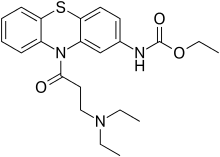
Ethacizine
Ethacizine (ethacyzine) is a class Ic antiarrhythmic agent, related to moracizine. It is used in Russia and some other CIS countries for the treatment of severe and/or refractory ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias, especially those accompanied by organic heart disease. It is also indicated as a treatment of refractory tachycardia associated with Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ethacizin |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | ~40% (oral)[1] |
| Protein binding | 90% |
| Metabolism | Extensive hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 2.5 hours |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H27N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 413.54 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
It is manufactured under the brand name Ethacizin (Этацизин) by Olainfarm.[2]
References
- "Этацизин (Ethacyzin) Prescribing Information. VIDAL Drug Compendium" (in Russian). Retrieved 5 February 2014.
- "Этацизин—4DOKTOR.RU Drug Information Handbook" (in Russian). Retrieved 5 February 2014.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.