Electrocardiophone
An electrocardiophone and cardiophone is a musical instrument or diagnostic tool[1] which uses heart waves (measured in the same way as an ECG) to generate or modulate sounds.
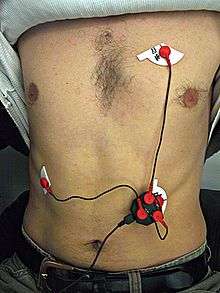
James Fung, Ariel Garten, and Steve Mann (~2003) have created a wide variety of underwater biophone systems that use physiological signals to control different musical variables in an intricate way, as well as to actually generate sounds, including underwater ECG and EEG concerts.[2]
The electrocardiophone is a quintephone in the sense that it creates sound from the "5th classical element" (i.e. from beyond the world of matter).
Related concepts
The electrocardiophone is related to the electroencephalophone. In addition to sound-production, regenerative brainwave musical performances use brainwave interfaces to modify or manipulate or play along with sounds of other instruments in a live performance context.
Gallery
 Preparing for underwater and water-based biophone concert: connecting ECG electrodes for electrocardiophone
Preparing for underwater and water-based biophone concert: connecting ECG electrodes for electrocardiophone Electroencephalophone as part of live performance. Using brainwaves the quintist directly interfaces to a music synthesizer, playing along with the other band members. A closed-loop system functions analogously with a regenerative receiver.
Electroencephalophone as part of live performance. Using brainwaves the quintist directly interfaces to a music synthesizer, playing along with the other band members. A closed-loop system functions analogously with a regenerative receiver.
See also
References
- "The Electrocardiophone: A New Instrument for Rapid Bedside Diagnosis of Cardiac Arrhythmias - GREEN 36 (6): 975 - Circulation". Circ.ahajournals.org. Retrieved 2008-11-27.
- http://wearcam.org/icmc2007/
