Delaporte distribution
The Delaporte distribution is a discrete probability distribution that has received attention in actuarial science.[1][2] It can be defined using the convolution of a negative binomial distribution with a Poisson distribution.[2] Just as the negative binomial distribution can be viewed as a Poisson distribution where the mean parameter is itself a random variable with a gamma distribution, the Delaporte distribution can be viewed as a compound distribution based on a Poisson distribution, where there are two components to the mean parameter: a fixed component, which has the parameter, and a gamma-distributed variable component, which has the and parameters.[3] The distribution is named for Pierre Delaporte, who analyzed it in relation to automobile accident claim counts in 1959,[4] although it appeared in a different form as early as 1934 in a paper by Rolf von Lüders,[5] where it was called the Formel II distribution.[2]
|
Probability mass function 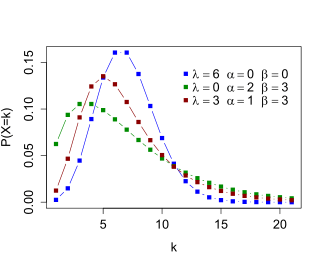 When and are 0, the distribution is the Poisson. When is 0, the distribution is the negative binomial. | |||
|
Cumulative distribution function  When and are 0, the distribution is the Poisson. When is 0, the distribution is the negative binomial. | |||
| Parameters |
(fixed mean) (parameters of variable mean) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Support | |||
| pmf | |||
| CDF | |||
| Mean | |||
| Mode | |||
| Variance | |||
| Skewness | See #Properties | ||
| Ex. kurtosis | See #Properties | ||
| MGF | |||
Properties
The skewness of the Delaporte distribution is:
The excess kurtosis of the distribution is:
References
- Panjer, Harry H. (2006). "Discrete Parametric Distributions". In Teugels, Jozef L.; Sundt, Bjørn (eds.). Encyclopedia of Actuarial Science. John Wiley & Sons. doi:10.1002/9780470012505.tad027. ISBN 978-0-470-01250-5.
- Johnson, Norman Lloyd; Kemp, Adrienne W.; Kotz, Samuel (2005). Univariate discrete distributions (Third ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 241–242. ISBN 978-0-471-27246-5.
- Vose, David (2008). Risk analysis: a quantitative guide (Third, illustrated ed.). John Wiley & Sons. pp. 618–619. ISBN 978-0-470-51284-5. LCCN 2007041696.
- Delaporte, Pierre J. (1960). "Quelques problèmes de statistiques mathématiques poses par l'Assurance Automobile et le Bonus pour non sinistre" [Some problems of mathematical statistics as related to automobile insurance and no-claims bonus]. Bulletin Trimestriel de l'Institut des Actuaires Français (in French). 227: 87–102.
- von Lüders, Rolf (1934). "Die Statistik der seltenen Ereignisse" [The statistics of rare events]. Biometrika (in German). 26: 108–128. doi:10.1093/biomet/26.1-2.108. JSTOR 2332055.
Further reading
- Murat, M.; Szynal, D. (1998). "On moments of counting distributions satisfying the k'th-order recursion and their compound distributions". Journal of Mathematical Sciences. 92 (4): 4038–4043. doi:10.1007/BF02432340.
External links