Dalälven
The Dal River (Swedish: Dalälven) is a river in central Sweden that flows from the north of Dalarna and runs into the sea in northern Uppland; it is commonly considered to be the southern border of Norrland, however only the last part correlates with Limes Norrlandicus (the biological Norrland border). The northern part is split into two rivers: Österdalälven and Västerdalälven. The two connect in Djurås. It is over 520 kilometres (320 mi) long — the second longest river in Sweden, and has a hydropower potential of 1420 megawatts, of which 2/3 is utilized. The largest power plant is located at the Trängslet Dam. Dalälven has been significant historically as a raft transport route. Nedre Dalälven River Landscape, Sweden, covers 308,000 hectares (1,190 sq mi) with a mixture of wetlands, rivers, lakes, flood plains and productive forests. It includes Lake Hovran and Färnebofjärden Bay Ramsar site.
| Dal River | |
|---|---|
 | |
 Dalälven's position | |
| Native name | Dalälven |
| Location | |
| Country | Sweden |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Mouth | Gulf of Bothnia |
• coordinates | 60°38′30″N 17°27′00″E |
• elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Length | 520 km (320 mi)[1] |
| Basin size | 28,953.8 km2 (11,179.1 sq mi)[2] |
| Discharge | |
| • average | 379 m3/s (13,400 cu ft/s)[1] |
The region boasts high biodiversity, as the river forms a clear border zone between the northern and southern flora and fauna of Northern Europe. Agriculture and forestry have evolved as a result of changes in the steel and iron industries.
More than 100 ‘Leader+ projects’ designed for sustainable development testify to the high dynamism of the region. The biosphere reserve benefits from a highly participatory governance system as well as numerous partnerships with universities and research centres for environmental monitoring.
Description
Course

Sources
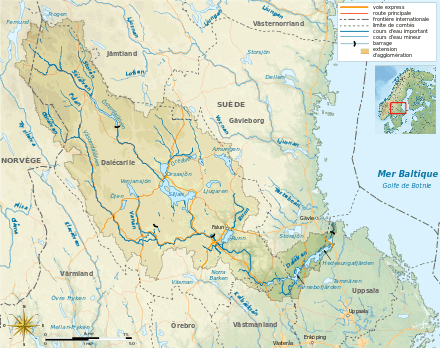
The Dalälven is the southernmost of the big rivers of northern Sweden. It extends 541 kilometres (336 mi) between the mountains of Dalarna and the Baltic Sea, which makes it the second longest river in the country after the Göta älv.[3] However, the river changes names several times, and only becomes the Dalälven at the confluence of the Västerdalälven (West Dalälven) and the Österdalälven (East Dalälven), which happens at Djurås.[4]
The principal of these two rivers, Österdalälven, begins where the Storån and Sörälven meet, near Idre.[5] Both the Storån and Sörälven begin in Norway, but soon reach the northwest of Dalarna.[6] After their confluence, the river enters into a series of narrow lakes (Idresjön, Alvrosfjorden, Kringelfjorden, Hedfjorden, Särnasjön, etc.). It then pools into the lake Trängsletsjön, 70 kilometres (43 mi) in length, formed by the Trängslet Dam.[7] The river then arrives at Mora where it receives the waters of the Oreälven, one of its major tributaries[1] and empties itself immediately after into the Lake Siljan, the largest lake in the entire catchment area, and the seventh largest in all of Sweden, with a surface area of 292 kilometres (181 mi).[8] This lake is formed by the largest impact crater in western Europe, of a diameter of 75 kilometres (47 mi).[9] The river leaves the lake at Leksand and continues south to its confluence with Västerdalälven.
Västerdalälven is itself born of the confluence of two rivers, the Görälven and Fuluälven.[10] These rivers have their sources not far from each other in Älvdalen Municipality in the Scandinavian Mountains. Fuluälven heads south along the east face of the mountain Fulufjället, while the Görälven flanks Fulufjället to the west, crossing the frontier with Norway where it takes the name Ljøra. After the confluence this river continues south, passing Sälen and then Malung and forking east to arrive in Vansbro Municipality. At Vansbro, it is met by the Vanån, its principal tributary. Its course then becomes more sinuous, tracing broad loops. It then enters Gagnef Municipality where it joins Österdalälven.
From Djurås to the sea

