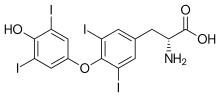
Dextrothyroxine
Dextrothyroxine (trade name Choloxin) is a dextrorotary isomer of thyroxine.[1] It saw research as a cholesterol-lowering drug[2] but was pulled due to cardiac side-effects. It increases hepatic lipase which in turn improves utilization of triglycerides and decreases levels of lipoprotein(a) in serum.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Choloxin |
| Other names | D-3,5,3',5'-tetraiodothyronine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Multum Consumer Information |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.094 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H11I4NO4 |
| Molar mass | 776.874 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- "Dextrothyroxine (Code C61719)". NCI Thesaurus. National Cancer Institute. 2011-11-14. Retrieved 2020-01-28.
- Bantle JP, Hunninghake DB, Frantz ID, Kuba K, Mariash CN, Oppenheimer JH (September 1984). "Comparison of effectiveness of thyrotropin-suppressive doses of D- and L-thyroxine in treatment of hypercholesterolemia". The American Journal of Medicine. 77 (3): 475–81. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(84)90107-4. PMID 6475988.
- Bommer C, Werle E, Walter-Sack I, Keller C, Gehlen F, Wanner C, et al. (January 1998). "D-thyroxine reduces lipoprotein(a) serum concentration in dialysis patients". Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 9 (1): 90–6. PMID 9440092.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.