December 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake
The December 2015 Hindu Kush earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 6.3[1][3] in South Asia on 25 December 2015.[4] One woman was killed in Pakistan. At least 100 people were injured in Pakistan and Afghanistan.[5] The quake was also strongly felt in Tajikistan and India. The epicenter of the earthquake was in the Afghanistan-Tajikistan border region at a depth of 203.4 km.[6]
| UTC time | 2015-12-25 19:14:47 |
|---|---|
| ISC event | 612128431 |
| USGS-ANSS | ComCat |
| Local date | 25 December 2015 |
| Local time | 23:44:47 |
| Magnitude | 6.3 Mw |
| Depth | 203.4 km (126.4 mi) |
| Epicenter | 36.486°N 71.138°E[1] |
| Areas affected | |
| Max. intensity | V (Moderate) |
| Casualties | 4[2] |
Background
| Region | Number of deaths[2] | Number of injuries |
|---|---|---|
| 3 | 83 | |
| 1 | 5 | |
| 12 | ||
| Total | 4 | 100 |
An earthquake of 7.3 Mw was felt in the same region[7] in October 2015 causing 398 deaths and 2,536 injuries in Pakistan[8] and Afghanistan.[9]
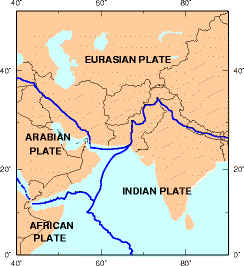
The Himalayan mountains are pushed up by the collision of tectonic plates, making them prone to devastating quakes. An earthquake in April 2015, Nepal's worst in 80 years, killed over 8,600 people.[10]
The last major earthquake in the same region of similar magnitude (7.6 Mw) was almost ten years prior in October 2005, which resulted in 87,351 deaths, 75,266 injured, 2.8 million people being displaced, and 250,000 farm animals deaths. The notable difference between this earthquake and the 2005 earthquake is the depth of the seismic activity. The 2005 earthquake was 15 km deep while this earthquake was 203.4 km deep, reducing its effects at the surface.[11]
In recent studies, geologists claim that global warming is one of the reasons for increased seismic activity. According to these studies melting glaciers and rising sea levels disturb the balance of pressure on Earth's tectonic plates thus causing an increase in the frequency and intensity of earthquakes. This could be one of the reasons why the Himalayas are getting more prone to earthquakes in recent years.[12]
See also
References
- ANSS. "Afghanistan 2015: M 6.3 - 42km WSW of Ashkasham, Afghanistan". Comprehensive Catalog. U.S. Geological Survey
- "Earthquake leaves 4 dead, more than 100 injured in Afghanistan and Pakistan". Fox News. 26 December 2015.
- "Strong 6.2 magnitude earthquake jolts parts of Pakistan, Afghanistan". The Express Tribune. 26 December 2015.
- "Quake rattles areas in Punjab, KPK, Azad Kashmir". Samaa TV.
- "Dozens injured in Afghan quake". The Australian. 26 December 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- The Associated Press. "6.2-Magnitude Earthquake Hits Northern Afghanistan and Pakistan". NBC News.
- "M7.5 – 45km N of 'Alaqahdari-ye Kiran wa Munjan, Afghanistan". United States Geological Survey. 26 December 2015.
- "Live Updates". ndma.gov.pk. 5 November 2015. Archived from the original on 21 November 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- "The Latest: UN Mobilizing to Aid Quake Victims". The Associated Press. ABC News. 26 October 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- Press Trust of India (23 May 2015). "Nepal earthquake death toll reaches 8,635, over 300 missing". The Indian Express. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- "Afghanistan Struck by Powerful Earthquake". The New York Times. 26 October 2015. Retrieved 26 December 2015.
- "Nepal earthquake could have been manmade disaster climate change brings". Newsweek. Retrieved 26 December 2015.