europe.
List of ecoregions
See also
References
- Geographical depiction of Europe Encyclopædia Britannica
- "European Plain". Encyclopædia Britannica. britannica.com. 10 January 2010. Retrieved 10 January 2010.