Earl of Kent
The peerage title Earl of Kent has been created eight times in the Peerage of England and once in the Peerage of the United Kingdom.
Earls of Kent, first creation (1020)
- Godwin, Earl of Wessex (1020–1053)
- Leofwine Godwinson (1053–1066)
Earls of Kent, second creation (1067)
- Odo, Earl of Kent, and Bishop of Bayeux (died 1097) (forfeit 1088)
Earls of Kent, third creation (1141)
- William de Ipres, 1st Earl of Kent (c. 1095–1165) (deprived 1155)
Earls of Kent, fourth creation (1227)
- Hubert de Burgh, 1st Earl of Kent (died 1243)
Earls of Kent, fifth creation (1321)
- Edmund of Woodstock, 1st Earl of Kent (1301–1330) (attainted 1330)
- Edmund, 2nd Earl of Kent (d. 1331) (restored 1331)
- John, 3rd Earl of Kent (1330–1352)
- Joan, 4th Countess of Kent (1327–1385)
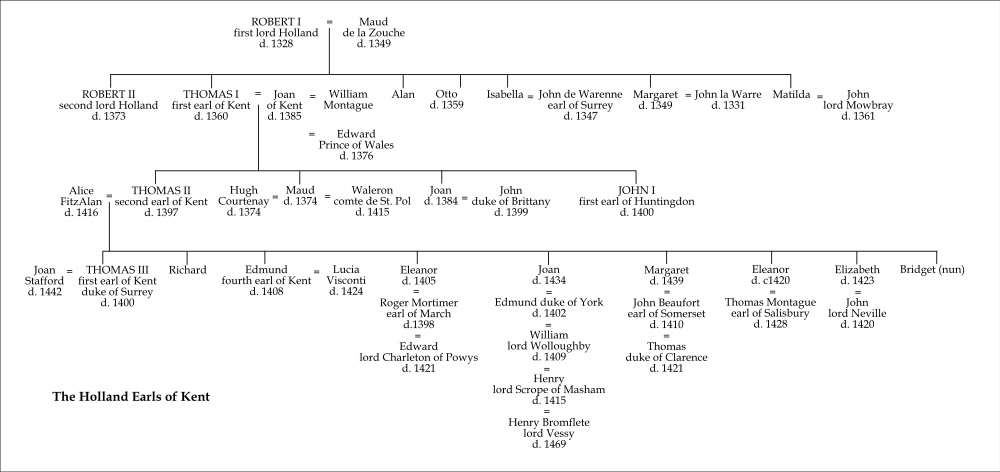
Earls of Kent, sixth creation (1360)
The earls of Kent of this creation used Baron Holand (1353) as a subsidiary title; it became abeyant 1408. The first earl of Kent by this creation was the husband of Joan of Kent of the fifth creation.
- Thomas Holland, 1st Earl of Kent (died 1360)
- Thomas Holland, 2nd Earl of Kent (1350–1397)
- Thomas Holland, 3rd Earl of Kent (1372–1400)
- Edmund Holland, 4th Earl of Kent (1383–1408)
The line of the earls of Kent became extinct with the death of Edmund, the fourth earl.
Earls of Kent, seventh creation (1461)
- William Neville, 1st Earl of Kent (died 1463)
Earls of Kent, eighth creation (1465)
The Greys were a baronial family with substantial property in Bedfordshire and Buckinghamshire, and later around Ruthin in Wales. They rose to greater prominence during the Wars of the Roses. Edmund Grey, Lord Grey of Ruthin, started out a Lancastrian, but switched to the Yorkist side at the Battle of Northampton. He was a member of Edward IV's council, became Lord Treasurer in 1463/4, was created Earl of Kent in 1465 and was keeper of the Tower of London in 1470. He remained loyal through Richard III's accession, taking part in his coronation (1483).
Edmund's son George, the 2nd Earl, had continued as a Yorkist, marrying Anne Woodville, a sister of Edward IV's queen Elizabeth Woodville. (He was half-first cousin - both being grandsons of Reynold 3rd Lord Grey of Ruthin - to Queen Elizabeth's first husband, Sir John Grey of Groby.) He later married Catherine Herbert, daughter of William Herbert, 1st Earl of Pembroke.
The third earl, Richard, was the son of the second earl and Anne Woodville. He wound up heavily in debt, probably through gambling, and was forced to alienate most of his property. A good part ended up in the crown's hands; historians disagree regarding what this says about Henry VII's relationship with the aristocracy.
He was succeeded as earl by his half-brother Henry, son of the second earl and Catherine Herbert. Henry tried, with little success, to reacquire the property Richard had sold, and had to live as a modest gentleman, never formally taking title as earl.
- Edmund Grey, 1st Earl of Kent (c. 1420–1490)
- George Grey, 2nd Earl of Kent (c. 1460–1503)
- Richard Grey, 3rd Earl of Kent (1481–1524)
- Henry Grey, 4th Earl of Kent (c. 1495–1562)
- Reginald Grey, 5th Earl of Kent (died 1573)
- Henry Grey, 6th Earl of Kent (1541–1615)
- Charles Grey, 7th Earl of Kent (c. 1545–1623)
- Henry Grey, 8th Earl of Kent (c. 1583–1639)
- Anthony Grey, 9th Earl of Kent (1557–1643)
- Henry Grey, 10th Earl of Kent (1594–1651)
- Anthony Grey, 11th Earl of Kent (1645–1702)
- Henry Grey, 12th Earl of Kent (1671–1740) (created Marquess of Kent in 1706, Duke of Kent in 1710) (all Kent titles were extinct on his death, though some others passed to Jemima Yorke, 2nd Marchioness Grey)
Earls of Kent, ninth creation (1866)
- Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, Earl of Kent (1844–1900)
References
- G.W. Bernard, "The Fortunes of the Greys, Earls of Kent, in the Early Sixteenth Century", The Historical Journal, 25 (1982), 671–685
- Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . Encyclopædia Britannica. 15 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 734–735.