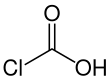
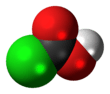
Chloroformic acid
Chloroformic acid is an unstable chemical compound with the formula ClCO2H. It is the single acyl-halide derivative of carbonic acid (phosgene is the double acyl-halide derivative). Chloroformic acid is also structurally related to formic acid, which has a hydrogen instead of the chlorine. Despite the similar name, it is very different from chloroform.
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Carbonochloridic acid[1] | |||
| Other names
Chloroformic acid Chlorocarbonic acid | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| CHClO2 | |||
| Molar mass | 80.47 g·mol−1 | ||
| Density | 1.576 | ||
Refractive index (nD) |
1.426 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Chloroformic acid itself is too unstable to be handled for chemical reactions. However, many esters of this carboxylic acid are stable and these chloroformates are important reagents in organic chemistry. They are used to prepare mixed carboxylic acid anhydrides used in peptide synthesis. Like other related halocarbons, it is a potentially dangerous alkylating agent.
Important chloroformate esters include 4-nitrophenyl chloroformate, fluorenylmethyloxycarbonylchloride, benzyl chloroformate and ethyl chloroformate.
References
- Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 776–777. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.