After the junction of the Österdalälven and Västerdalälven, the river heads east, passing Borlänge, Dalarna's largest city,[11] then receiving the waters of the Lillälven, itself fed by the Faluån, a river which goes through Falun, Dalarna's second largest city.[12]
The river then continues to Avesta where it strongly changes character.[N 1] It leaves a deep valley and enters into a flat country, uniquely marked by some eskers.[N 1] During the remaining 120 kilometres (75 mi) that it travels to the sea, the river, now called the Lower Dalälven (Nedre Dalälven), alternates between large bays (fjärdar) and rapids.[N 1] This section is also characterized by regular flooding, sometimes over vast areas.[N 2] The first rapids are those at Avesta, called Storfors and Lillfors (big chute and little chute), after which the river forms the lake Bäsingen, then the rapids Näs bruk, then the lake Bysjön. It forms the frontier between Västmanland County to the south and Dalarna County to the north. It then forms the rapids at Tyttbo, and right after, one of its largest fjärds, that of Färnebofjärden National Park, forming the frontier between Uppsala County to the south and Gävleborg County to the north. More than 200 islands are strewn over this fjärd.[13] The river continues to the rapids at Gysinge and then another great fjärd, Hedesundafjärden-Bramsöfjärden. The river passes through the rapids at Söderfors towards Untrafjärden, then by the rapids of Untra towards Marmafjärden, and then the rapids of Lanforsen. Finally, goes through its last rapids at Älvkarleby before rejoining the Baltic Sea.
History
First humans and agriculture
The first settlers in the region of the Dalälven arrived after the retreat of the ice sheet, 10,000 years ago. At that time, the Lower Dalälven was below sea level and was in the zone corresponding to today's Dalarna, which was the first area settled. The first settlers in the region settled the banks of the river and its tributaries, as well as the shore.[14] They were hunter-gatherers.[14] In the Lower Dalälven, which extended bit by bit, the eskers were the best sites for the first permanent settlements.[N 2] It was easy to nourish oneself, thanks to the river, and these places were also the easiest to defend.[N 2] Besides this, the river was easiest to cross at this point.[N 2]
When agriculture developed, the lands south of the basin proved most fertile, and so the rest of the basin was used principally for pasture.[V 1] There were some fields surrounding the villages, but were not very fertile.[V 1] The forests were used for pasturing animals and fodder was harvested in the wetlands.[V 1] Transhumance was adopted.[V 1] In certain cites, the wetlands and lakes were partially drained to try to recover good-quality agricultural lands.[V 1]
Log driving


Log driving in River Dalälven is documented from the 1600s onward. An important factor behind it was the 1607 prohibition from Charles IX of cutting wood closer than one Swedish mile from Falun Mine. However, until the Storskiftet land amalgamation reform and England's abolition of customs on wood products in 1849, the logging stayed small-scale.[15]
Four major sawmill companies dominated the logging in River Dalälven: Korsnäs AB at Lake Runn (Falun), established in 1858; Kopparbergs och Hofors Sågverks Bolag at Lake Hosjön (Falun), which started in 1861 and bought its competitor Carlfors Sågverksbolag in 1874; Stora Kopparbergs Bergslags AB, which modernized its mill at the rapids of Domnarvet (Borlänge) in 1863; and the mill in Älvkarleby, which was replaced by Skutskär sawmill in 1870.[15]
Log driving in River Dalälven reached its peak in 1952, when about 30 million logs per year were driven.[16] It ended in most of the river in 1970. However, in the river's lower reaches, the driving continued until 1971, with some final emptying of the stocks in 1972. In 1973 the whole river was closed for log driving, and in 1977 all logging installations along River Dalälven were decommissioned.[15]
In popular culture
In The Wonderful Adventures of Nils, Swedish author Selma Lagerlöf dedicates a chapter to the river. She describes the formation of the Dalälven as a race between the rivers Storån and Fuluälven from their sources to the sea. During the race, these rivers receive help from many tributaries, but also encounter many obstacles (lakes to fill, hills to pierce, etc.), so that halfway through, upon recognizing each other's merits, they unite their efforts.[17]
References
- This article was initially translated from the French Wikipedia.
- "Nedre Dalälven" (PDF) (in Swedish). 2000.
- p. 32
- p. 44
- Länssyrelserna i Dalarna län (2009). "Vattenvårdsplan för Dalälvens avrinningsområde" (PDF) (in Swedish). ISSN 1654-7691.
- p. 23
- "Dalälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 11 July 2010. (subscription required)
- "Län och huvudavrinningsområden i Sverige" (PDF) (in Swedish). Swedish Meteorological and Hydrological Institute. Retrieved 11 July 2010.
- (in Swedish)."Sveriges vattendrag" (PDF). SMHI. Retrieved 14 November 2011.
- "Västerdalälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Österdalälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Vattenvårdsplan för Dalälvens avrinningsområde" (PDF). Länsstyrelsen i Dalarna (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Dalälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Sveriges sjöar" (PDF). SMHI (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- Henkel, Herbert; Aaro, Sven (2005). "Geophysical Investigations of the Siljan Impact Structure – A Short Review". Impact Studies. pp. 247–283.
- "Västerdalälven". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Borlänge". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Falun". Allt om Dalarna (in Swedish). Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 12 November 2011.
- "Färnebofjärden National Park". Naturvårdsverket (in Swedish). Archived from the original on 25 August 2011. Retrieved 5 November 2011.
- "Dalarna". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- Hellstrand, Gösta (1980). Flottningen i Dalälven: utveckling, teknik, organisation (in Swedish). Dalarnas Museum. pp. 18–33, 44.
- Burman, Eva; Eriksson, Henry (1987). Dalälven: från havet till källorna (in Swedish). Rabén & Sjögren. p. 37. ISBN 91-29-58214-8.
- The Swedish text is available on the website of Project Runeberg
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Dalälven. |