Clevudine
Clevudine (INN) is an antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis B (HBV). It is already approved for HBV in South Korea and the Philippines. It is marketed by Bukwang Pharmaceuticals in South Korea under the tradenames Levovir and Revovir.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
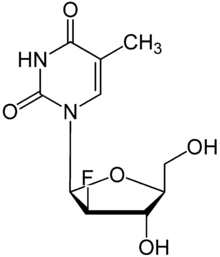
| Formula | C10H13FN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 260.221 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Researchers in South Korea are testing clevudine at lower doses in combination with adefovir for continued use.[2]
It is a nucleoside analog.[3]
References
- WHO International Working Group for Drug Statistics Methodology (August 27, 2008). "ATC/DDD Classification (FINAL): New ATC 5th level codes". WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. Archived from the original on 2008-05-06. Retrieved 2008-09-05.
- Tak WY, Yang JM, Kim BI, Baik SK, Cheon GJ, Byun KS, Kim DY, Yoo BC, et al. (May 2014). "A randomized, open-label study comparing low-dose clevudine plus adefovir combination therapy with clevudine monotherapy in naïve chronic hepatitis B patients". Hepatology International. 8 (3): 375–381. doi:10.1007/s12072-014-9537-5. PMC 4116600. PMID 25101150.
- Lee HS, Chung YH, Lee K, et al. (May 2006). "A 12-week clevudine therapy showed potent and durable antiviral activity in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B". Hepatology. 43 (5): 982–8. doi:10.1002/hep.21166. PMID 16628625.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.