Difluoride
Difluorides are chemical compounds with two fluorine atoms per molecule (or per formula unit).
| Order and disorder in difluorides | |
_-_cropped.png) |
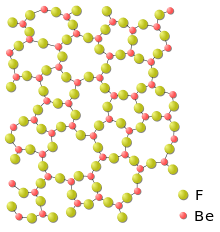 |
| The fluorite structure | Beryllium fluoride glass |
Metal difluorides are all ionic. Despite being highly ionic, the alkali earth metal difluorides generally have extremely high lattice stability and are thus insoluble in water. One exception is beryllium difluoride. In addition, many transition metal difluorides are water-soluble.
Calcium difluoride is a notable compound. In the form of the mineral fluorite it is the major source of commercial fluorine. It also has an eponymic crystal structure, which is an end member of the spectrum starting from bixbyite and progressing through pyrochlore.
List of the difluorides
Examples of the difluorides include:
Alkaline earth metal difluorides
The alkaline earth metals all exhibit the oxidation state +2, and form difluorides. The difluoride of radium is however not well established due to the element's high radioactivity.
- Beryllium difluoride
- Magnesium fluoride
- Calcium fluoride
- Strontium difluoride
- Barium fluoride
- Radium fluoride
Solubility-related constants of alkaline earth metal fluorides Metal M2+ HE[1] F− HE[2] "MF2" unit
HEMF2 lattice
energies (−kJ/mol)[3]Solubility
(mol/L)[4]Be 2,455 458 3,371 3,526 25 Mg 1,922 458 2,838 2,978 0.0012 Ca 1,577 458 2,493 2,651 0.0002 Sr 1,415 458 2,331 2,513 0.0008 Ba 1,361 458 2,277 2,373 0.006
Transition metal difluorides
Compounds of the form MF2:
- Cadmium difluoride
- Chromium(II) fluoride
- Cobalt difluoride
- Copper(II) fluoride
- Iron(II) fluoride
- Manganese(II) fluoride
- Mercury difluoride
- Nickel difluoride
- Palladium difluoride
- Silver difluoride
- Zinc difluoride
Post-transition metal difluorides
- Lead difluoride
- Tin(II) fluoride
Nonmetal and metalloid difluorides
- Dinitrogen difluoride
- Oxygen difluoride
- Dioxygen difluoride
- Selenoyl difluoride
- Sulfur difluoride
- Disulfur difluoride
- Thionyl difluoride
- Germanium difluoride
Noble gas difluorides
Bifluorides
The bifluorides contain the two fluorine atoms in a covalently bound HF2− polyatomic ion rather than as F− anions.
Organic difluorides
- Ethanedioyl difluoride
- Ethylidene difluoride
- Carbonyl difluoride
- Carbon dibromide difluoride (dibromodifluoromethane)
- Carbon dichloride difluoride (dichlorodifluormethane)
- Methyl difluoride
- Methylphosphonyl difluoride
- Polyvinylidene difluoride
References
- Wiberg, Wiberg & Holleman 2001, pp. XXXVI–XXXVII.
- Wiberg, Wiberg & Holleman 2001, p. XXXVI.
- Lide 2004, p. 12-23.
- Wiberg, Wiberg & Holleman 2001, p. 1073.
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/101282799#section=2D-Structure
- https://www.americanelements.com/europium-ii-fluoride-14077-39-5
- http://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB8426459.htm
- Georg Brauer: Handbuch der Präparativen Anorganischen Chemie. 3., umgearb. Auflage. Band I. Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6, p. 255.
Bibliography
- Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1998). Chemistry of the Elements (second edition). Butterworth Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)
- Lide, David R. (2004). Handbook of chemistry and physics (84th ed.). CRC Press. ISBN 0-8493-0566-7.CS1 maint: ref=harv (link)