Carbonyl cyanide-p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone
Carbonyl cyanide-4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenylhydrazone (FCCP) is an ionophore that is a mobile ion carrier. It is referred to as an uncoupling agent because it disrupts ATP synthesis by transporting hydrogen ions through the mitochondrial membrane before they can be used to provide the energy for oxidative phosphorylation.[2] It is a nitrile and hydrazone. FCCP was first described in 1962 by Heytler.[3]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
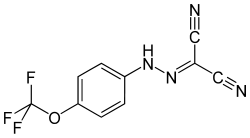
| IUPAC name
2-[[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]hydrazinylidene]propanedinitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.119 |
| MeSH | FCCP |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H5F3N4O | |
| Molar mass | 254.16811 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- FCCP - Compound Summary, PubChem.
- MeSH Descriptor Data, MeSH.
- Heytler, P G (1962). "A new class of uncoupling agents — Carbonyl cyanide phenylhydrazones". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 7 (4): 272–275. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(62)90189-4.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.